31
Shot of the Month – July 2018
So there I was sitting in the back seat of the car. I was tired but feeling content — it was the final day of our trip to the Pantanal to see, primarily, jaguars. We were driving to the local airport to begin our series of flights home. We had some amazing sightings and I had gotten some very nice photos. I always hate to see a trip end but my wistfulness was less than usual given all that we had experienced. By the second hour of our three-hour drive, the scenery went by like a blur as my mind wandered. I was jolted from my dreamy state when Naun, our guide, yelled.
“STOP! STOP! Michael get your camera ready!!!”
Huh, What? I didn’t bother to look as I knew that if Naun was this excited, it must be something good. The problem was that all our gear was completely packed up. My camera bodies were in one bag next to me. My lenses were in another bag, in the back of the vehicle. As we pulled over I yanked a camera body out and got out of the car. I opened the rear hatch of the car, yanked my camera bag out, and quickly pulled off all of the covers and caps and put the kit together. Naun waited impatiently by the edge of the road and motioned for us to go through the wire fence that he was holding up. We walked into the field and there it was — a Giant Anteater (GA)!! And he was ambling across the field with purpose!! He was still a fair distance from us but he was heading in our direction. I raised my camera to try and at least document this amazing sight. As I looked through the viewfinder I could see nothing. The car was air conditioned and when we jumped out into the heat of the day the sudden temperature change caused the front element of my lens to fog over.
F&^%$$!!
I took the bottom of my shirt and used it to wipe off the glass (I normally loathe to touch the glass, but this was an emergency!). I got a few shots off but then the anteater saw us and went in another direction. We got back in the car and moved forward. We set up and waited — it was clear that the Giant Anteater wanted to cross the road.
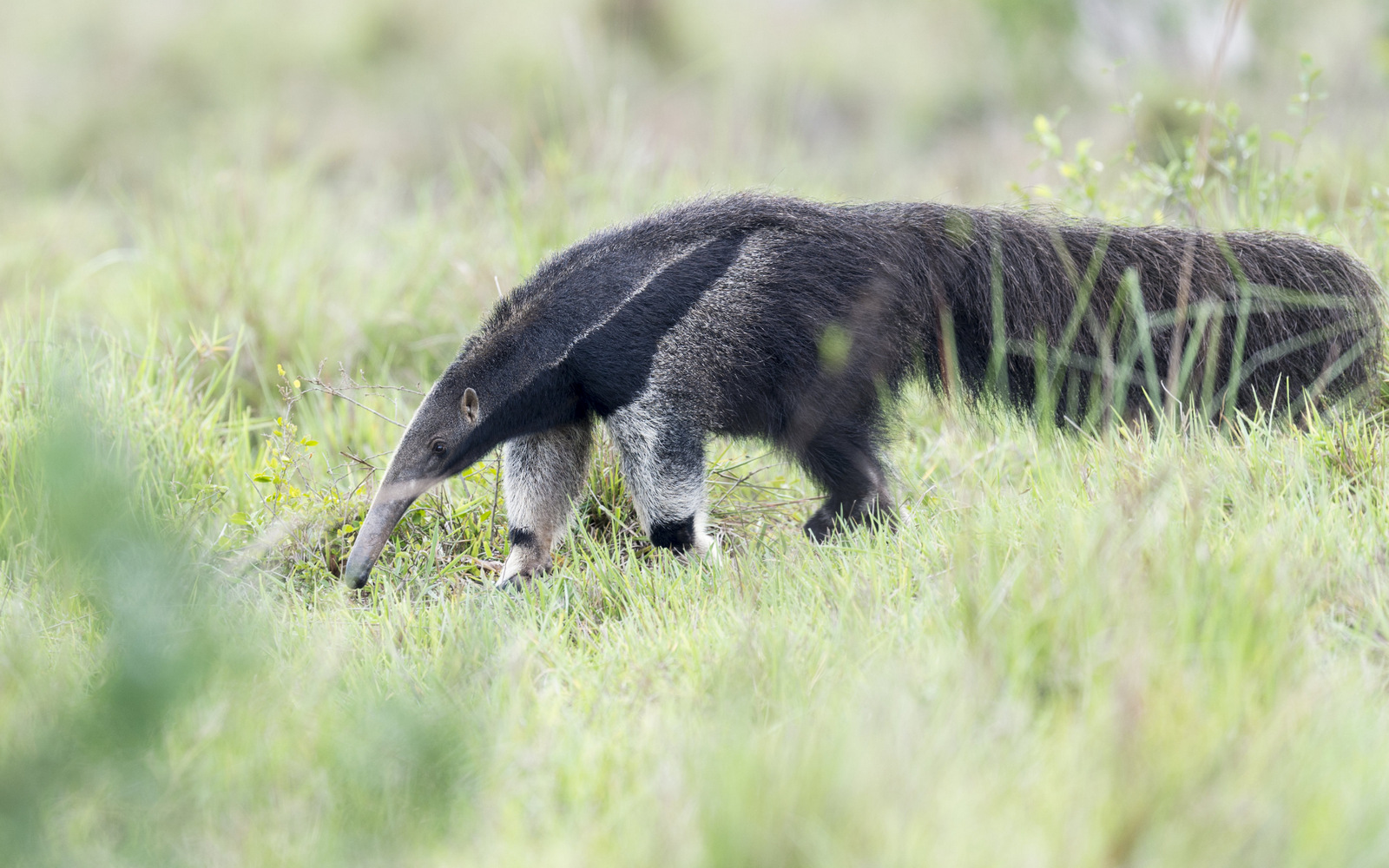
In the end, I managed to get a few shots and eventually, the GA crossed the road just a few feet from us. Wow! Even though the images are not great, I had to share this wonderful, other-worldly beast. The Giant Anteater is surely one of the world’s stranger-looking creatures.
Refuge from another dimension?
At a distance, the GA looks supremely flat – as if he escaped from the pages of a purely two-dimensional world. The Giant Anteater can reach seven feet in length from head to tail and he just looks soooo looong. His width seems so oddly out of proportion to his length giving the appearance of a “flat screen” creature. They say that black is thinning, but come on…
Winner by a nose
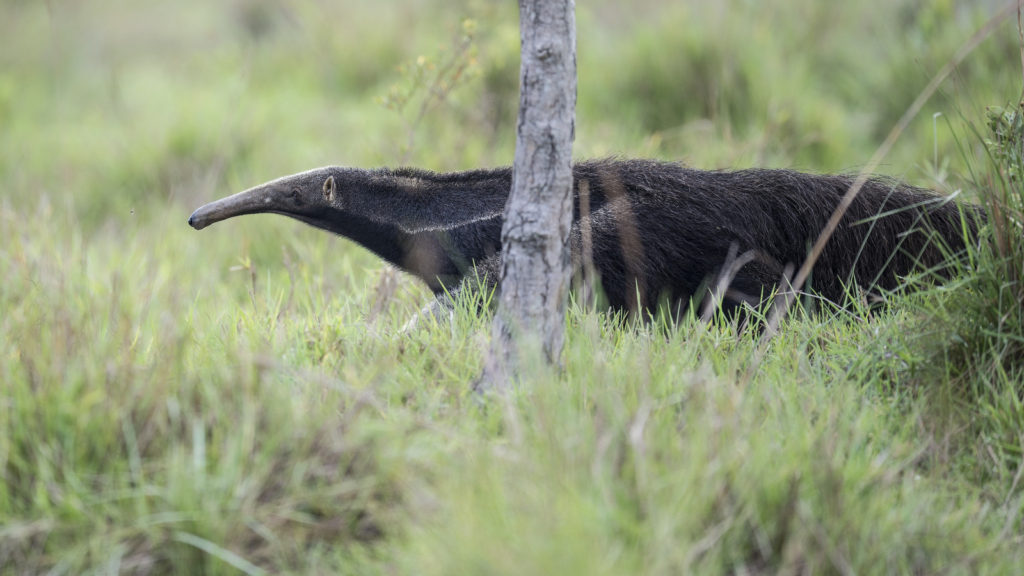 And then there is that snout. Try not to stare but that is a doozy of honker. The snout takes up most of his head and ends with a tiny mouth and nostrils. As you may have guessed from his name the Giant Anteater specializes in eating ants and termites. That nose is well shaped for plunging into the narrow passageways of the termite mounds in search of the small insects. The Ant Bear, a much more endearing moniker, can eat 30,000 insects a day. That tiny mouth has no teeth so the GA crushes the insects against its palate before swallowing them.
And then there is that snout. Try not to stare but that is a doozy of honker. The snout takes up most of his head and ends with a tiny mouth and nostrils. As you may have guessed from his name the Giant Anteater specializes in eating ants and termites. That nose is well shaped for plunging into the narrow passageways of the termite mounds in search of the small insects. The Ant Bear, a much more endearing moniker, can eat 30,000 insects a day. That tiny mouth has no teeth so the GA crushes the insects against its palate before swallowing them.
The GA has a narrow tongue that is 2 feet long. is shaped like a strand of spaghetti, and is covered in tiny backward-pointing spines covered in sticky saliva — making it a great tool for catching insects. The GA can dart its tongue inside a mound up to 150 times a minute to catch its prey.
The ant bear has terrible eyesight and equally bad hearing but its sense of smell is 40x more sensitive than ours – he can smell termites and ants that may be miles away. Ok, respect for the nose!
The Claw! (obscure movie reference)
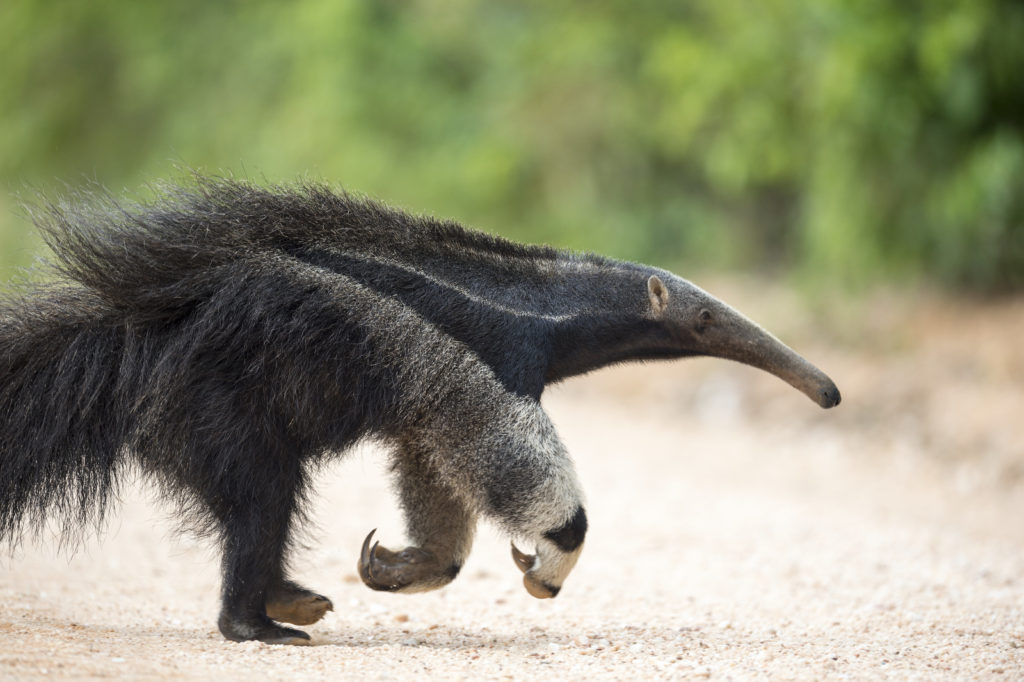
Adding to the peculiar nature of this beast, the GA walks on its knuckles, like a gorilla. Why? To protect those impressive claws that it uses to tear apart termite mounds, of course. Below we have a GA in full gallop providing a good view of the claws and how he folds his front feet over while walking to keep these vital tools sharp. The ant bear has five toes on each foot — the front feet have claws, which are particularly elongated on the second and third digits. The GA is careful to not completely destroy a mound to ensure a reliable food supply. He tears a mount open just enough to allow his narrow snout to reach inside. He only spends about 1 minute feeding at a site before moving on and in a given day he may visit up to 200 nests. These claws can also be used for defense. If a GA is attacked, say by a puma or a jaguar, the GA will stand up on its tail and slash those claws from side to side with great effect. These creatures are very shy but they have been known to kill humans when cornered or if startled in the wild.
That Tail
The body of the GA is about 3-4 feet in length and that wonderful tail can add another 2-3 feet to the length of the animal. The tail has extra long hairs and helps make the GA seem much bigger than he really is. When resting the GA will carve a shallow cavity in the ground and then curl up and use its tail as a blanket!! A-dorable! The tail can help conserve heat and act as camouflage.
Wow, what a gift to see what is becoming an increasingly rare animal. In just 10 years, from 2000 to 2010 the total population of GAs has declined by 30%. Tragically, in 1994 close to 350 Giant Anteaters died due to wildfires at Emes National Park in Brazil. Currently, scientists think there may be about 5,000 ant bears left in the world. Giant Anteaters are native to Central and South America though it seems that they have been extirpated from most of Central America. (source)
Why did the ant bear cross the road?
Heck if I know, but I am eternally grateful that this one did! Until next month…..m
Check out this amazing interaction between a jaguar and a giant anteater!
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm f/4, 1/500 sec, ISO 400, +1 EV
30
Shot of the Month – June 2018
The glorious Bald Eagle – can one imagine a more revered and awe-inspiring bird? Perhaps this quote captures the sentiment most people have of this famous raptor:
The American bald eagle is perhaps the most majestic and revered of all birds of prey across North America. Chosen by our forefathers as a symbol of strength and pride for the United States, and honored and respected by Native Americans for centuries, this beautiful bird is perhaps the most famous of all birds of prey. (source)
The American bald eagle was adopted as the national bird symbol of the United States of America in 1782. This regal bird can be found on most official seals of the U.S. government, including the presidential seal, the presidential flag, and the logos of many U.S. federal agencies. Here are a few examples:
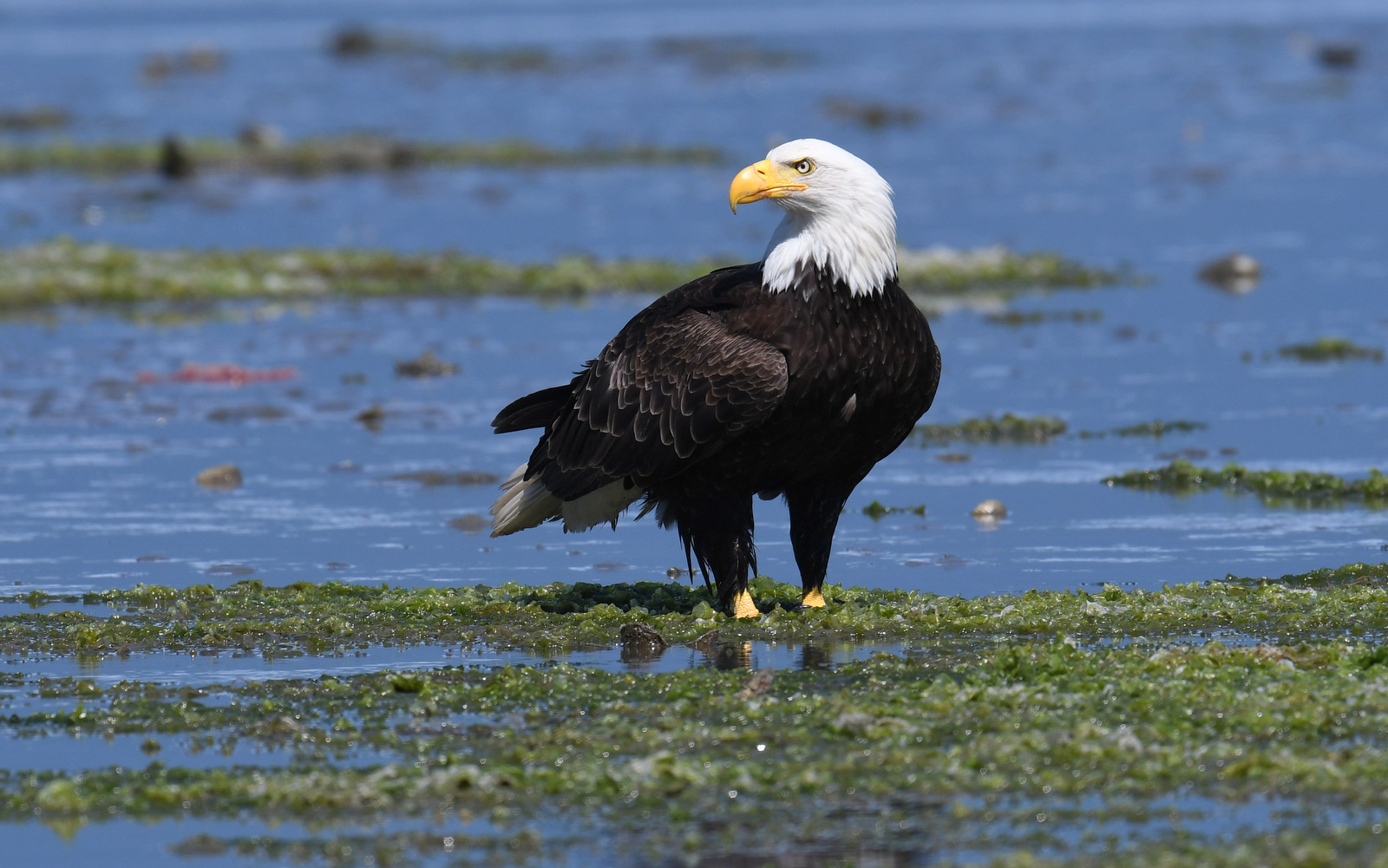
Alas, it turns out our regal eagle has more in common with Al Capone than with Thomas Jefferson. Ben Franklin was aware of the bird’s bad behavior and was opposed to the bald eagle being chosen as our national symbol. As he wrote to his daughter in a January 26, 1784 letter:
For my own part I wish the Bald Eagle had not been chosen the Representative of our Country. He is a Bird of bad moral Character. He does not get his Living honestly. You may have seen him perched on some dead Tree near the River, where, too lazy to fish for himself, he watches the Labour of the Fishing Hawk; and when that diligent Bird has at length taken a Fish, and is bearing it to his Nest for the Support of his Mate and young Ones, the Bald Eagle pursues him and takes it from him. (source)
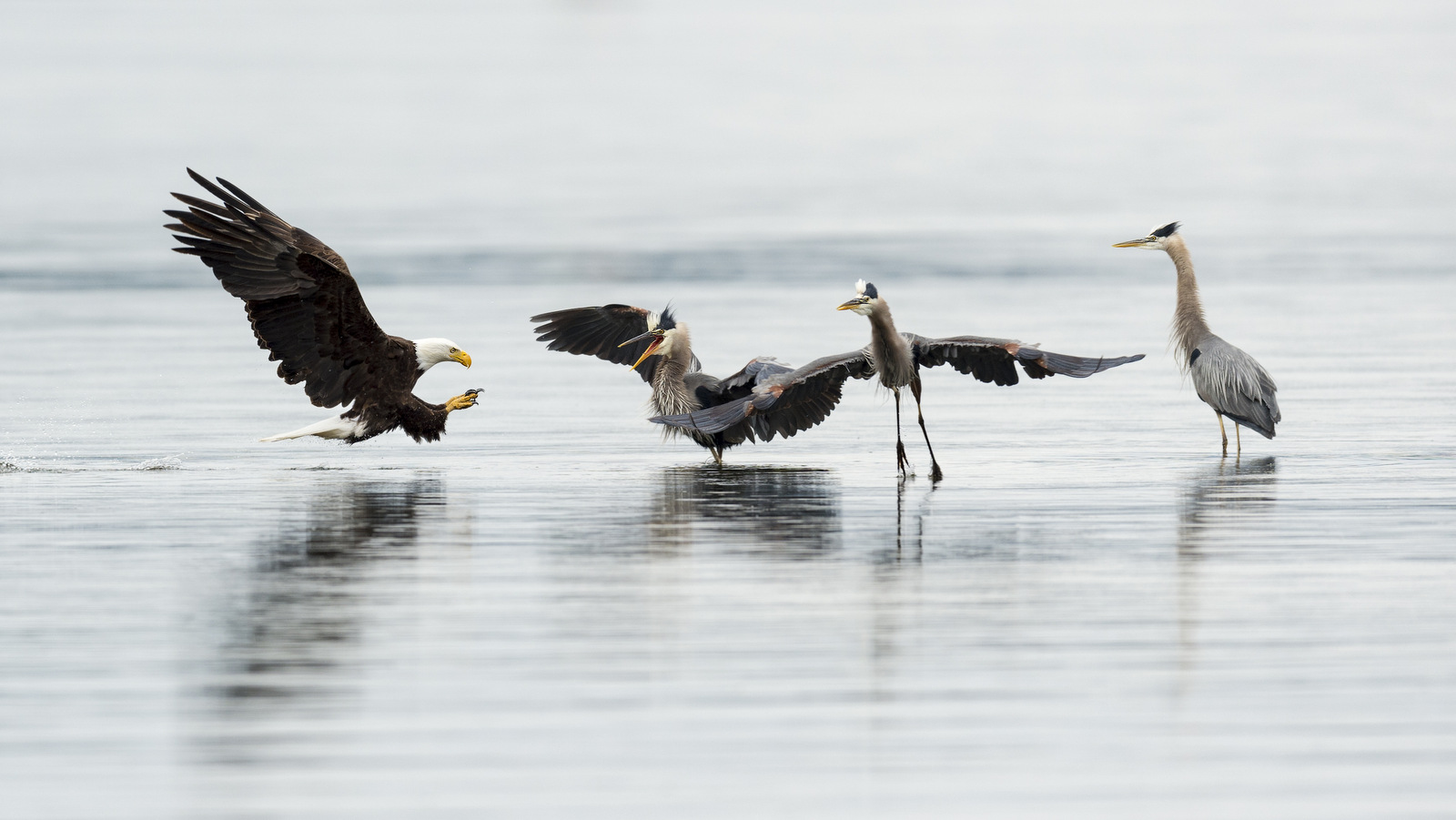
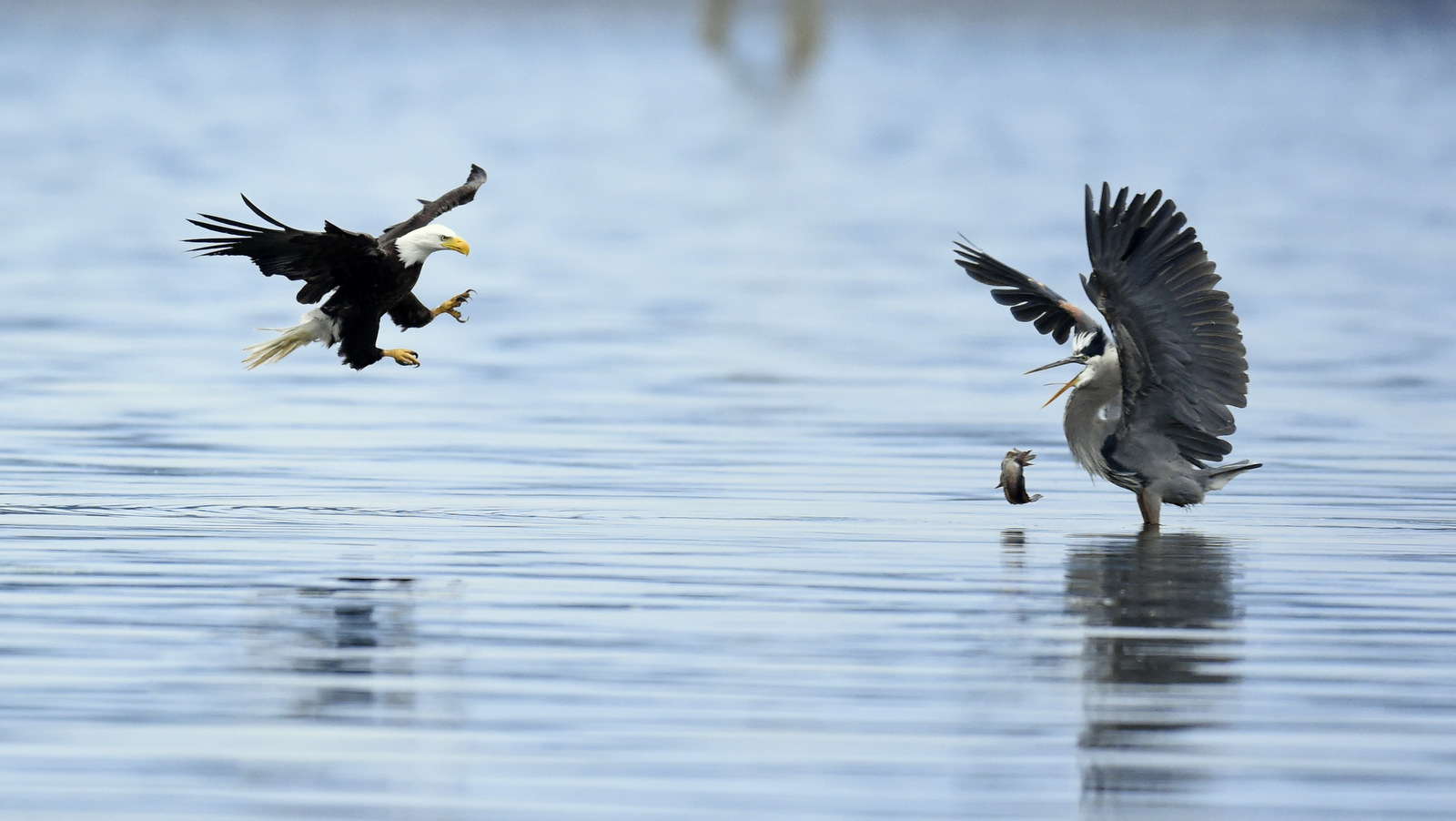
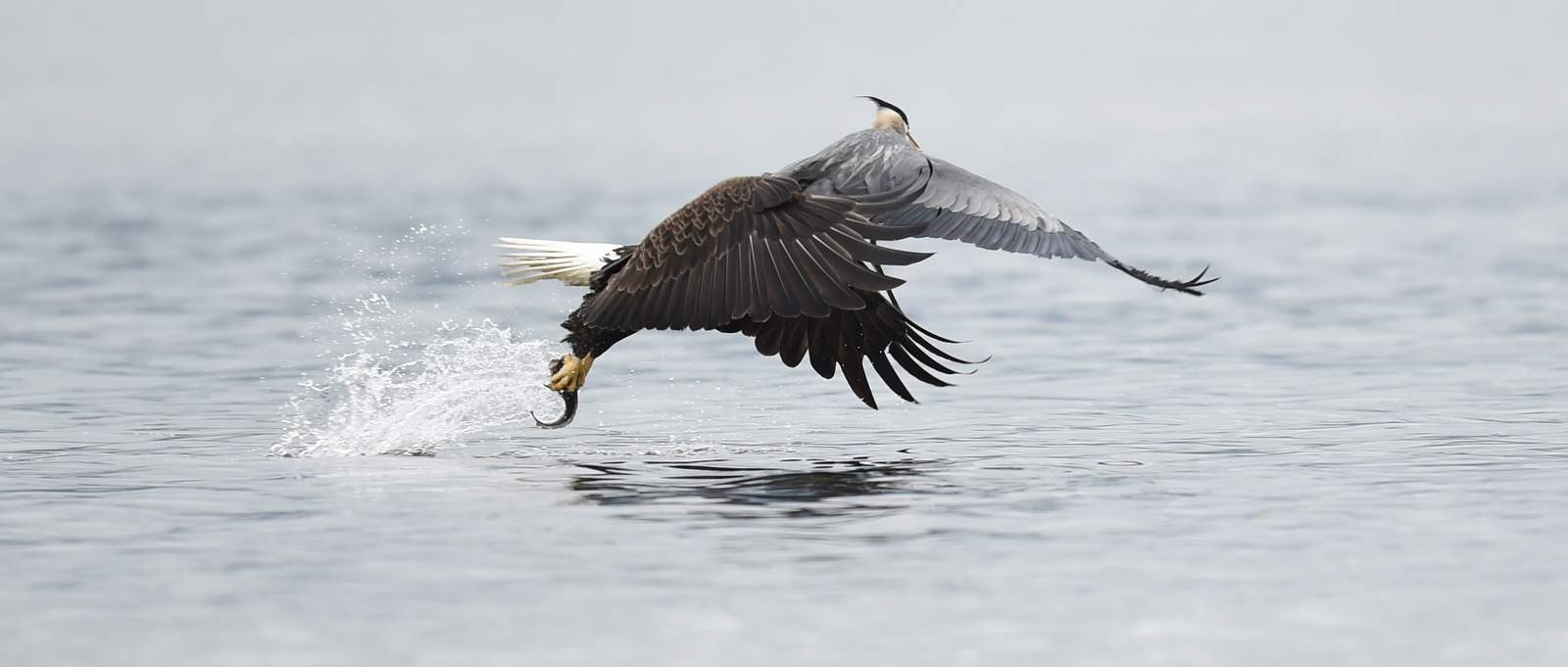
Alas, it is true, the bald eagle is a bit of a thug. In my photo above the eagle is about to steal a fish that a blue heron just caught. I have seen such behavior many times while out in the field. I have seen bald eagles harass otters numerous times until they give up their latest catch. Ospreys (that is the Fishing Hawk that Ben referred to above) also must often give up their fish to the bigger raptor. The bald eagle is also a common scavenger feeding on dead fish and other carcasses.
