31
Shot of the Month – July 2020
In October 2019 I made a quick, mid-week run down to Oregon (Portland is about 3 hours away) to work on my landscape photography skills. I mainly shoot wildlife so I need all the practice I can get. I had visited some of the waterfalls of the Columbia River Gorge in the summer and I wanted to see if autumn brought any interesting color to the compositions. On this quick run, I only had Wednesday afternoon and Thursday morning to make images – not much time but my goal was to try and get at least one good photo from the trip. The falls can get quite busy on the weekends so I went down in the middle of the week to, hopefully, avoid the crowds.
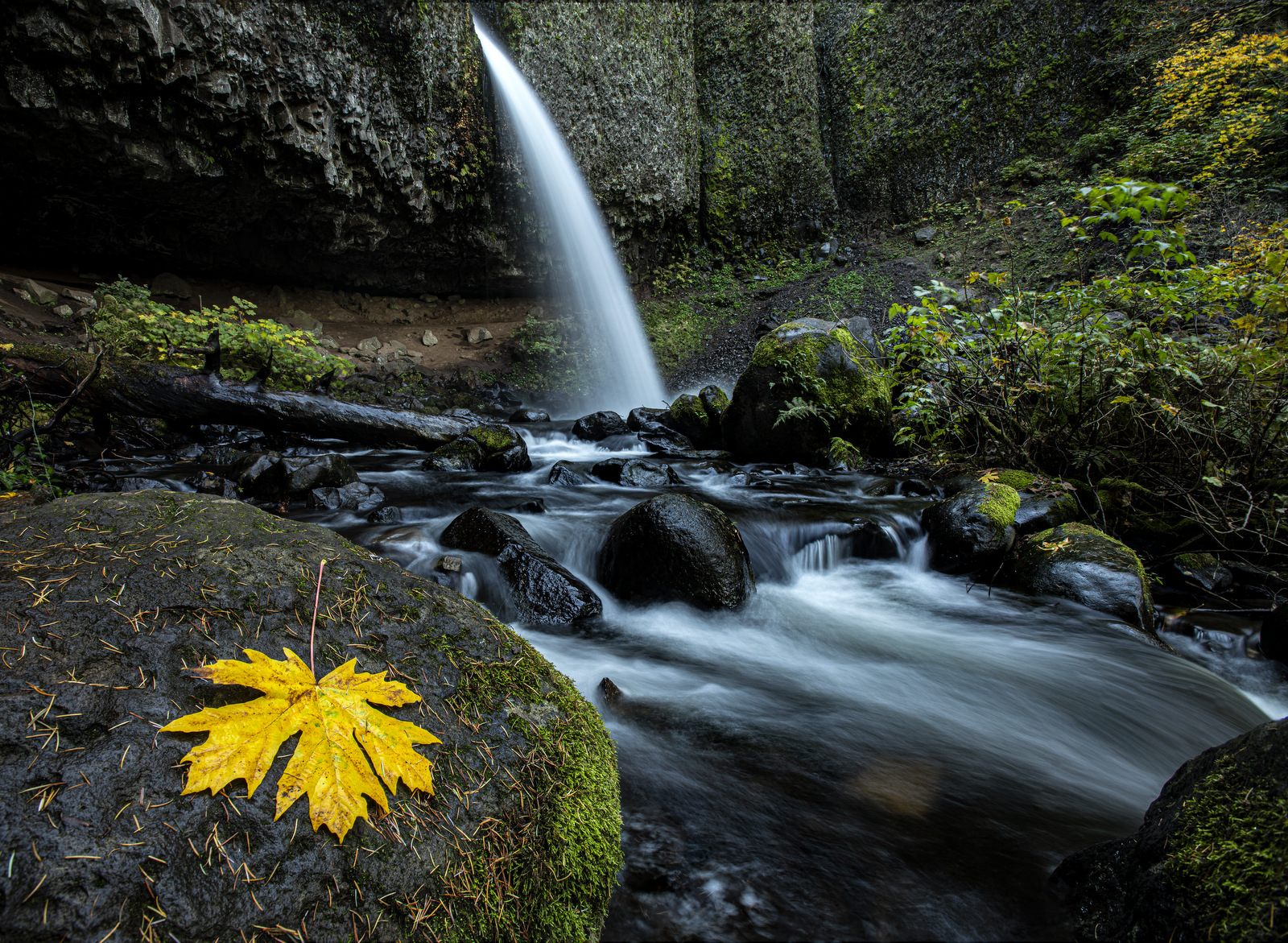
Late Wednesday afternoon I hiked up to Ponytail Falls and found the place deserted. Ahhh, heaven. I could commune with nature and compose my shots in peace. I consider the trip a booming success having created this image — not bad for a wildlife guy!