Oh, the shame…
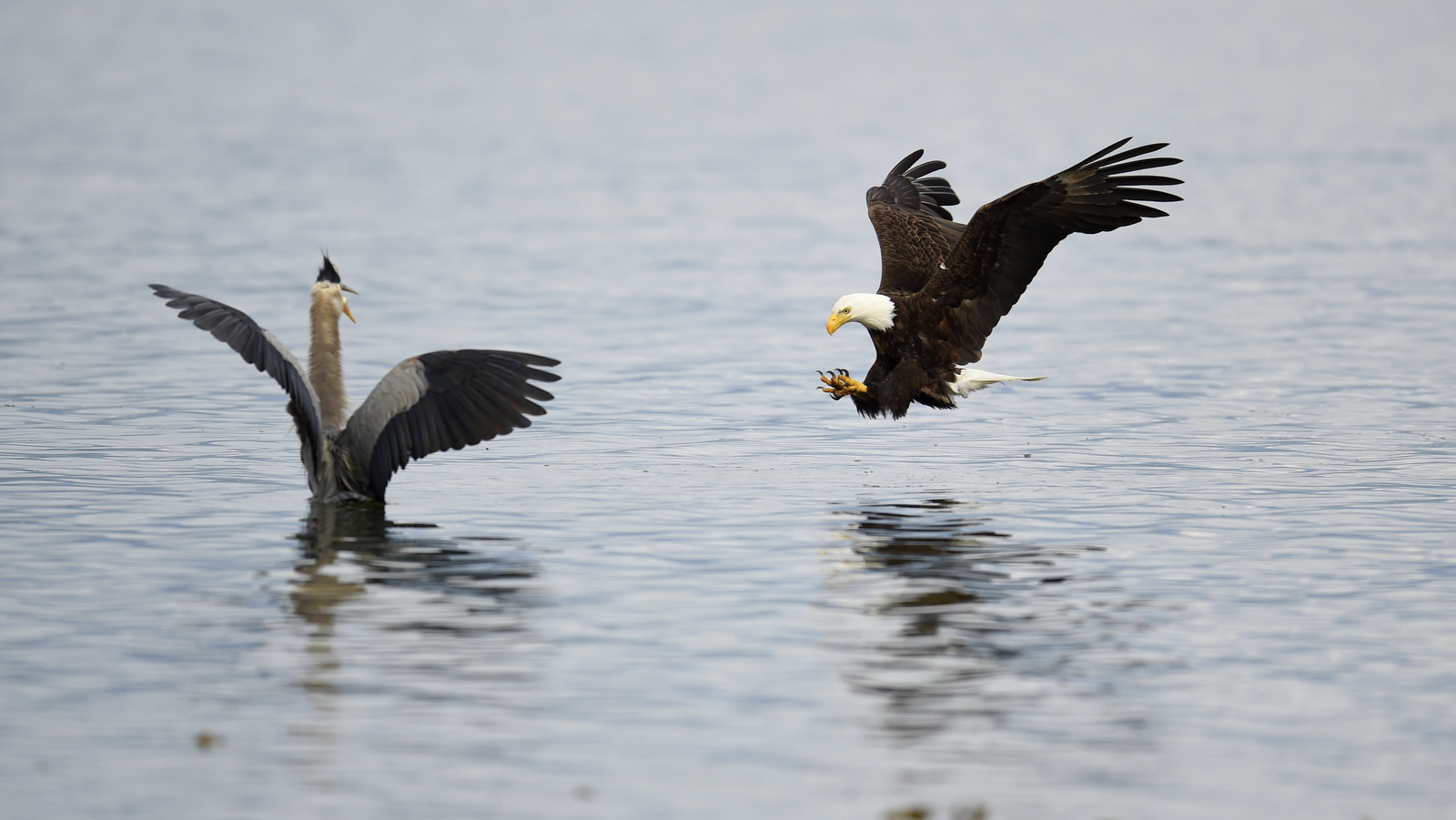
Here is the follow-up to the image above:
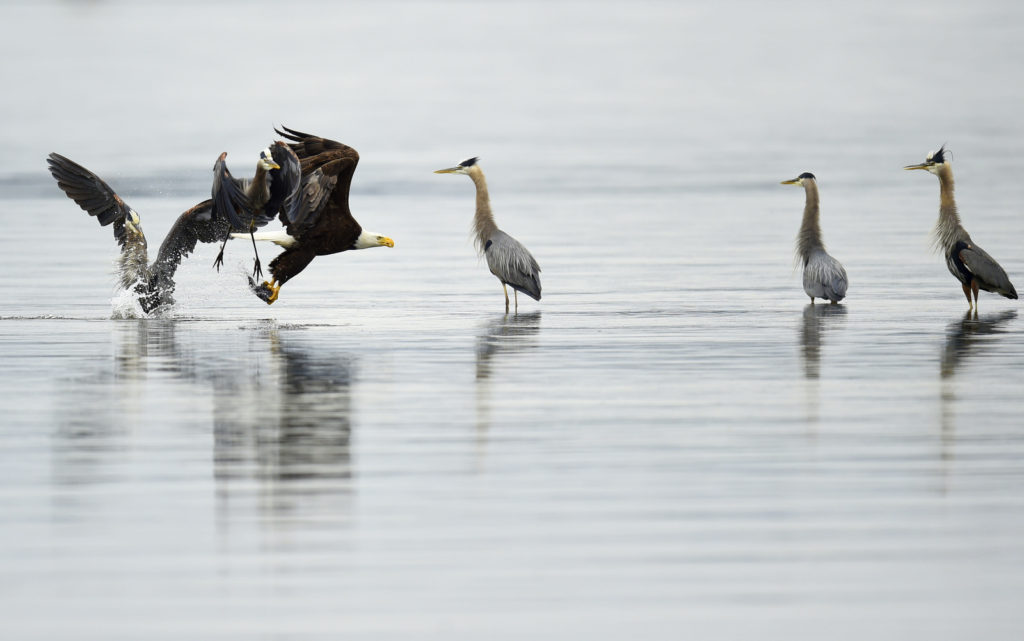
Here is another example. The heron wisely drops the fish…
And another
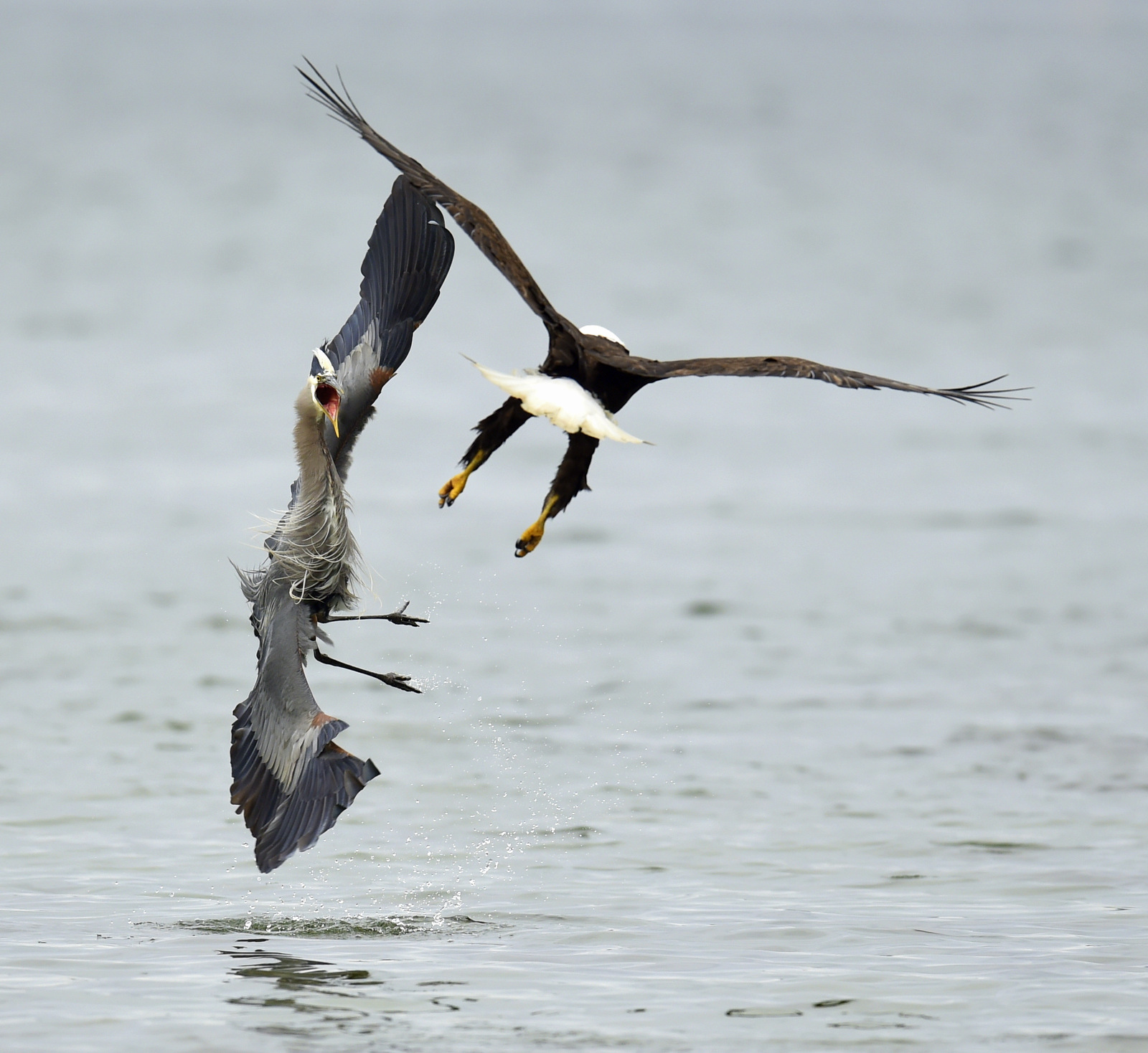
And…this is one hacked-off heron!
We know how this will end…
Thank you very much…
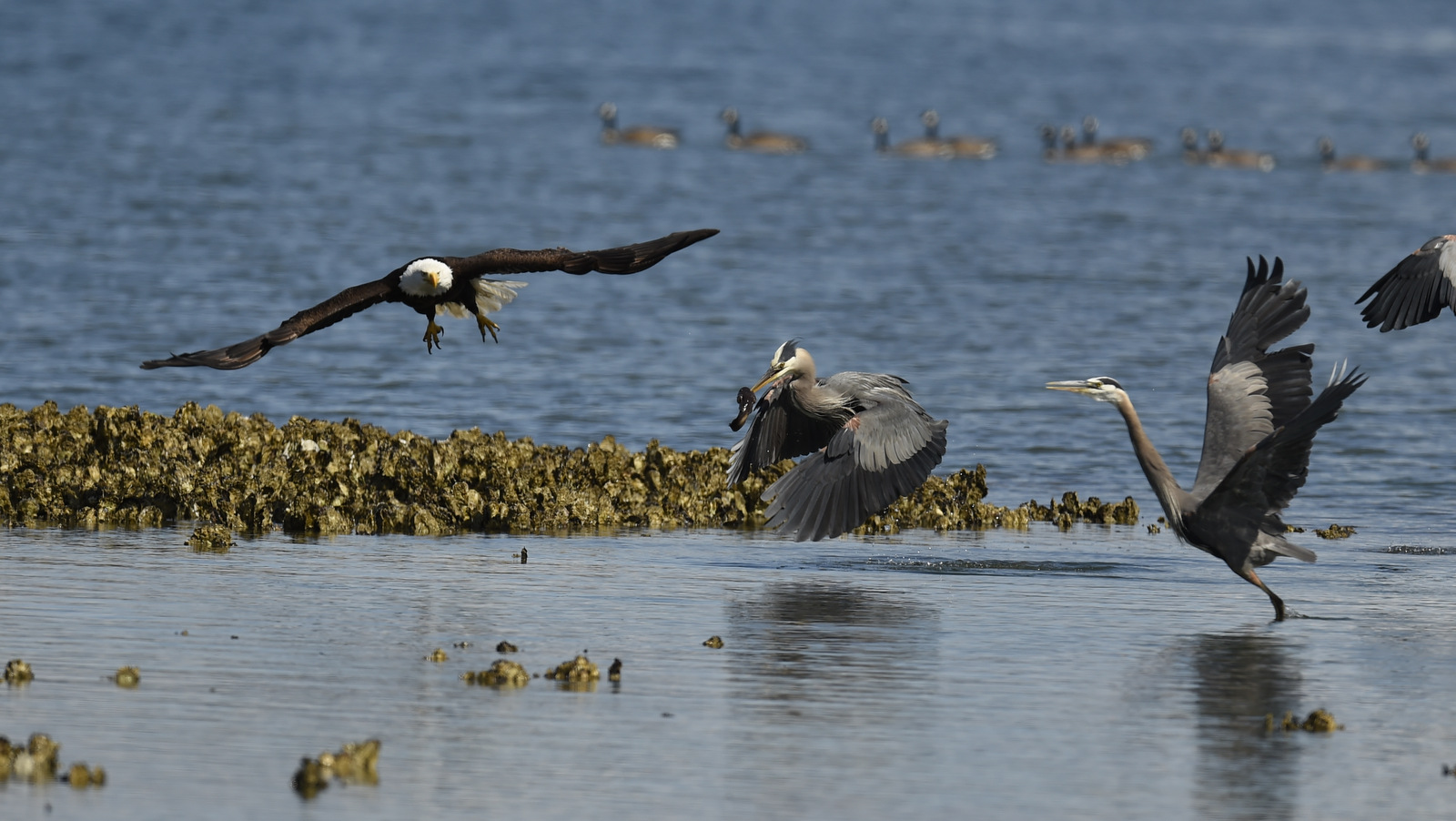
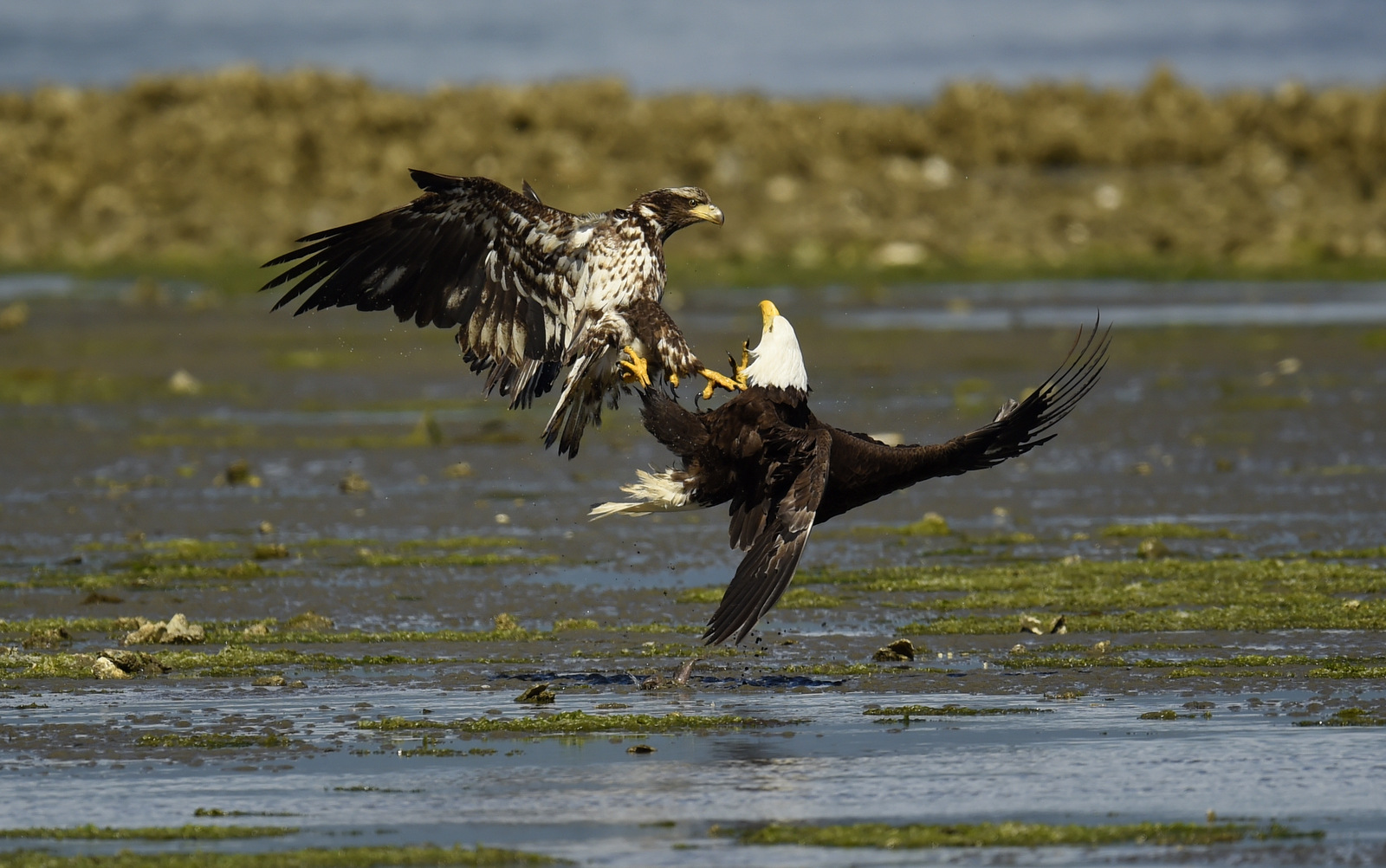
Bald Eagles also steal from each other. Here we see a “discussion” between an immature eagle (on the left) and a full-grown adult over a fish.
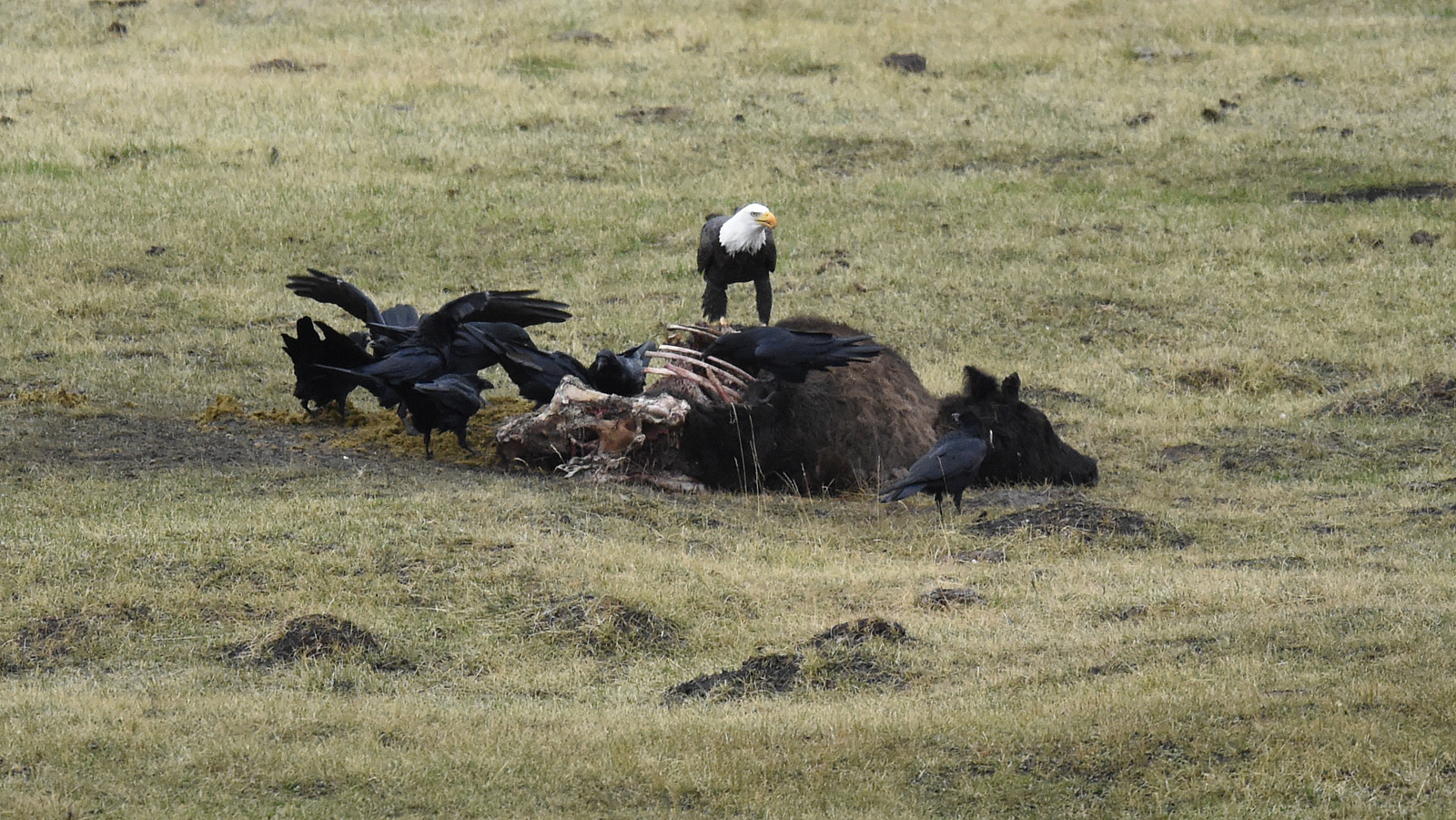
And here we see a Bald Eagle dining on a bison carcass in Yellowstone National Park
The American Bald Eagle, majestic in appearance and eh, well, let’s just leave it at that…

Until next month….m
And don’t forget, you can click on any image above to see it bigger (highly recommended).
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, f/4, 1/2000 sec, ISO 720, +1.5 EV
31
Shot of the Month – May 2018
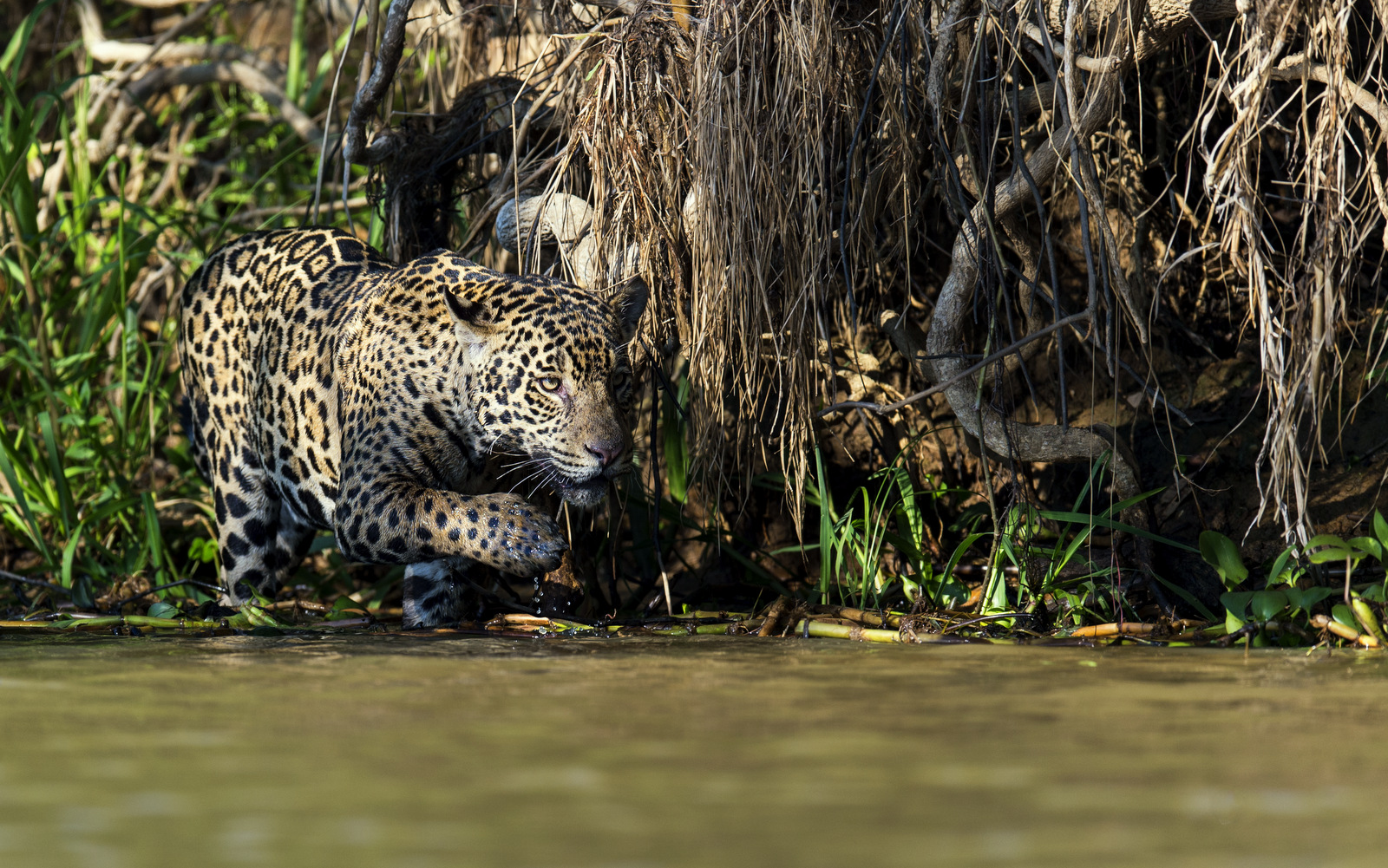
So much better than I ever dared to imagine. This image of a Panthera onca, that is. Pardon my Latin, I mean this image of a J-A-G-U-A-R, that is! I have been doing nature photography long enough (29 years! gulp) to keep my expectations very, very low. Last year we were making plans for our first trip to the Pantanal region of Brazil in search of jaguars and I was doing my best to dampen my expectations. Years of experience told me that it would be great fortune just to see a jaguar let alone get a decent image of one. I did my best to temper my bubbling excitement at the prospect of seeing the only “big cat” that I had not yet seen in the wild — I kept reminding myself that it would probably take 2-3 trips to Brazil before getting a “keeper.” This certainly was the case in trying to photograph tigers — only the third trip to India produced some agreeable images.
And from spending more than 18 years in Africa, I know how difficult it is to see a leopard. On an African safari, seeing a leopard once or twice over a 10-day period would be considered a success and I assumed that should be my benchmark for the jaguar.
Boy, was I wrong. First the “safari” is done in a very different way. In Africa, you spend 12 hours a day bumping up and down on hot, dusty trails in a 4×4 jeep in search of fauna (at least the way this fanatic does it). In the Pantanal, we spent our time on a small boat navigating a collection of rivers in search of wildlife. Let me tell you, riding in a boat is infinitely more enjoyable (and much easier on the back!). Each morning we would leave by 5:30 am and spend about 3-5 hours in search of the big cat. We would return by noon at the latest and then rest until heading out again around 3 pm until dark. So you do two “game drives” each day. During our time there we completed six boat drives and we found at least one cat EACH time. Sometimes we would find more than one cat! Sometimes we would spend a few hours with a cat watching him/her stalking along the river. I was blown away. What a gift to get to spend so much time with such a spectacular beast. And when not seeing jaguars we were beguiled by giant river otters, capybara, kingfishers, caiman and other wildlife. Given that it was our first trip, it was all new and everything we saw was a “first”. Turns out that the jaguars love hunting along the river, and by being on a boat, we typically had a gloriously unobstructed view of the cat. And so many sightings!! I still can’t believe it.
Also, my mental picture of a jaguar was all wrong. Previously I saw jaguars and leopards as being more or less equivalent. The jaguar was the “leopard” of the Western Hemisphere – there are no leopards here. And the leopard was the “jaguar” of Africa and Asia — no jaguars found there. And the two cats have a very similar spot pattern. Both cats are stalk-and-ambush predators. But what I didn’t fully appreciate was the size of the jaguar. Wow. They are massive. Jaguars are the third largest cat in the world right behind the tiger and the lion. They have massive heads, and powerful, stocky, muscular bodies – in the Pantanal male jaguars can reach 300 pounds. Leopards are leaner in stature and rarely weigh more than 200 pounds.
Jaguars are in fact just as elusive as leopards, normally. It is only really along this relatively small stretch of river in Brazil where these cats can be seen with reasonable frequency — however, it took ten years of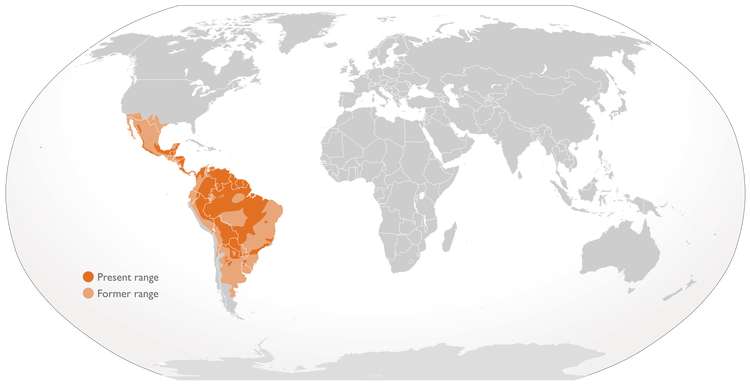 effort to habituate the resident jaguars to the boats. Prior to this, sightings were leopard-like rare. Likewise, one should not assume that such frequent sightings imply that the cat is thriving. Alas no — as with most big cats, we are rapidly pushing them off the planet as we wipe out their habitat. Jaguars are mostly found in Central and South America though they used to be found in North America. A couple of jaguars have been seen in the United States though some idiot just killed one of them. Rage. The jaguar’s range currently includes Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Columbia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.
effort to habituate the resident jaguars to the boats. Prior to this, sightings were leopard-like rare. Likewise, one should not assume that such frequent sightings imply that the cat is thriving. Alas no — as with most big cats, we are rapidly pushing them off the planet as we wipe out their habitat. Jaguars are mostly found in Central and South America though they used to be found in North America. A couple of jaguars have been seen in the United States though some idiot just killed one of them. Rage. The jaguar’s range currently includes Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Columbia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.
I have seen many a critter in my day but I don’t think that I have ever seen an animal that embodies “wild” more than a jaguar. There is an intensity in their gaze that sends a jolt down my spine. There is no doubt that this cat is an apex predator and everything about it from its unbelievably powerful build to its absolute fearlessness makes it clear that this beast is the King of the Jungle.
Below is a quick and dirty video that will give you a sense of what it is like looking for jaguars by boat (stay to the end for some more jaguar images from our trip!) And here is a YouTube link to the same video.
Until next month…michael
Bonus Material: Earlier I mentioned that the jaguar was the last of the “big cats” that I had not seen yet. What are the other big cats you ask? They include:
- Tiger
- Lion
- Leopard
- Jaguar
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, f/4, 1/2000 s, ISO 400
30
Shot of the Month – April 2018
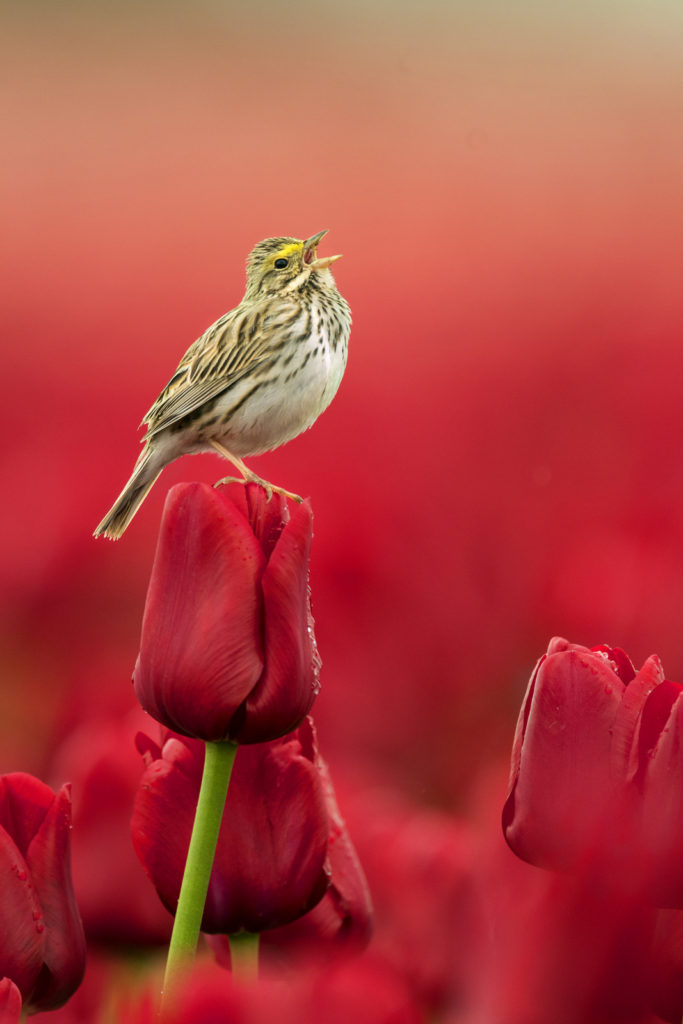
With my third spring in Washington State approaching I finally had some time to explore a tulip festival that is held each year about an hour north of Seattle. Given that the “subject” of this photo shoot was going to be expansive fields of colorful tulips I packed up my wide angle lenses and a tripod and off I went, leaving my long lenses behind. Time to do some landscape photography.
On our first visit we drove from site to site to explore the different fields to try different compositions and identify the photographic possibilities. At one site I spotted a bird sitting on flower as you can see below. My heart suddenly raced with excitement. With my largest lens only going out to 200 mm my options were limited but I sensed the massive potential for something special — I would have to come back with the right gear and try for the shot that I could see in my mind’s eye.
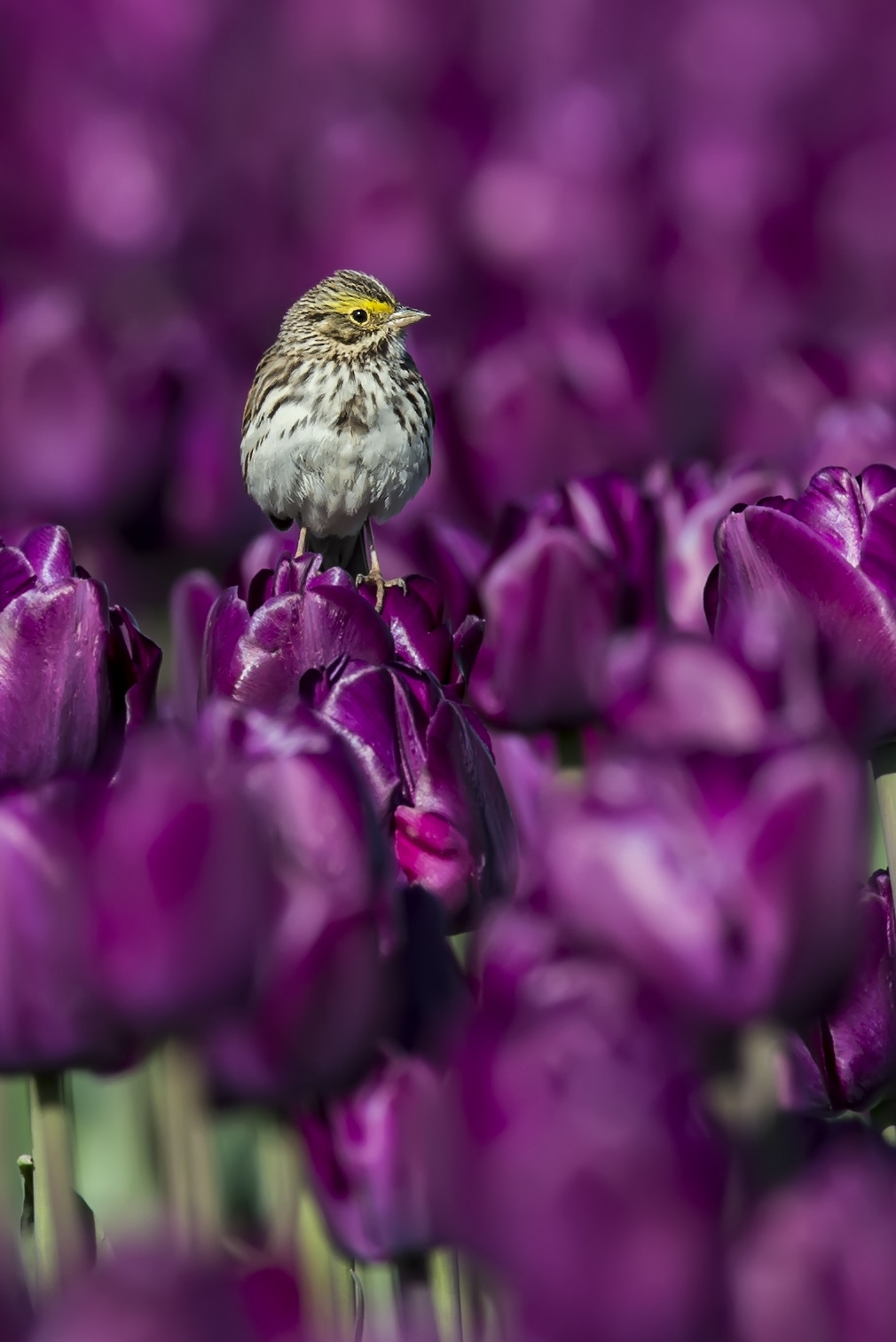
So, a few weeks later I returned, this time with my 600 mm lens and a monopod. I started the morning with more traditional landscape gear as I awaited the sunrise. I explored the scene at 24 mm until the sun was too high for that shot to work and it was time to bring out the long lens. For the next 4-5 hours I slowly walked among the rows of tulips looking for my quarry — a Savannah Sparrow (SS). The SS sparrow likes open terrain and typically feeds on the ground so the tulips fields were a perfect setting for him. After a few trips to the fields I began to understand the patterns — the birds would become more active by “mid” morning; by around 9:30 am the birds would begin to perch on the tulips and sing, proclaiming their territory. After a bit of time I could identify the circuit a bird would make as he traveled along the perimeter of his part of the field. I could even begin to identify his preferred tulips to sit upon. Of course, this would vary, but he often like to find the tallest tulip in an area to maximize the effect of his song.
I imagine that from the road that people were perplexed as to what that guy (me) was doing out in the fields with such a massive lens – “What in the hell is that guy shooting,” I assumed that many a visitor muttered to themselves. Some were even brave enough to ask. My reply was simply, “Just the birds.”
Each bird stayed in its territory so a given SS would only provide me the opportunity for one color of shot. The fellow above provided me with my “red” shot. To get the “purple” shot I would have to move to another section of the field and find a new bird, and learn his unique patrolling pattern. And from there I just looked for opportunities to mix and match as many colors as possible. Birds stopping along the edge of two adjacent, but different colored fields, provided opportunities for multi-colored scenes.
As I seem to have a knack for doing, I yet again managed to transform a typical landscape outing into a wildlife focused affair. In this case a tulip landscape morphed into a fanciful, magical perhaps, technocolor birdscape. So much fun…
Until next month…..m
Nikon D500, Nikon 600mm, 1.4x TC, (effective 1275mm), 1/1000s, f/5.6, +0.333 EV, ISO 400
31
Shot of the Month – March 2018
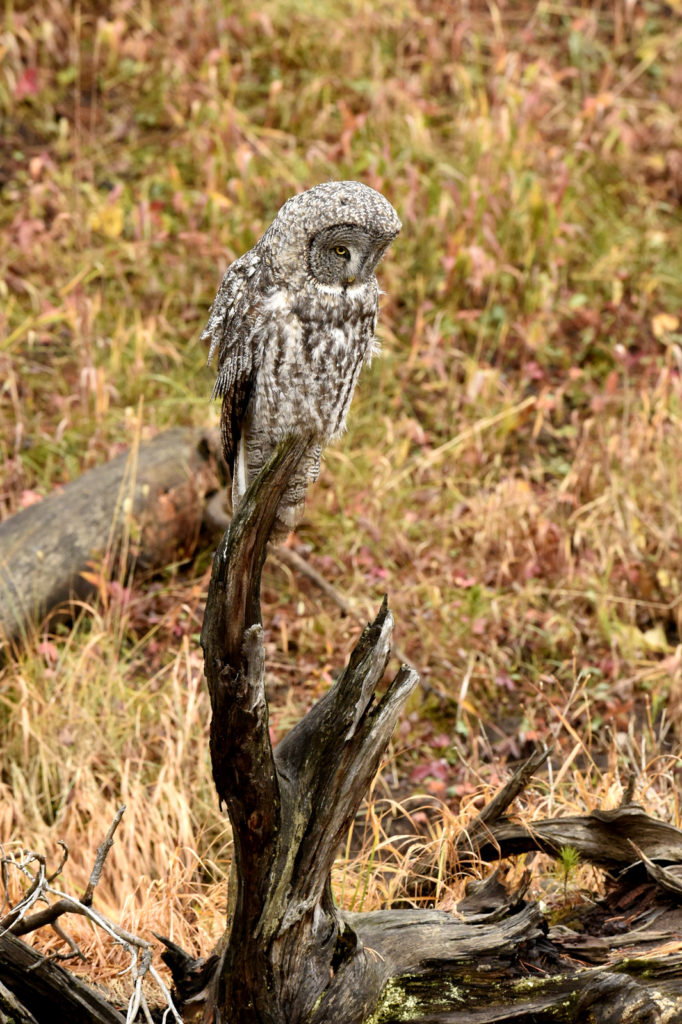
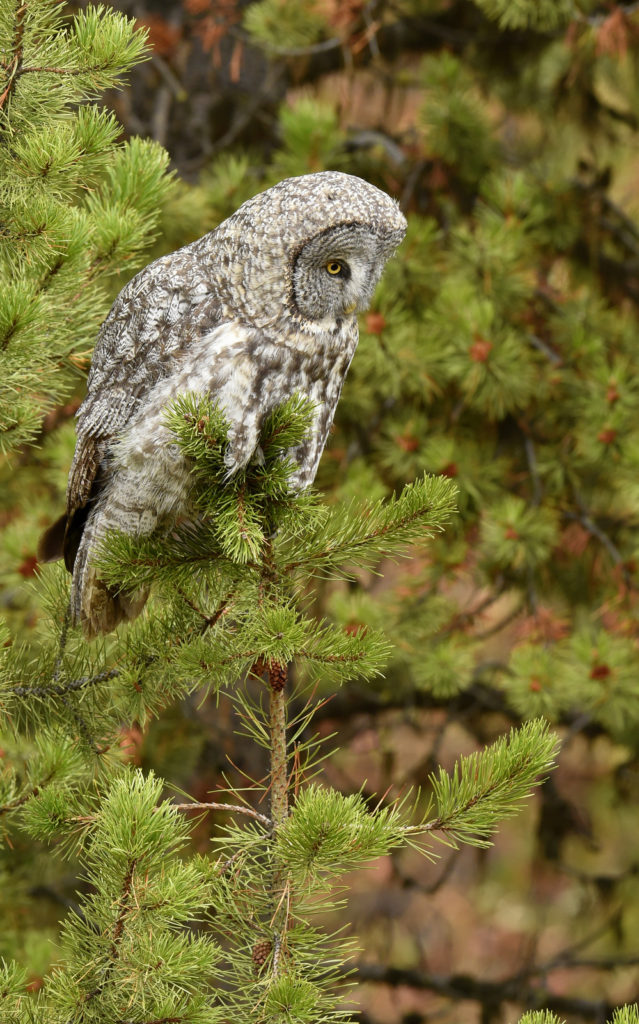
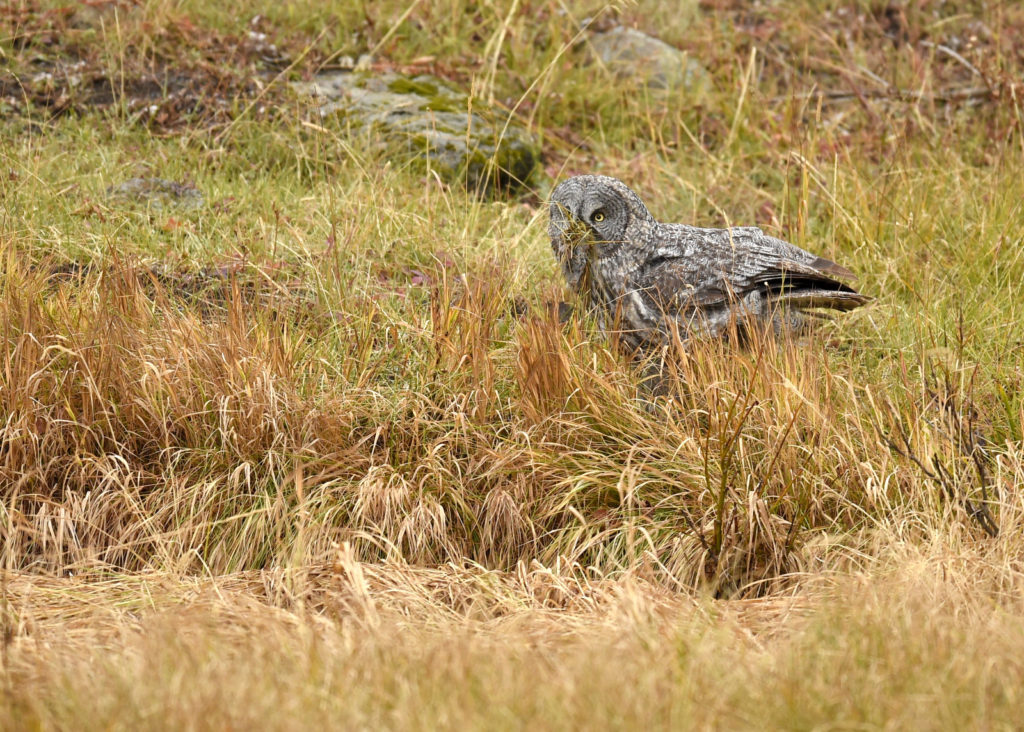
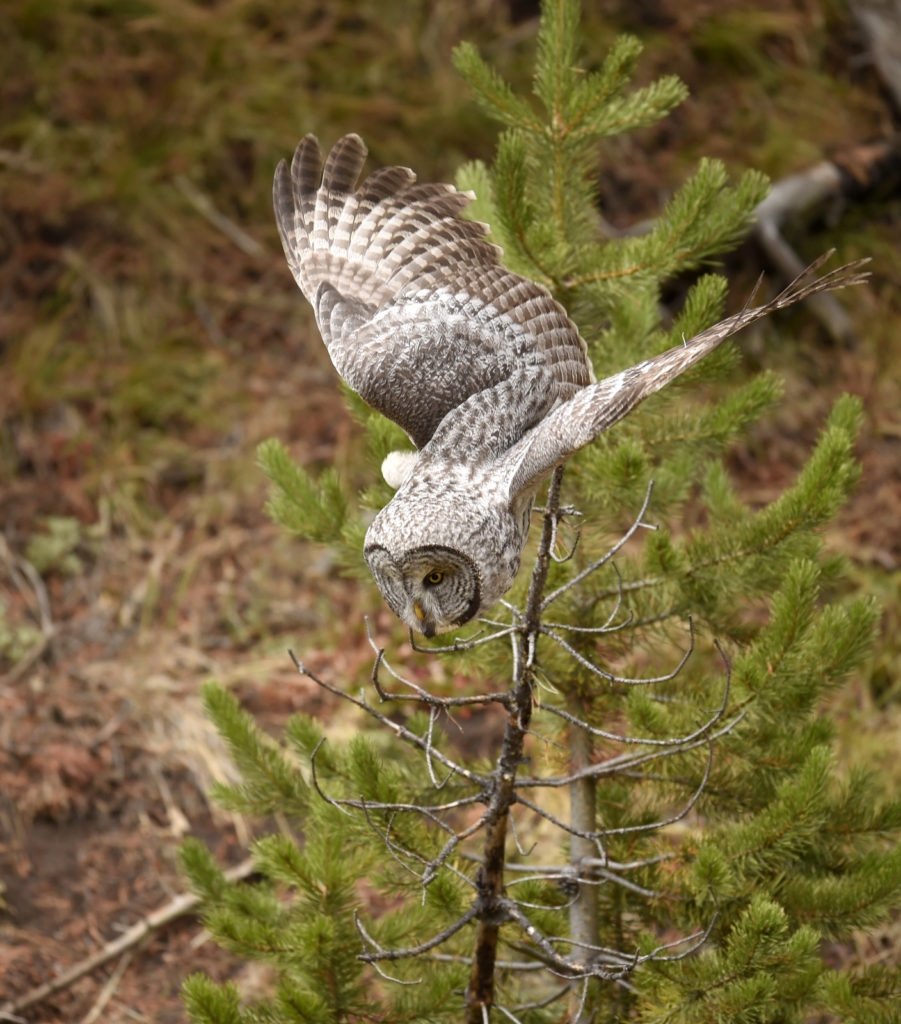
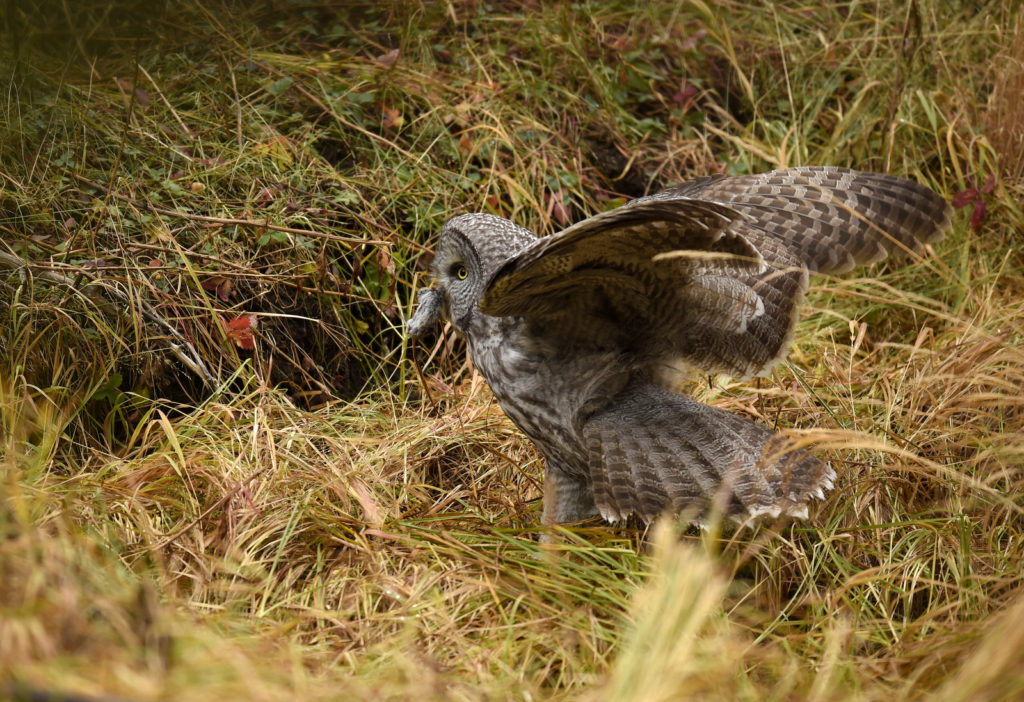
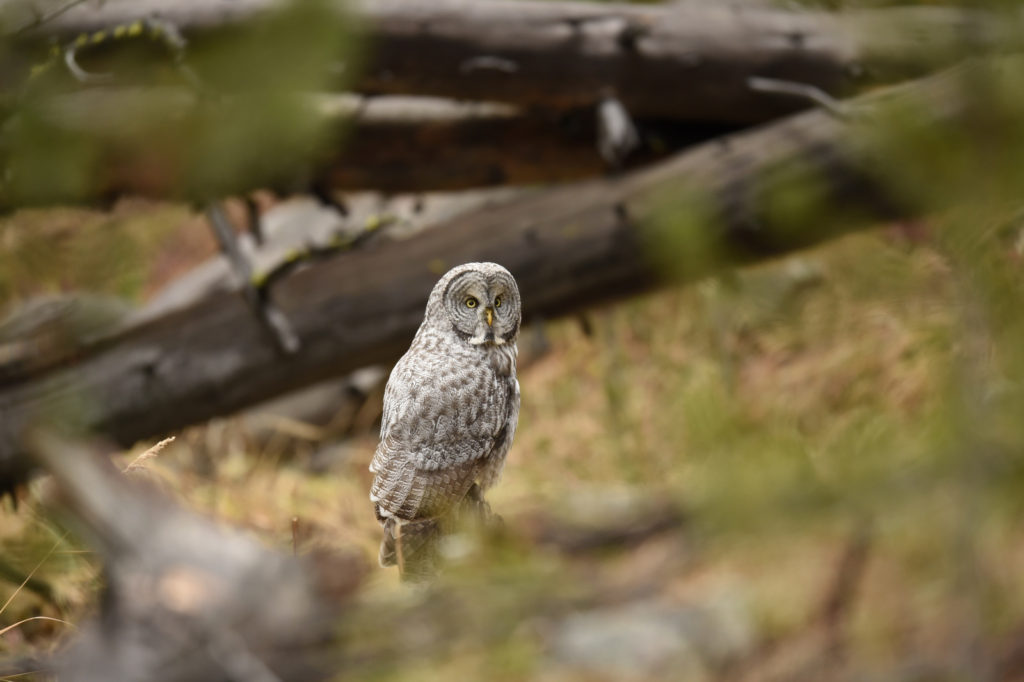
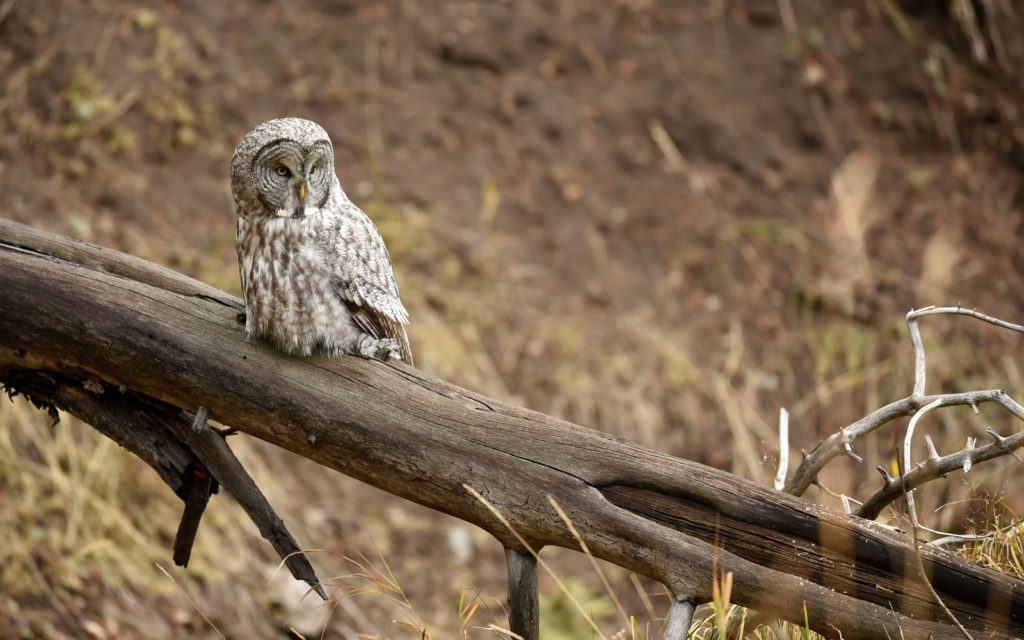
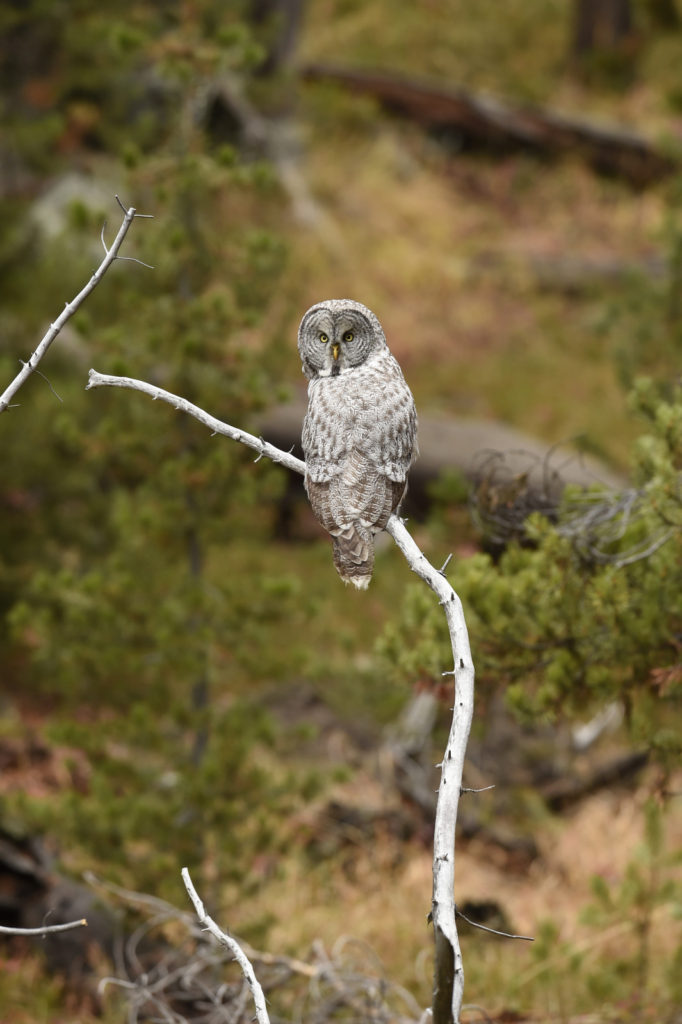
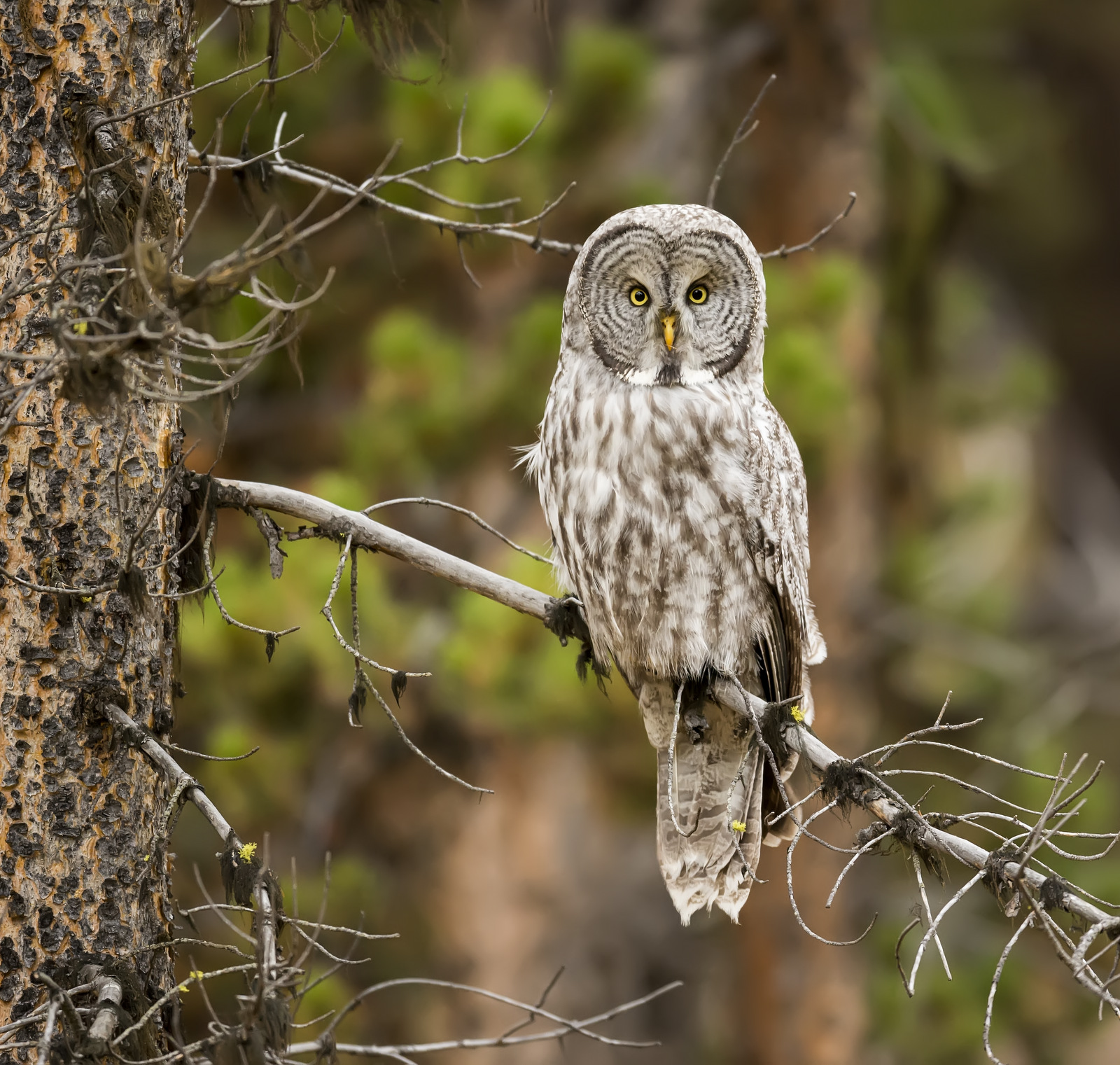 So, there I was driving along a road in Yellowstone NP when I noticed a collection of cars pulled off to the side of the road — always a sign of wildlife nearby. Luckily, I found a place close by where I could completely pull off and park. I got out and ran across the road to where I could see the tops of a few heads of people gathered together. As I made my way down a small hill I saw this lovely Great Grey Owl. I ran back to my car and collected my gear and made my way back.
So, there I was driving along a road in Yellowstone NP when I noticed a collection of cars pulled off to the side of the road — always a sign of wildlife nearby. Luckily, I found a place close by where I could completely pull off and park. I got out and ran across the road to where I could see the tops of a few heads of people gathered together. As I made my way down a small hill I saw this lovely Great Grey Owl. I ran back to my car and collected my gear and made my way back.
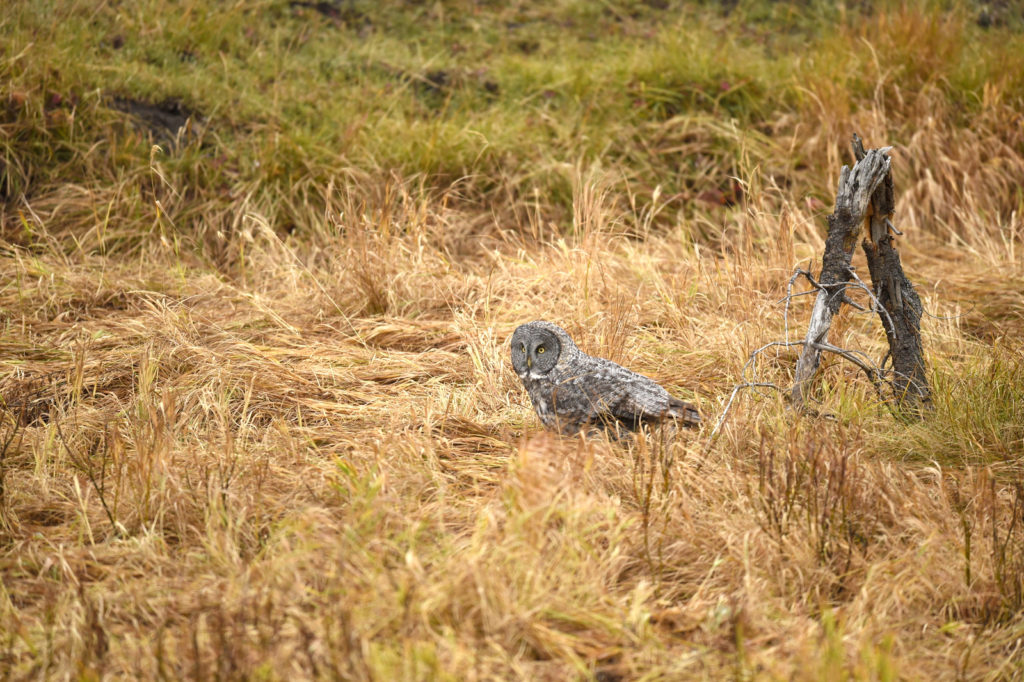
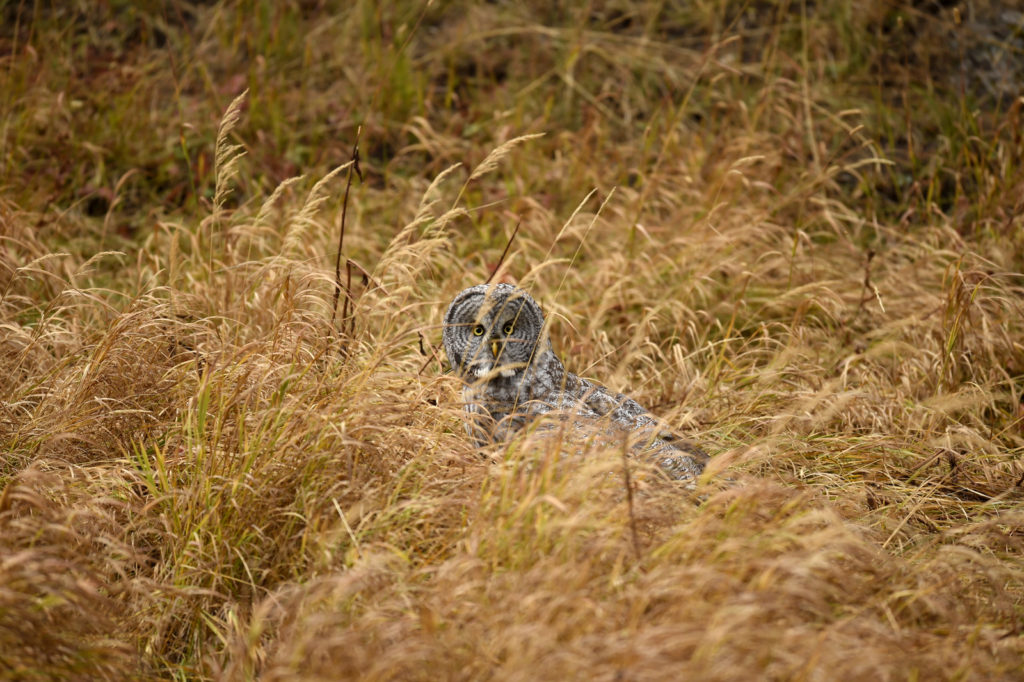
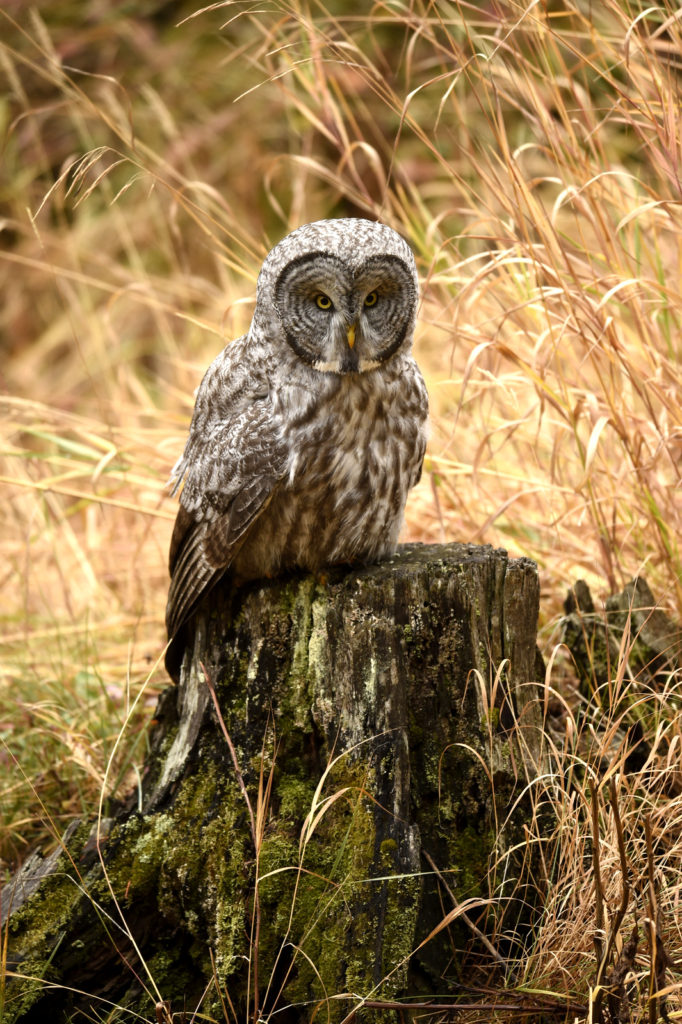
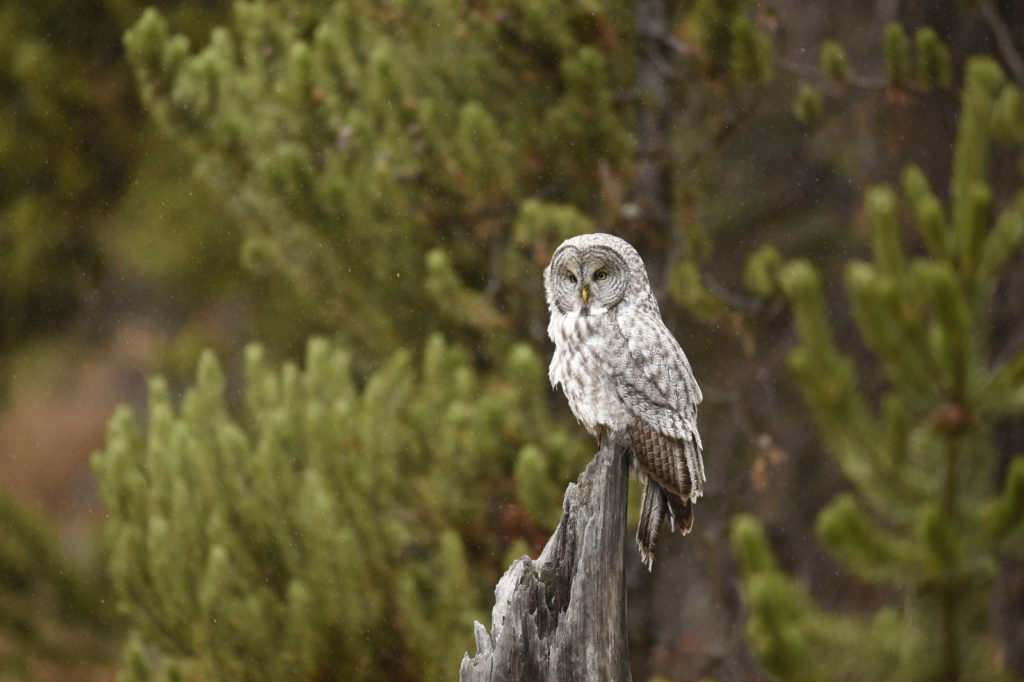
There were perhaps 12-15 people in a semi-circle around the bird as she (I am not sure if it is a he or she, but let’s go with she) was perched on a dead tree stump. I was annoyed as folks with smaller lenses were, in my opinion, getting too close to the bird. One of the benefits of shooting with a 600 mm lens is that I don’t need to get super close to my animal subjects and can avoid the risk of disturbing them. That all being said, this magnificent owl didn’t seem to take any notice of the humans — she was in hunting mode and was focused on listening and scanning the grass below.
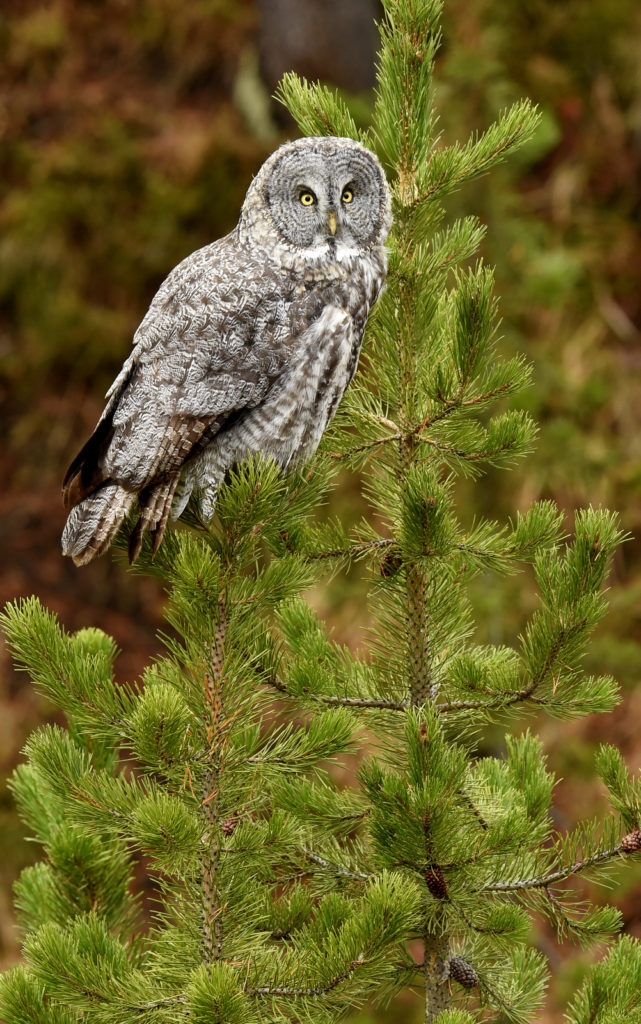
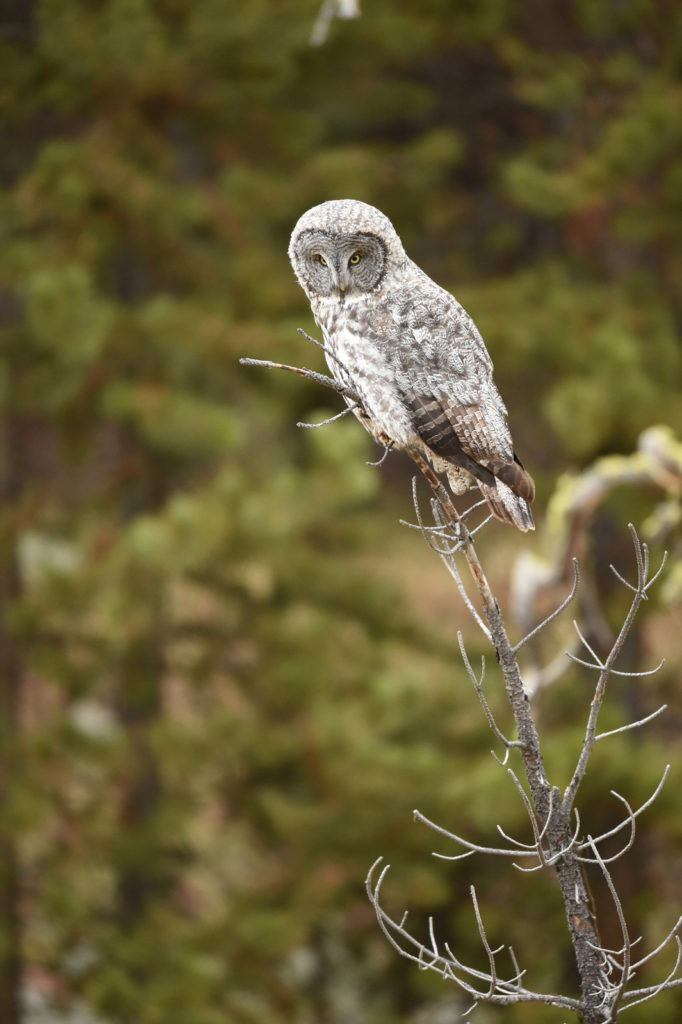
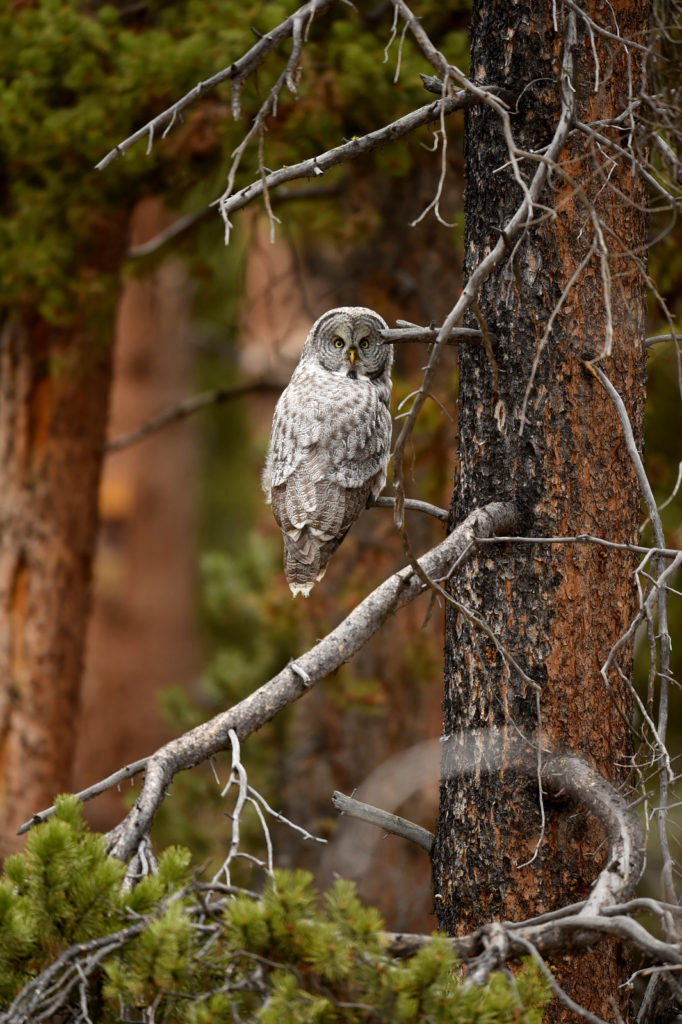
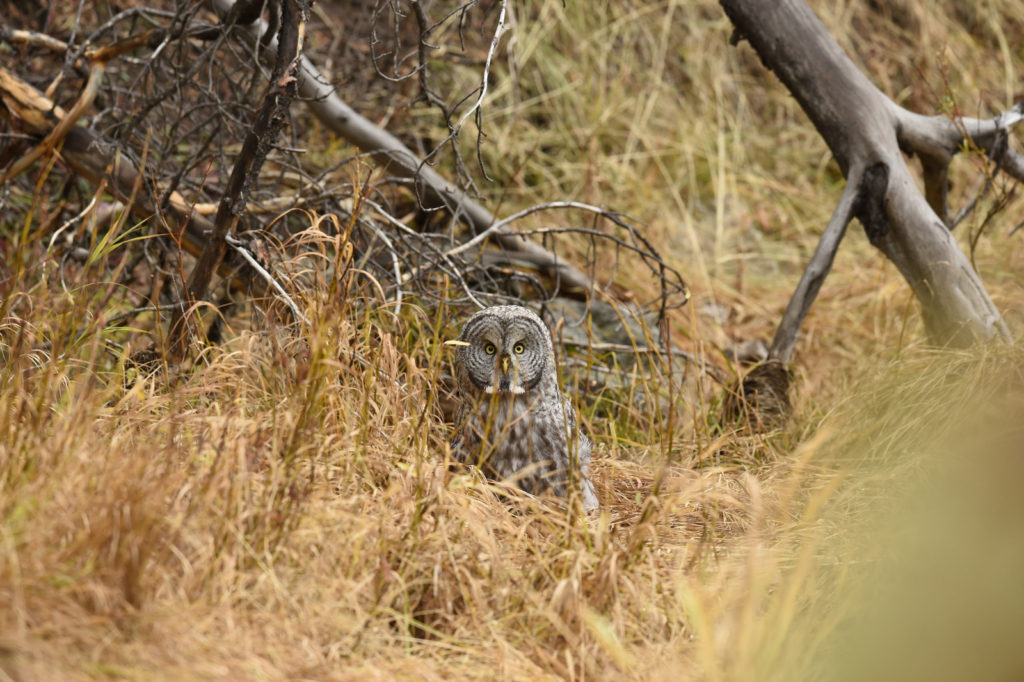
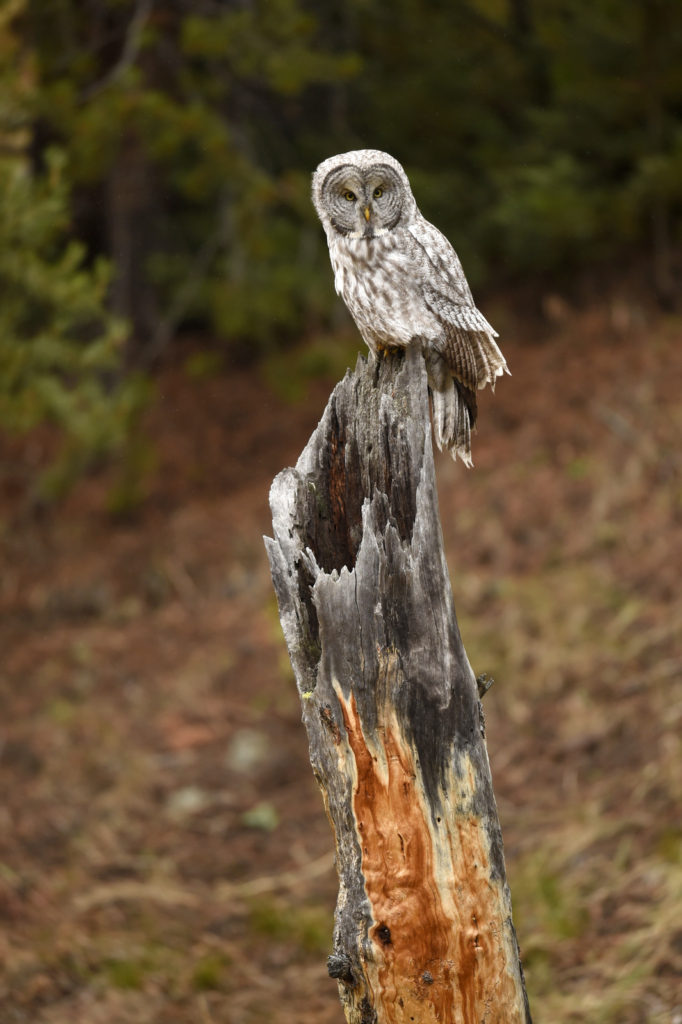
After a few moments the owl took off and flew about 20 yards to a nearby tree. And with that most of the humans started walking back to their cars. I was amazed by this, given that the bird was just right over there, not that far really. But I said nothing and just watched as the crowd left. After a few minutes I walked over to the tree. Sure enough there she was, sitting at the top of a pine tree, still hunting. Now there was just 3 humans- me and two other photographers.
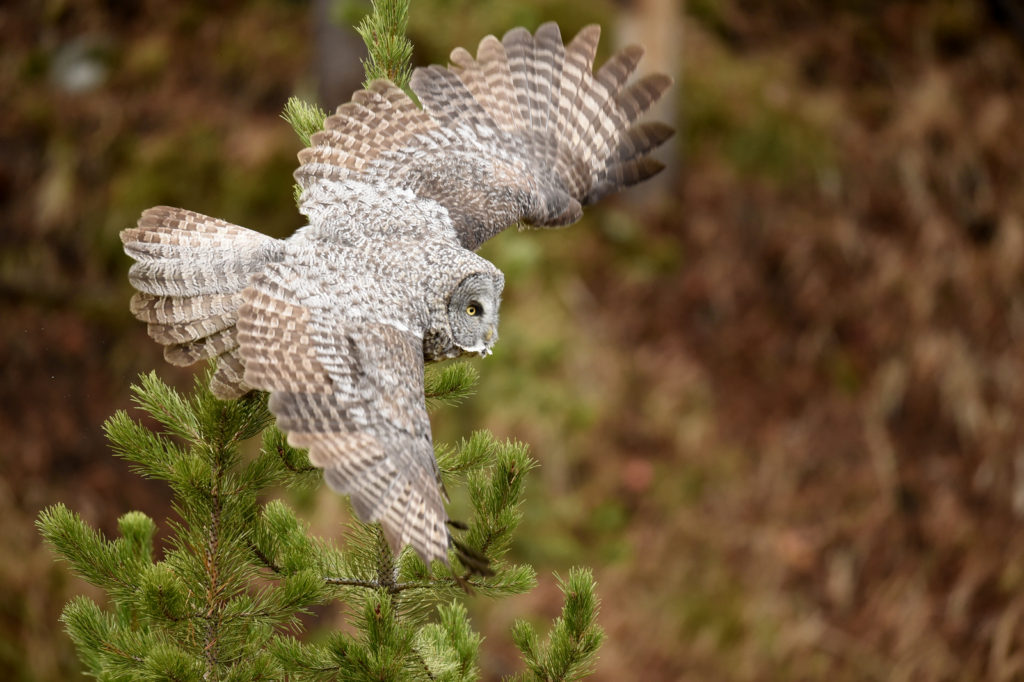
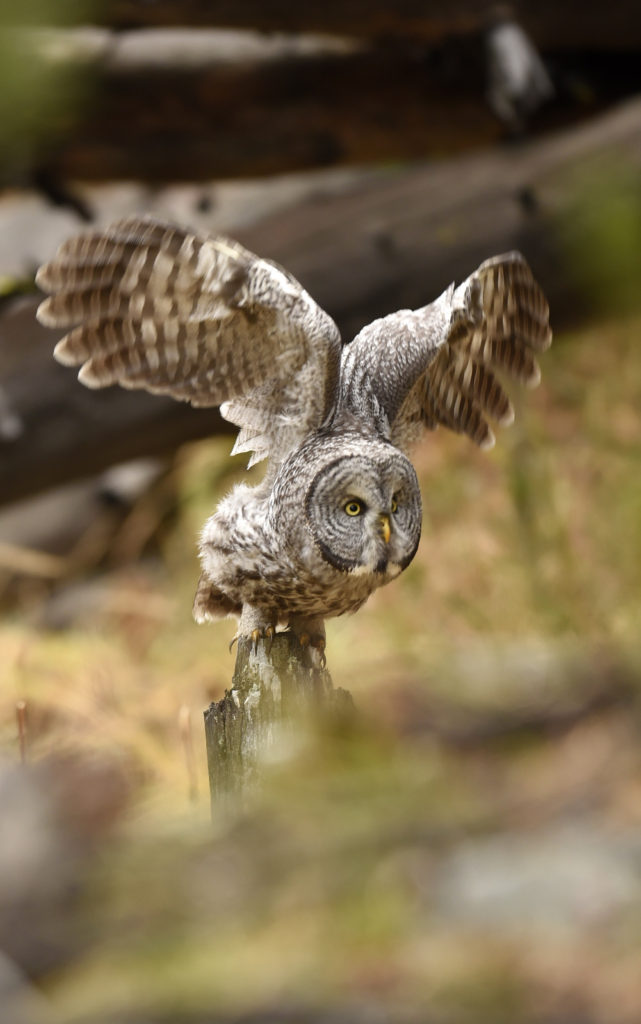
The owl took off again and followed the line of the narrow valley leading to the forest – she was still hunting and apparently following the rustling sounds of mice that we certainly could not hear. She flew from tree to tree as she listened for prey in each little meadow. After about 45 minutes the other two humans lost interest and went back to their cars.
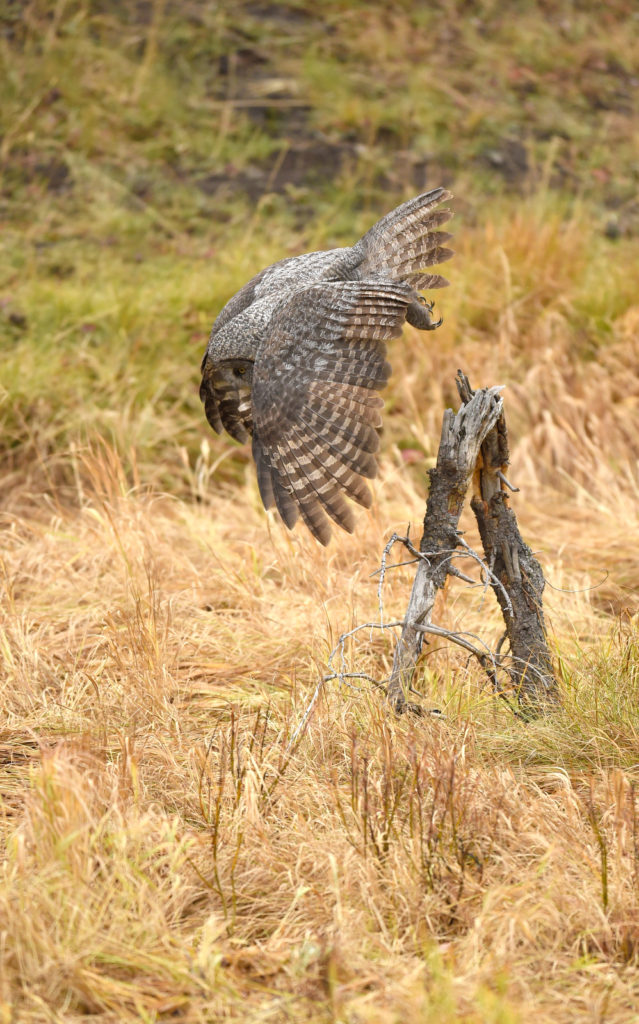
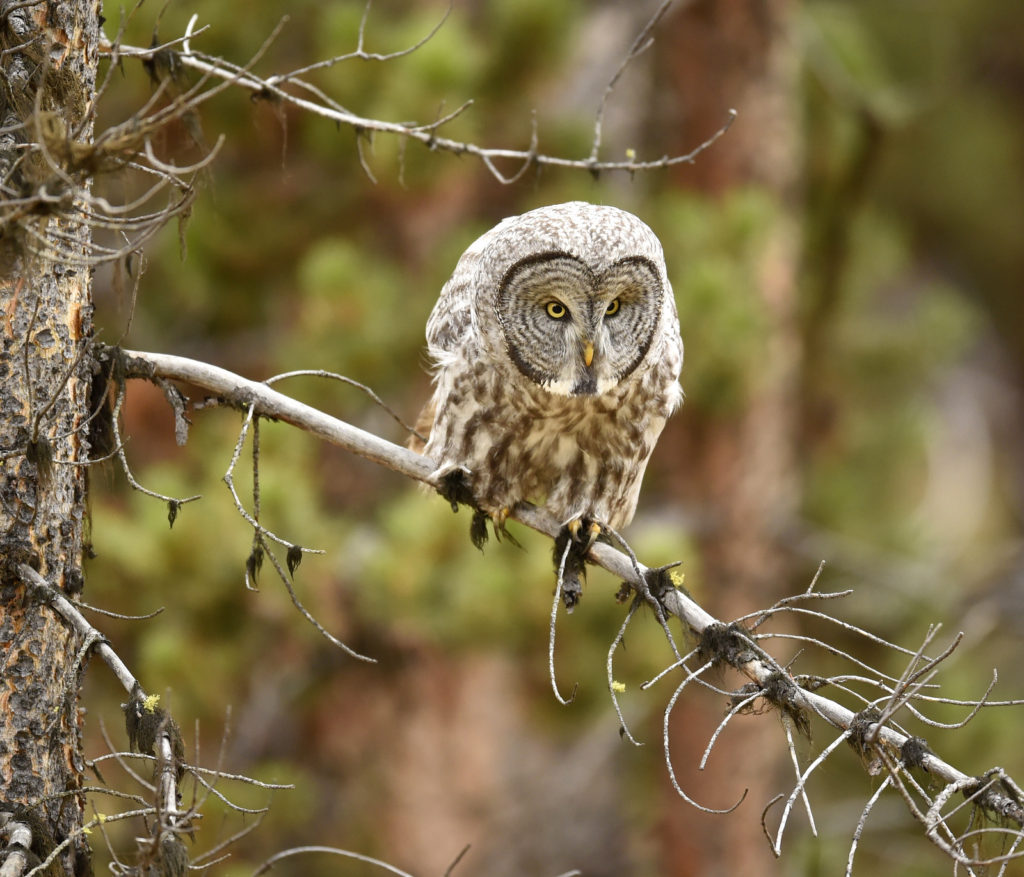
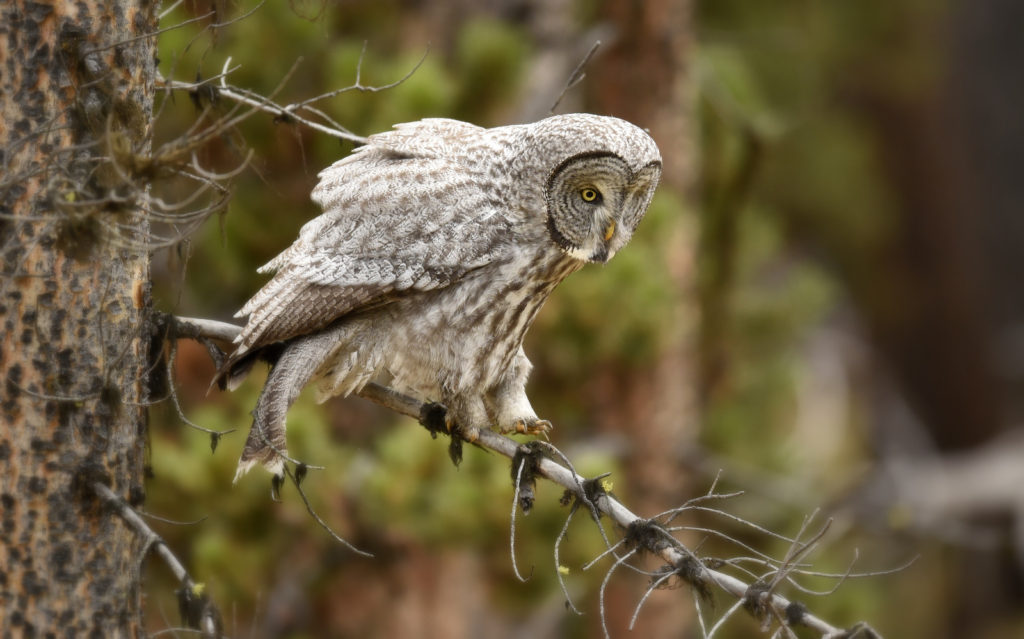
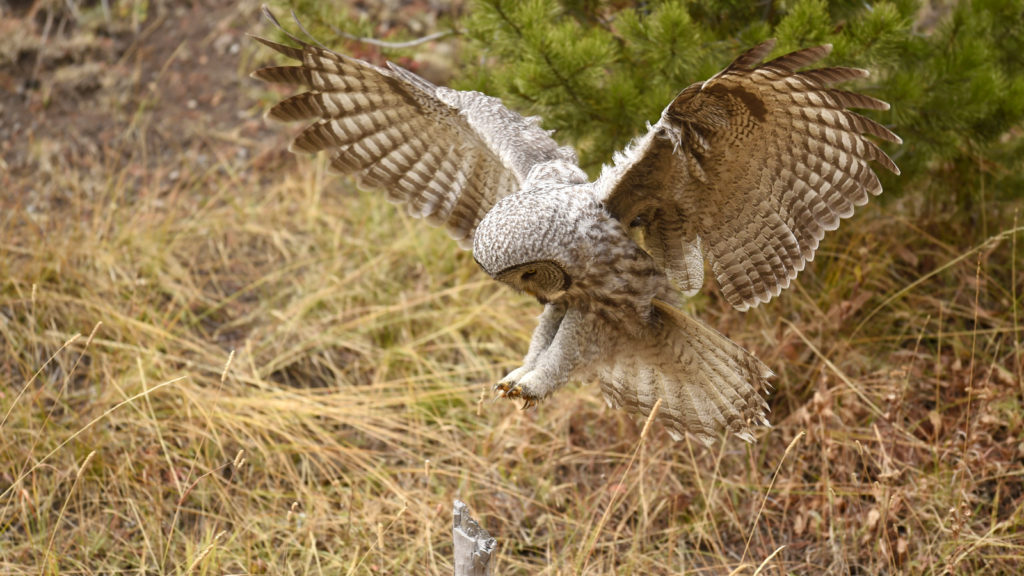
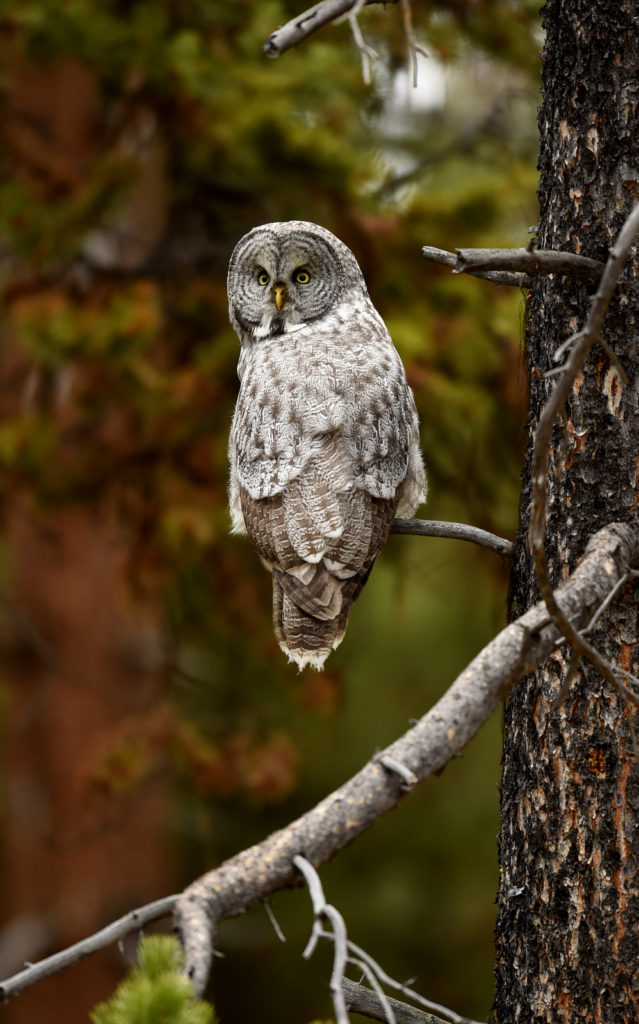
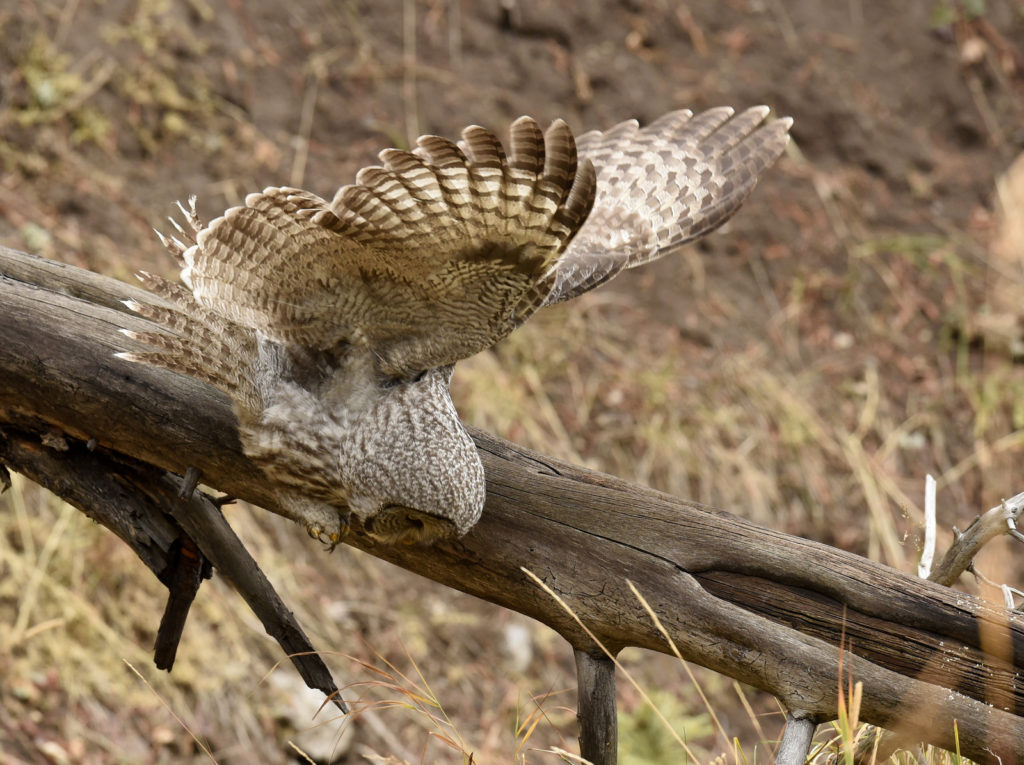
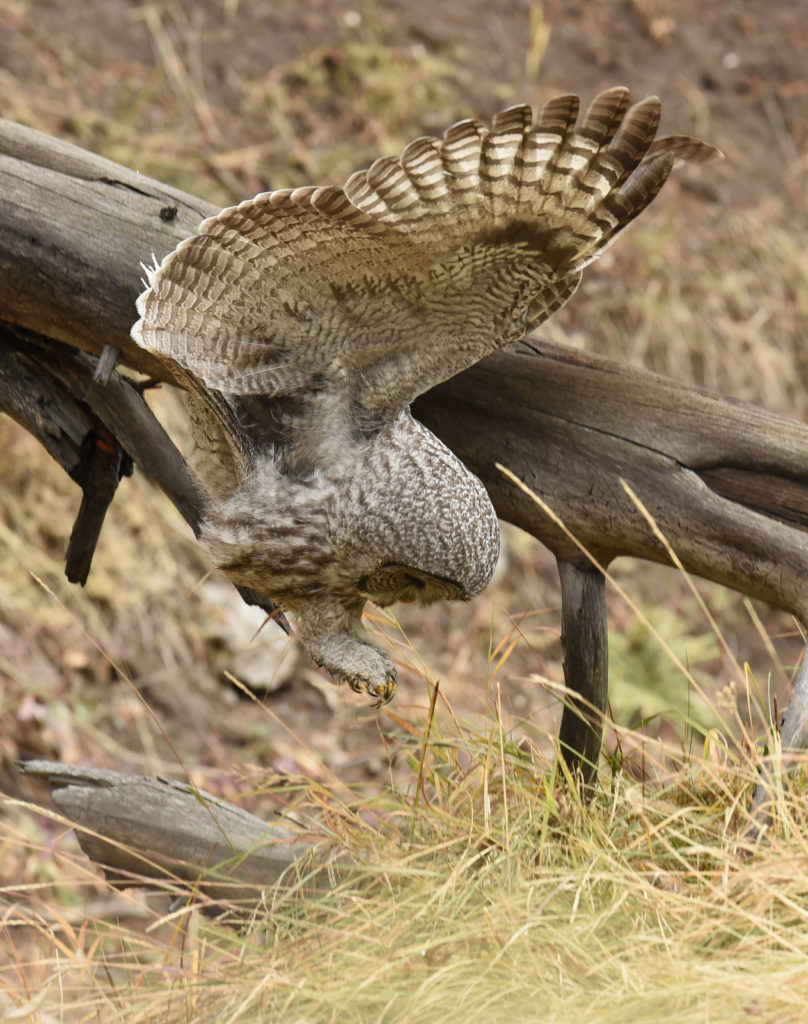
And now here I was, alone with this incredible owl — the largest owl in North America by length. We were now far enough into the forest that we could not be seen from the road. No one would be able to find us here. In total I spent 3 magical hours observing this beauty. During this period I saw her catch at least 2 mice. It was always over in a few seconds. Leap from a tree, dive head first toward to the ground and at the last second pull up and strike feet first. Gulp down the meal and on to the next tree. Repeat. She was not perfect and there were several pounces where she only caught grass and stems.
Wildlife photography can often be fast and furious — worrying too much about apertures, shutter speeds and other technical minutiae. I often don’t really “see” my subject until after I get back and can review my images. And with the growing number of people on this planet, and with more and more people with cameras, one’s time in the “wild” is far too often spent with a gaggle of other humans. Crowds of folks with long lens and tripods like myself. Usually, such forays are not prone to communing with nature and reflecting on life.
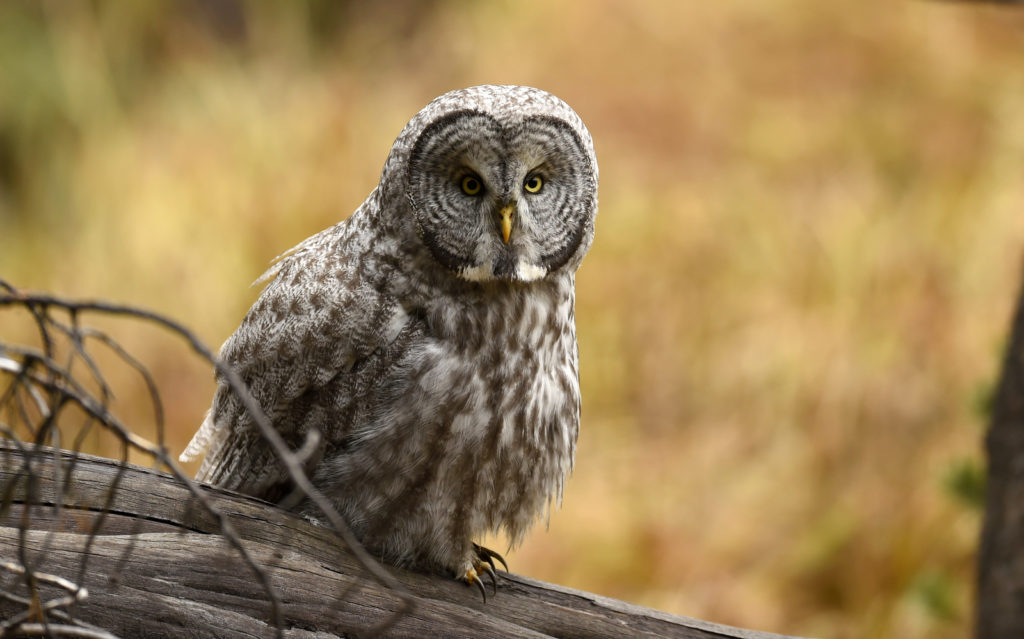
But spending three hours, in a pristine Yellowstone forest, with this larger than life owl? Heaven. The experience captured the ideal of what draws me to nature photography. No sounds but that of the forest birds. No banal banter. Just the occasional sound of the rustling wind. I could sit on the ground and just stare at the owl and really soak her beauty in. Sure, there were some frantic moments when the hunt was on – but then many, actually most moments were spent just sitting and being. A forest. An owl. A man.
But our spirit has an instinct for silence. Every soul innately yearns for stillness, for a space, a garden where we can till, sow, reap, and rest, and by doing so come to a deeper sense of self and our place in the universe. Silence is not an absence but a presence. Not an emptiness but repletion. A filling up.
~ from LISTENING BELOW THE NOISE by Anne D. LeClaire
Below are a collection of images from our journey into the forest together. Click on the first image and then use your right arrow (if on a computer) to move through from one scene to the next.
- This is where I first saw her
- She flew to this tree, most people left
- Listening…
- Time to move on…
- Going in for the kill…
- She missed
- A few minutes later, better luck
- Now deeper into the forest
- She hears something
- Preparing to leap…
- Dive!
- Landing
- Another miss
- A closer look…
- and success!
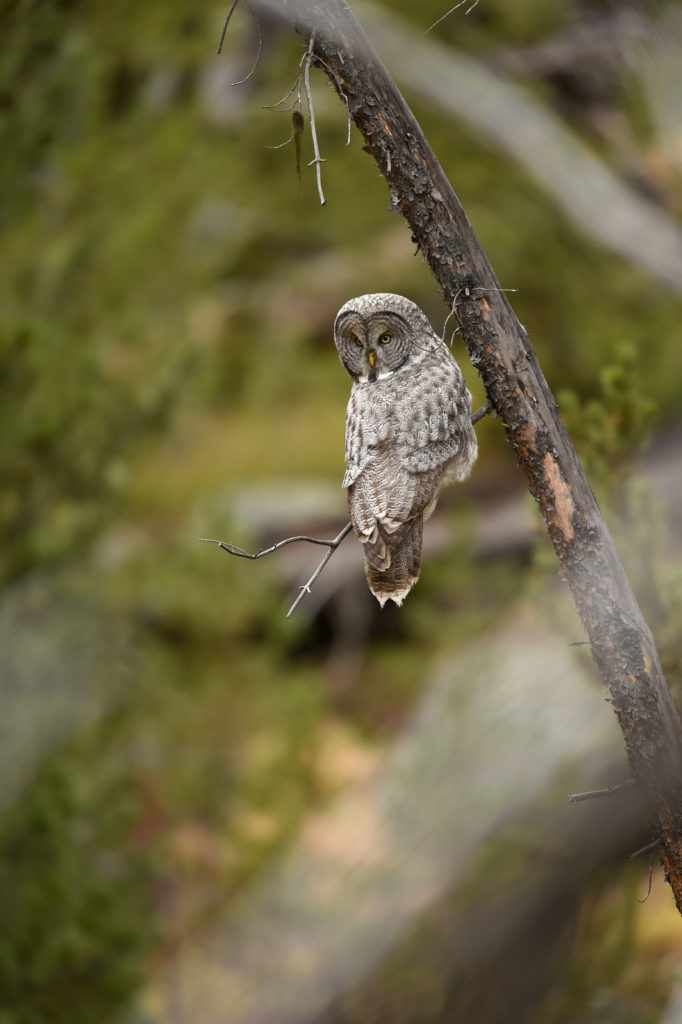
- Continues deeper into the forest
- Listening..
- More listening
- Still hunting..
- Moving to another spot
- Listening from a fallen tree
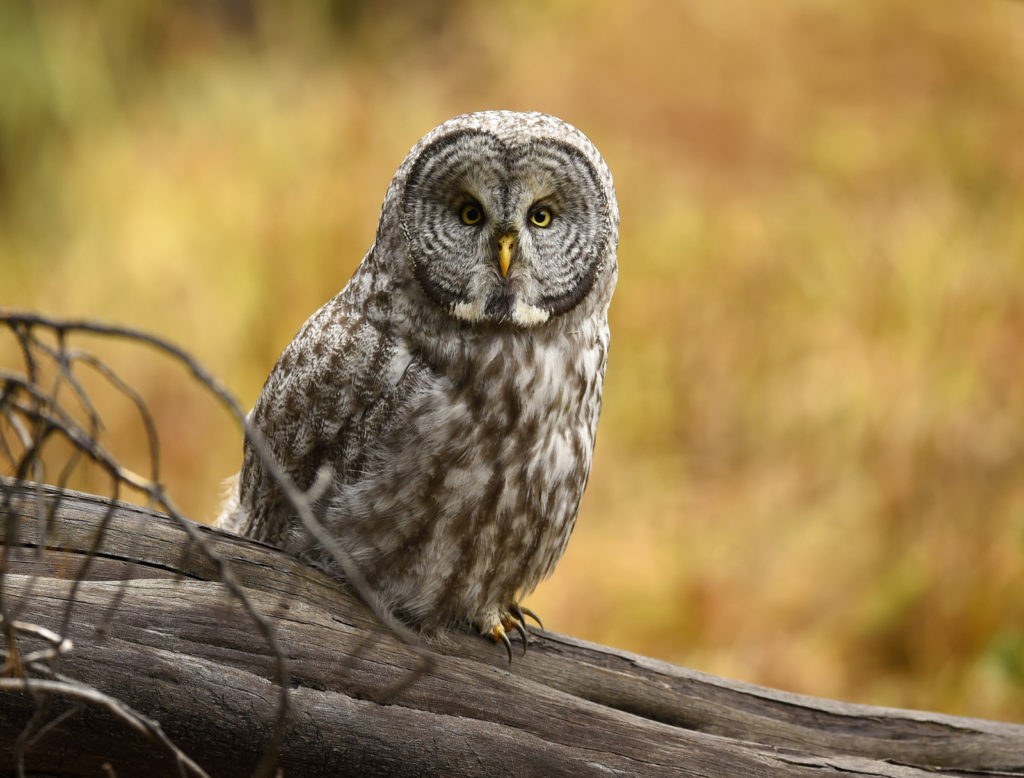
- Lovely
- She hears something
- Dive!
- Talons forward…
- Missed
- Deeper into the forest
- She perched here and began to preen (and a quick snow flurry)
- After three hours, I left her here…
Until next month….
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm f/4, 1/800 s, ISO 360,
28
Shot of the Month – February 2018
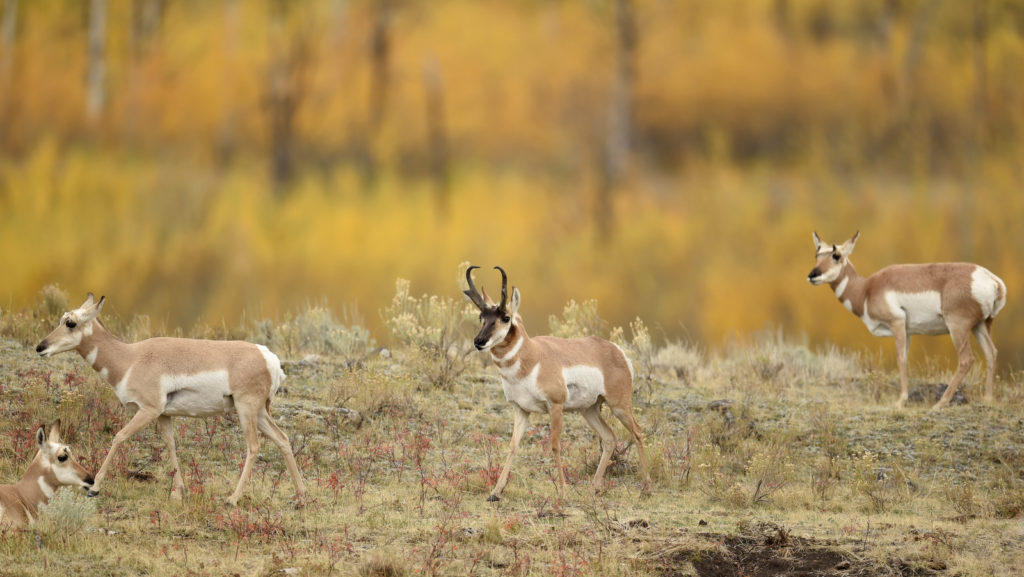
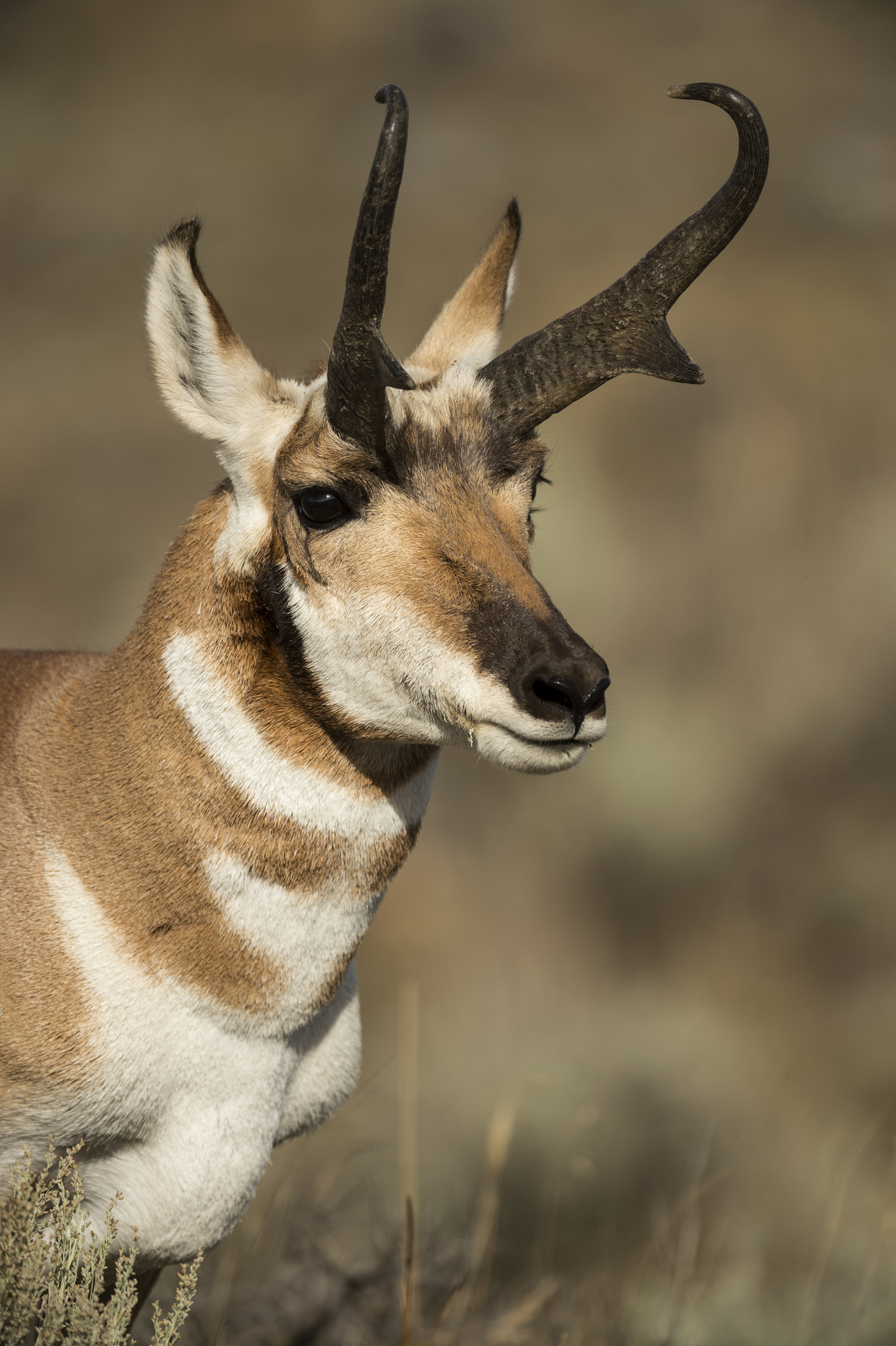 Despite living in a herd, the Pronghorn is really not prone to following the crowd. For example this ungulate (hoofed animal) looks like an antelope, but it is not. They are related to goats and antelope but actually belong to the family Antilocapridaea — they are the only members of this family.
Despite living in a herd, the Pronghorn is really not prone to following the crowd. For example this ungulate (hoofed animal) looks like an antelope, but it is not. They are related to goats and antelope but actually belong to the family Antilocapridaea — they are the only members of this family.
Pronghorn are named after their namesake antlers. Or are they horns? Following their rule breaking tendencies, they are both, and neither. I have a hard time keeping track of the difference between antlers and horns in the best of times, so let’s break it down:
Antlers
Antlers are made of pure bone tissue and are shed and regrown annually. Typically antlers only grow on the males of the Cervidae family and include all species of deer, moose, and elk. Caribou are the exception in that the female caribou also grow antlers.
Horns
Horns have a bony core which is covered with a sheath of keratin, the same stuff that makes up hair and fingernails. Horns are found on members of the Bovidae family which includes a diverse crowd — cows, sheep, goats, water buffalo, antelopes and gazelles. Horns can appear on both male and female. Unlike antlers, horns are never branched, and never shed, and in many species, never stop growing. (source)
So the pointy things on the head of the Pronghorn take on characteristics of both horns and antlers:
— They have two points or “prongs” which makes them like an antler. True horns only have one point.
— They have a layer of keratin like true horns, but they shed the horns each year, as if they were antlers.
— Female Pronghorn also have pointy things on their heads, though smaller. Antlers only grow on the males, usually. Horns can be found on both.
Sooo, I guess they have “Hantlers?” “Horntlers”? “Antlorns”?
These nonconformists are wreaking havoc with our science books and making life tough for biology students.
And I didn’t even delve into rhino horns — yes they are similar but not quite the same. And giraffe horns – again a bit different…but time to end before we fall into “antlarchy.” (See what I did there?)
Until next month….
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm f/5.6, 1/800s, ISO 125
31
Shot of the Month – January 2018
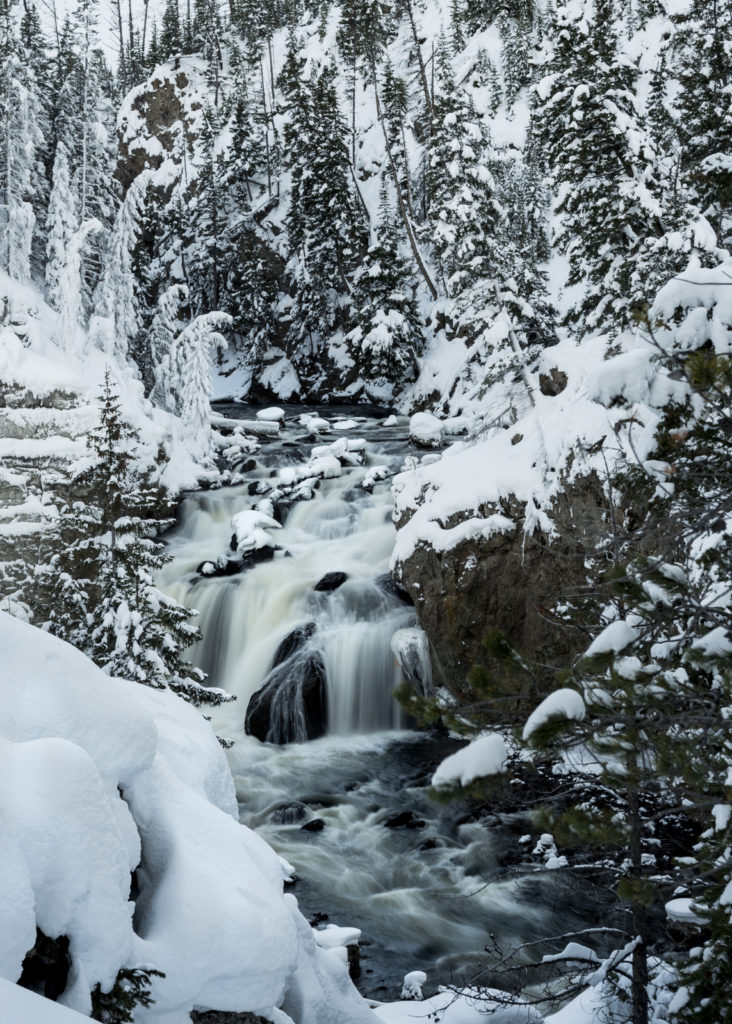
Regardless of the country, people seem drawn to explore, visit, and photograph the natural beauty of waterfalls. How big a draw are waterfalls? Well, over 12 million people travel to see Niagara falls each year along the US-Canada border! That’s just one waterfall out of thousands across the planet.
The dramatic settings and wild beauty of waterfalls are the visual equivalent of catnip for photographers and they hit the trails in droves to take images of falls, big and small, throughout the year. Capturing a compelling image of a waterfall can be a fairly technical, tricky affair — one can’t really just walk up to the water’s edge and snap a picture and expect to get something special.
A few tips for those of you inclined to try your hand at shooting the shoots:
Primary Task: Achieve A Slow Shutter Speed (Confused by shutter speed? Check out this great article)
When we look at a waterfall our eyes transform the falling water into a lovely silky cascade. In order to create this effect in a camera we need to use a slow shutter speed. This means that we want to keep the shutter open for a “long” time. This means, probably a shutter speed of 1/4th of a second. Or 1/3rd of second. 1/2 a second. Perhaps one whole second. You may even want to keep the shutter open for several seconds to make a dramatic looking image. There is no “ideal” speed. You need to experiment with different shutter speeds and find the look that you like best.
High Shutter Speed = The shutter is opens for a short duration (e.g. 1/1000 of a second or less)
Slow Shutter Speed = The shutter is open for a long duration (e.g. 1/2 of a second or more)
The challenge is that during the day, if there is a lot of light available, your camera will not allow you to access those slow shutter speeds as the images will come out overexposed. How do we get there?
Use a Low ISO
Set your ISO to its lowest setting to help keep the shutter speed down.
Use a low Aperture Setting (Great article on understanding Aperture)
Stop your aperture down to f/11 or f/16 or smaller to reduce the amount of light that reaches your camera sensor — this will help create longer shutter speeds and will maximize the depth of field of your shot.
Avoid the Sun
The best time to photograph waterfalls is when it is cloudy – this will make it easier to achieve those long shutter speeds. And shoot at sunrise or sunset when there is less light in the sky. If the sun is out in full force, it might be best to go photograph something else.
Use a Tripod
With slow shutter speeds a tripod is essential to avoid motion blur. No hand holding your camera for a great waterfall shot.
Use Neutral Density Filters ( Learn more here)
Still too much light? Most professional photographers use Neutral Density Filters to reduce the amount of light that can enter into the lens. This allows for the lower shutters speeds that we need to photograph waterfalls and streams. A polarizing filter can also be used as this will reduce the light and will also help remove unwanted reflections from wet rocks, leaves, etc.
I know, all this techno-geekness is rather tedious, but using these techniques and equipment will now allow you to explore the full creative range of one of nature’s natural wonders. From here let your artistic juices flow. How can you create a compelling composition? What should be in the foreground? Any interesting scenery that can be included? How about an unusual viewpoint or angle? Try different lenses – wide angle, zoom lenses, etc. Shoot in portrait and then in landscape. Find a way to get something new or fresh – not the same old shot that every other traveler took of the scene. If you can, go back again and again and explore how the scene is transformed at different times of the day and during different seasons of the year.
Or, leave the camera at home and enjoy the hike and commune with nature. Whatever it takes to get you out there….enjoy.
Here a few good articles on photographing waterfalls:
The Secrets of Stunning Waterfall Photography
Nikon D4S, Nikon 28-105mm (@ 55mm), f/16, 3/5 sec, ISO 100
31
Shot of the Month – December 2017
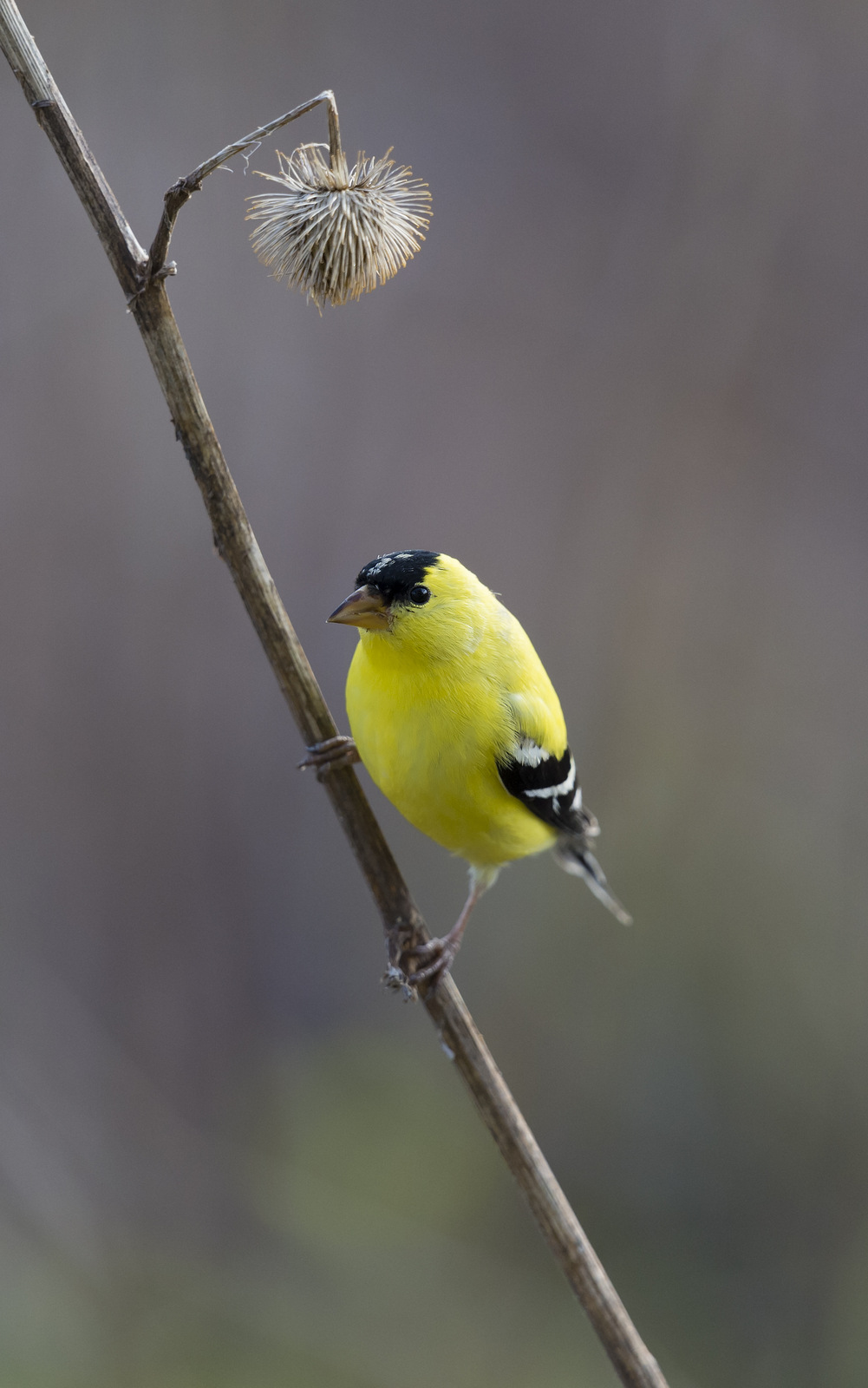 This month a dash of gold to help ward off those winter blues. The American Goldfinch (AG) is a very popular, triple threat kinda bird. First, the bright lemon yellow of the male in full mating plumage is a visual wonder. After a long winter, nothing gives a jolt of hope like catching a glimpse of that bright yellow near the end of spring — it is a clear indication that warmer weather is just around the corner. Second, the AG is not only a looker but also renowned for its lovely song. And last, the AG flies with a bouncy, undulating pattern that is fun to watch — the males often call while singing to draw attention to themselves. Triple threat, and not shy about showing it off.
This month a dash of gold to help ward off those winter blues. The American Goldfinch (AG) is a very popular, triple threat kinda bird. First, the bright lemon yellow of the male in full mating plumage is a visual wonder. After a long winter, nothing gives a jolt of hope like catching a glimpse of that bright yellow near the end of spring — it is a clear indication that warmer weather is just around the corner. Second, the AG is not only a looker but also renowned for its lovely song. And last, the AG flies with a bouncy, undulating pattern that is fun to watch — the males often call while singing to draw attention to themselves. Triple threat, and not shy about showing it off.
The AG prefers open country where weeds thrive, such as fields, meadows, flood plains, as well as roadsides, orchards, and gardens. The AG is also a frequent visitor to bird feeders.
As part of the finch family the AG has a short stocky bill that is useful for extracting seeds from the seedheads of thistles, sunflowers, teasel, dandelion, ragweed, mullein, cosmos, goatsbeard, alder and other plants. This small finch is strictly vegetarian though they may eat the occasional insect inadvertently – hey, we’ve all been there; but generally they eat seeds almost exclusively. Unlike most finches, the AG uses its agile feet extensively to grip the stems of seedheads while feeding. (source)
This strict diet is a problem for Brown-headed cowbirds. How so? Well, the Brown-headed cowbird lays its eggs in other bird’s nests and let’s those parents raise their chicks. It is an incredibly lazy, if not brilliant parenting approach. This strategy fails however if the egg is placed in a goldfinch nest. Once hatched, the poor cowbird chick rarely survives more than three days in their adopted home as they cannot get enough nutrition from that all-seed diet that goldfinch parents feed their chicks.
The AG nests later than most other birds, usually around June or July, to allow the birds to feed on the abundance of milkweed and thistle present at the time of the summer.
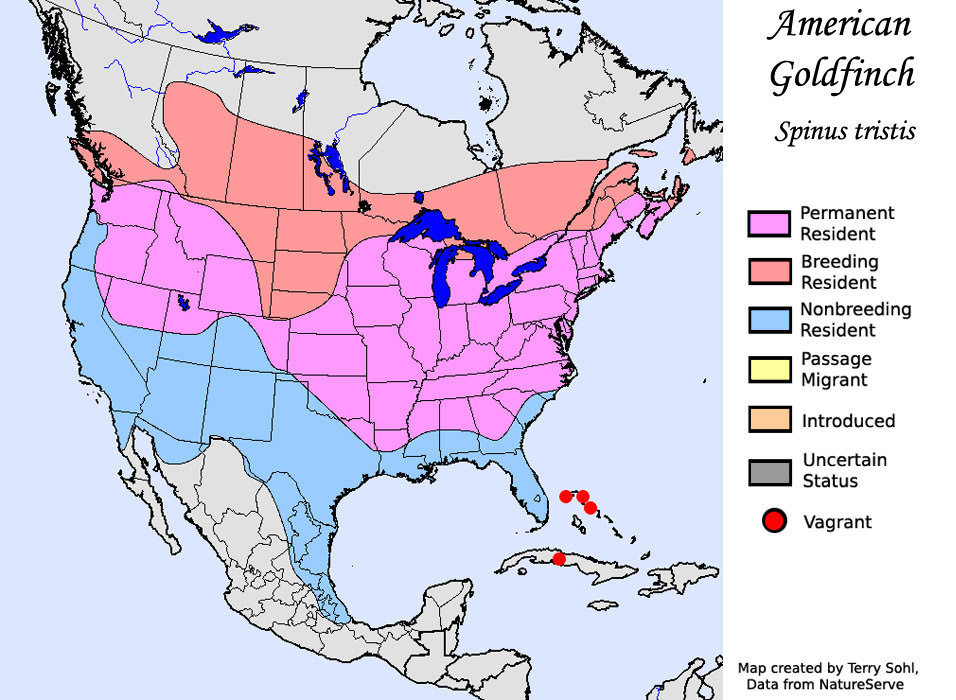
American Goldfinch Range (source)
The AG can be found across most of the United States though these finches will migrate during the winter. Birds in northern areas will move south just enough to reach areas where the minimum average January temperature is no colder than zero degrees Fahrenheit. Wow, that is precise.
The AG is the state bird of Iowa and New Jersey, where it is called the “Eastern Goldfinch”, and Washington where it is called the “Willow Goldfinch”.
The AG is not threatened by human activity and is widespread throughout its range. The clearing of forests by humans, though harmful to many species, has benefited the AG. Clearing of woodlands reduces the number of other birds and creates open spaces where weeds thrive — the preferred habitat for AG.
Good looks, favorable and expanding habitat, and a crowd favorite – for this little finch life is indeed golden.
Until next month….
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, f/4, 1/1000s, ISO 1100,
30
Shot of the Month – November 2017
 One of the great challenges of photography is that our images are forever trapped in a two-dimensional plane. Alas, this often renders our images a poor representation of our richly three-dimensional world and many images can look flat and, well, boring. While we can’t overcome the physical realities of this space-time conundrum, we can use some nifty composition techniques to create the appearance of depth in our photographs.
One of the great challenges of photography is that our images are forever trapped in a two-dimensional plane. Alas, this often renders our images a poor representation of our richly three-dimensional world and many images can look flat and, well, boring. While we can’t overcome the physical realities of this space-time conundrum, we can use some nifty composition techniques to create the appearance of depth in our photographs.
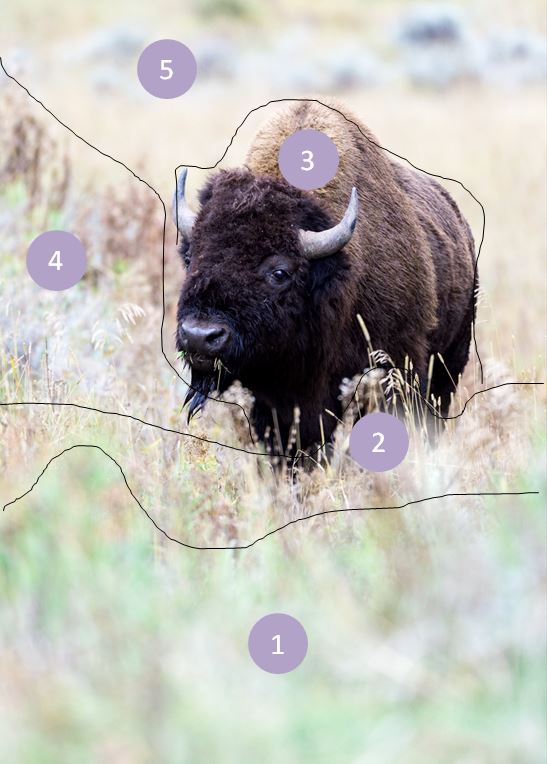
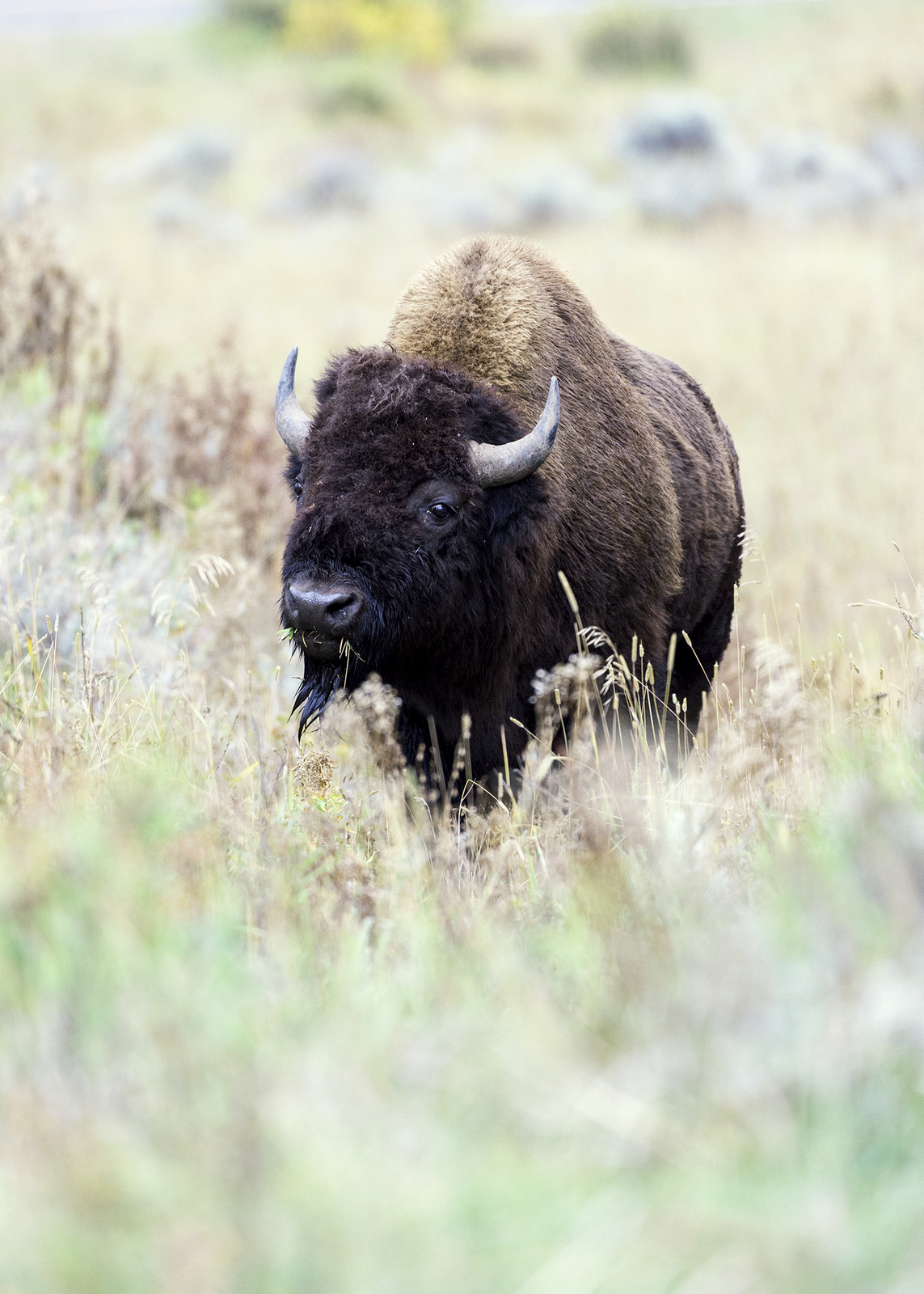
For example, I have dozens of photographs of bison — most of which are pretty mundane — a large brown creature not doing very much. But look at this image — wow, I love how my eye is drawn in. There are so many layers that the image becomes much closer to giving a sense of our 3D world. With this image, we don’t just observe, but we are pulled in and explore the space.
How did we get so much depth in this shot? Let’s break the image up into different zones as shown in the image to the lower right and see how they build depth into the scene.
Depth of Field
By using a wide aperture on my lens the resulting shallow depth field leaves only the bison in sharp focus. Our eyes are naturally drawn to elements that are in sharp focus. In this image, the bison really pops compared to the grasses in front and behind her and provides a sense of depth. (Zone 3) For the basics on understanding depth of field, click here.
Foreground
A visual element in the foreground can add depth. In this image, the out-of-focus green grass provides the first layer to the image. (Zone 1)
Images with the greatest amount of perceived depth will include elements in the foreground, middle ground, and background. In this image, we have the green grass in the foreground, the bison in the middle ground, and the out of focus, but visible bushes of different colors, in the background. Zone 1 is out of focus and green. Zone 2 is still out of focus but now a different color. With zone 3 the bison is in sharp focus compared to all the other zones, and its rich brown color also provides a clear distinction. The color transition of zone 4 from front to back and the verticality of the brown plants in the rear of this zone lead the eye back away from the bison to the empty plain and colored bushes in zone 5.
Overlapping Elements
By having elements in different layers partially block elements behind it one creates the impression of depth. The green grass in the foreground is the first barrier to entry and then we have that yellow grass just before the bison that partially obscures the massive beast. It doesn’t seem like much, but that little bit of yellow grass in front of the bison does a lot to help add a sense of depth to the image. (Zone 2)
Shoot in Portrait
Shooting in portrait helps encourage seeing depth. How so? Well, look straight ahead and then move your head from side to side. Your eyes will naturally fall on objects which are about the same distance away. But if you move your head up and down, now your eyes will focus on objects at varying distances from very near to very far away. Shooting in portrait recreates that dynamic and can help you to create more depth in your image. (source)
These are just a few of the techniques one can use to create images that people will want to reach out and touch because they seem so real.
Photographs often act like a mirror, providing a two-dimensional reflection of the world. With a bit of vision and technique, we can transcend these flat worlds much as Alice did when she walked through her looking glass into a fantastical world of adventure. Try some of these techniques to get beyond photo to portal and transform your photographic reflection into a full-bodied world rich in layers and depth that the viewer will want to leap into and explore.
Here is a very good article with great examples of how you can work a scene to infuse more depth. And here is an article with more techniques that you can use to create depth.
Until next month….m
Nikon D4S, Nikon 200-400mm (@400mm) f/4.8, 1/1000 s, ISO 1000,
31
Shot of the Month – October 2017
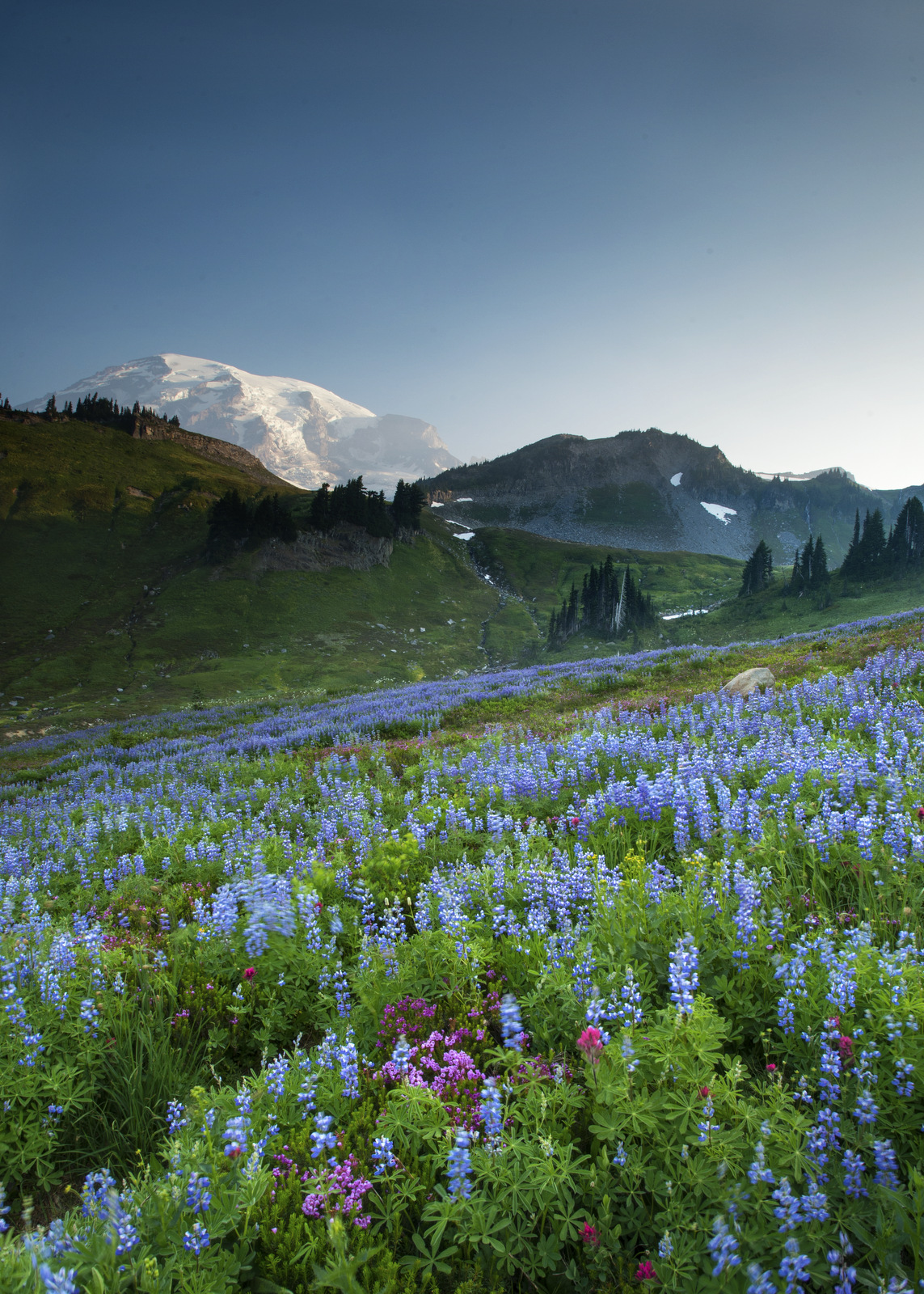 If you love color, check your calendar and your compass as it is likely that Mother Nature is putting on a glorious show somewhere near you. In the northeast of the US, the best time is in the autumn with the fall foliage. Here in Washington state there is a lovely explosion of color in the meadows near Mount Rainier each summer. How good is the display? Well, Bob Gibbons, in his book, “Wildflower Wonders: The 50 Best Wildflower Sites in the World” lists Mt. Rainier as the #1 location to visit!
If you love color, check your calendar and your compass as it is likely that Mother Nature is putting on a glorious show somewhere near you. In the northeast of the US, the best time is in the autumn with the fall foliage. Here in Washington state there is a lovely explosion of color in the meadows near Mount Rainier each summer. How good is the display? Well, Bob Gibbons, in his book, “Wildflower Wonders: The 50 Best Wildflower Sites in the World” lists Mt. Rainier as the #1 location to visit!
The best time to see the show? Well, Mother Nature is an artist and is not fond of strict schedules and the like. She creates as the mood suits her. This mountain park is divided into three zones by altitude. Dense forests cover the low to mid-elevations of the park from 2,000 to 4,500 feet. The cool, shady conditions found here suit wildflower species that won’t be found higher up. These flowers tend to bloom earlier in the summer. Next, we have the subalpine zone from 4,500 to 6,500 feet. The subalpine zone often has the most impressive wildflower displays because the growing season is so short here. Snow can linger in the subalpine meadows into June and even July — so the flowers need to burst out as quickly as they can before the snows return. Climbing higher is the alpine zone from 6,500 feet to the summit of the mountain. There are a few hearty flowers in this zone but it is not where you want to be for the most color. (source)
The “peak” bloom for subalpine wildflowers is very dependent on weather and precipitation patterns. Typically, most flowers will be blooming by mid-July and by early August the fields can be bursting with color. But some years the peak happens in late June. Also, climate change is starting to impact the timing and seems to be shifting the bloom to earlier in the summer. So far I have found the 1st or 2nd week of August to be the most colorful.
What will you see? Mt. Rainier has hundreds of species of wildflowers — a cornucopia of blues, purples, oranges, reds,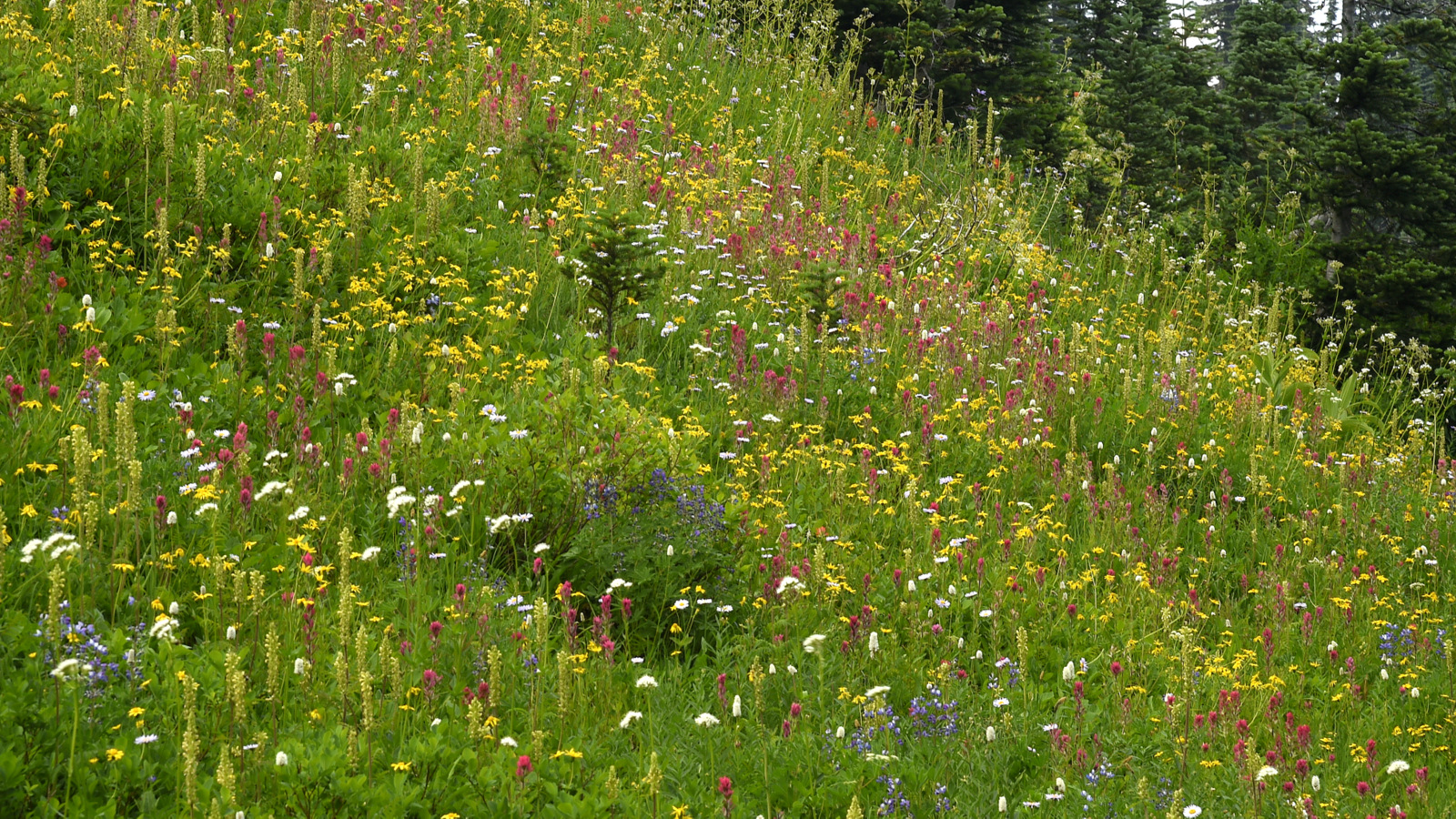 whites, greens, pinks, and on and on. In this quiet, peaceful sunrise image above we look over a long sloping meadow dominated by sub-alpine lupines (purple) that leads to snow-covered Mt. Rainier off in the distance. There are also dashes of red (Scarlet Paintbrush) and pink (Pink Mountain Heather). Come on a different day, at a different time of day, on a different trail and you can see a completely different color palette. Here to the right is a rambunctious burst of afternoon color dominated by yellows (Broadleaf Arnica and Bracted Lousewort)) and reds (Scarlet Paint Brush) amongst others.
whites, greens, pinks, and on and on. In this quiet, peaceful sunrise image above we look over a long sloping meadow dominated by sub-alpine lupines (purple) that leads to snow-covered Mt. Rainier off in the distance. There are also dashes of red (Scarlet Paintbrush) and pink (Pink Mountain Heather). Come on a different day, at a different time of day, on a different trail and you can see a completely different color palette. Here to the right is a rambunctious burst of afternoon color dominated by yellows (Broadleaf Arnica and Bracted Lousewort)) and reds (Scarlet Paint Brush) amongst others.
The canvas changes by the hour.
If you do dig your hiking boots out of the closet to take in a mountainside color exhibition do take great care. Mountain wildflowers are exceptionally fragile. Each step you take off the trail can crush 20 plants. Even if a plant survives the weight of your footstep its growth can be stunted for years!! Stay off the artwork!!
A few resources:
Here is a good article on planning a trip to Mt. Rainier to see wildflowers.
A nice collection of hikes on Mt. Rainier to see wildflowers.
A handy wildflower guide of Mt. Rainier.
Until next month….m
Nikon D4S, Nikkor 17-35mm (@17mm), f/16, 1/10 sec, ISO 200, EV -0.666




























