I had to shoot two images to get the entire scene in sharp focus. In the first image, I focused on the rocks in the foreground (leaving most of the scene behind blurry) while in the second image, I focused on the rocks about 2/3rds back in the scene (which left the rocks in the foreground blurry). By merging the sharp elements from the two images together we get one image that is sharp from front to back.
A great way to improve your landscape images is to ensure that you have a strong element in the foreground of the image. In this case, I used the rock in the lower left corner to anchor the photo. The key to a compelling image is depth and this image has multiple layers — the rocks in the foreground, then the stream, the rocks and bushes a bit further back, then the falling water, and finally the rocks of the cliff face.
Truth be told I did place the yellow maple leaf on the rock — it was lying just next to the rock but I positioned it on the rock for better viewing as it helps tell the story and it is visually compelling. I tried positioning the leaf in multiple places and in various orientations. In the end, this composition worked best – I like how the leaf stem guides your eye into the rest of the image. I had started with “stem down” but it all clicked when I rotated the leave around into the “stem up” orientation. I also like how the yellow leaf mirrors the yellow leaves on the bush in the far back right portion of the scene.
Together, these elements convey “Falls in the Fall.” Just what I was looking for…
Until next month…..m
Here are a few links with ideas on how to improve your landscape compositions:
Importance of Foreground Elements (Video)
5 Landscape Mistakes to Avoid (Video)
How to get a perfect foreground (Article)
Importance of foreground in landscape photography (Article)
Nikon D850, Nikon 17-35mm (@ 17mm), f/8.0, 1.5 sec, -0.5 EV, ISO 64
29
Shot of the Month – June 2020
Warning: Objects on your screen may be smaller than they appear.
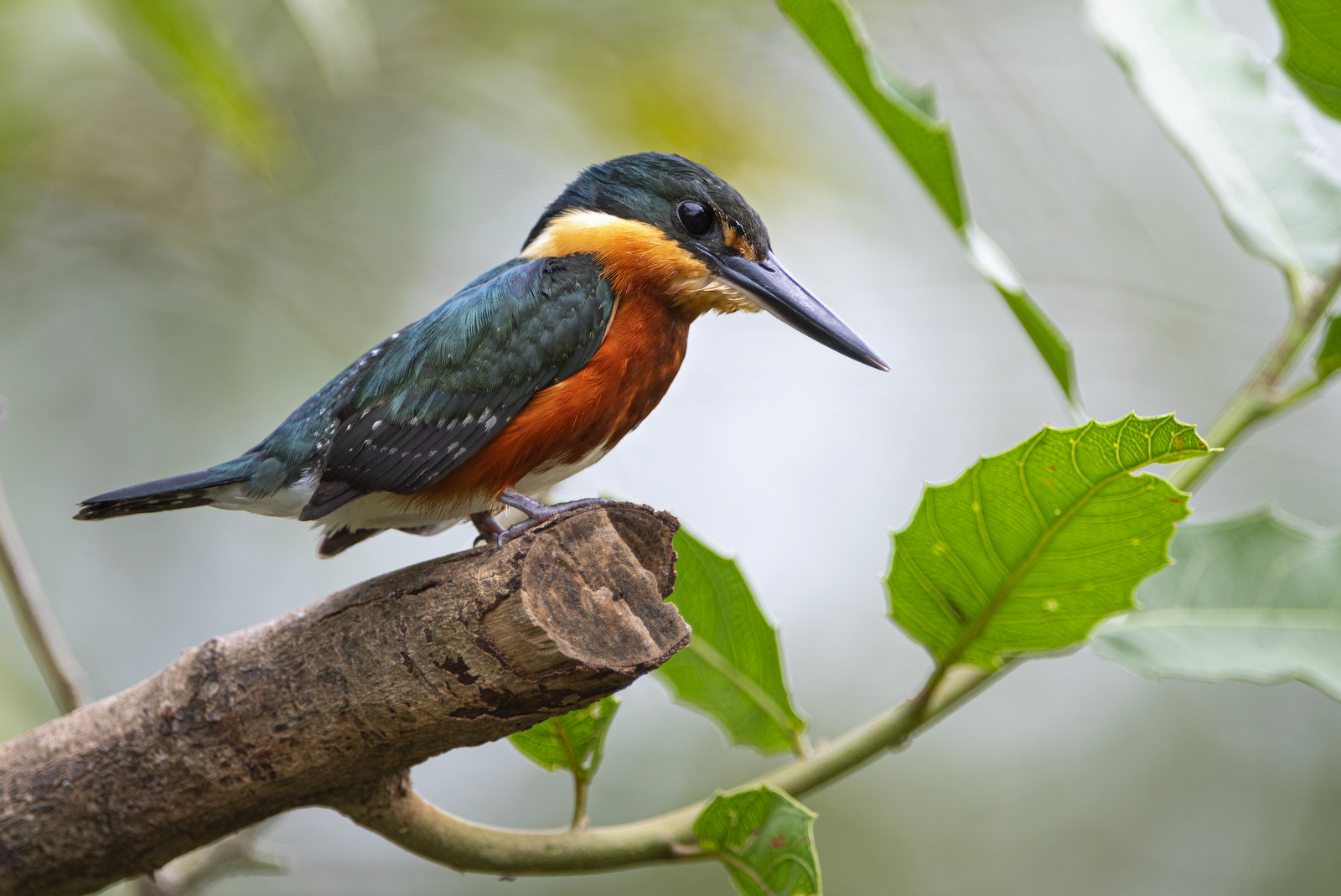
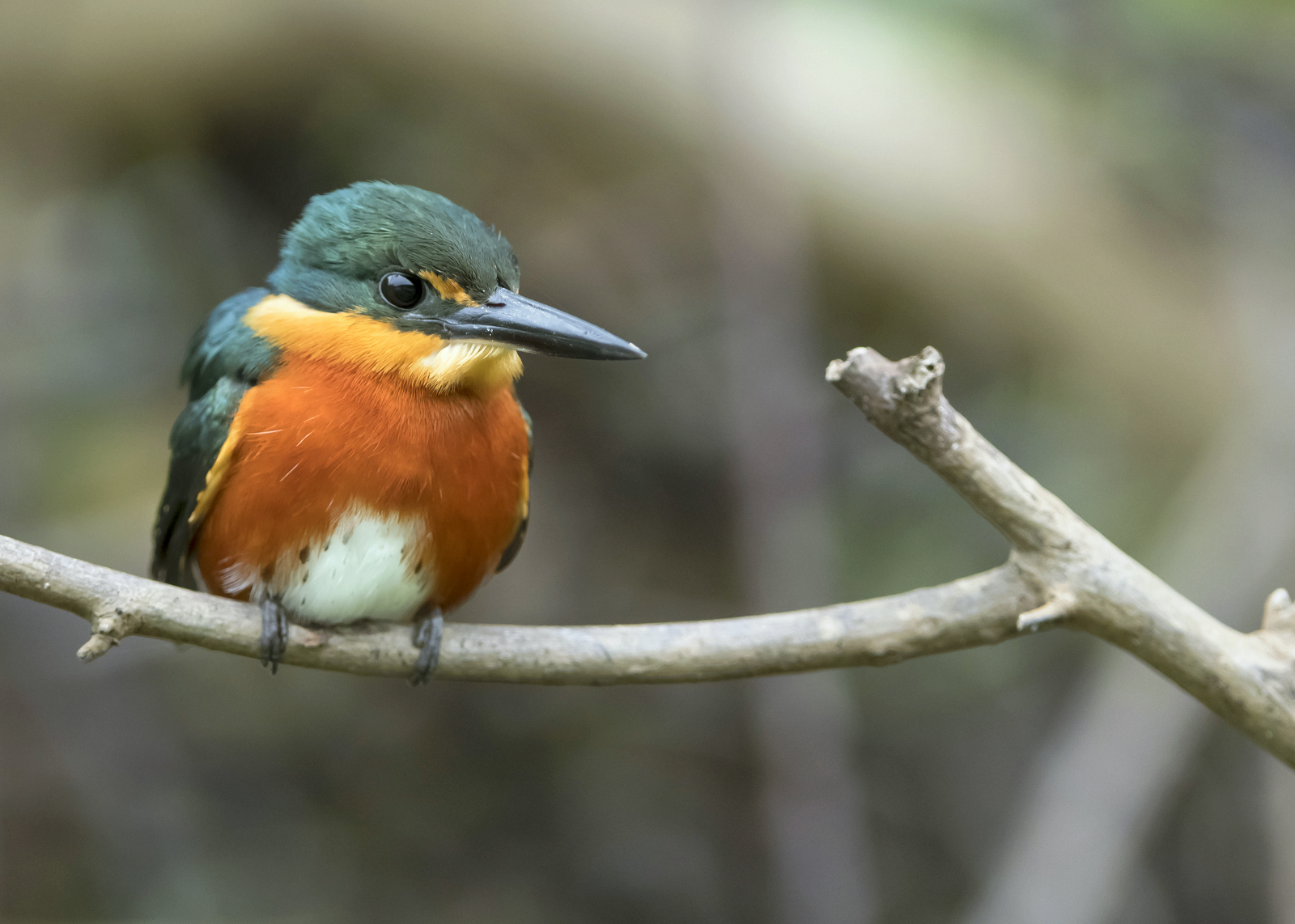
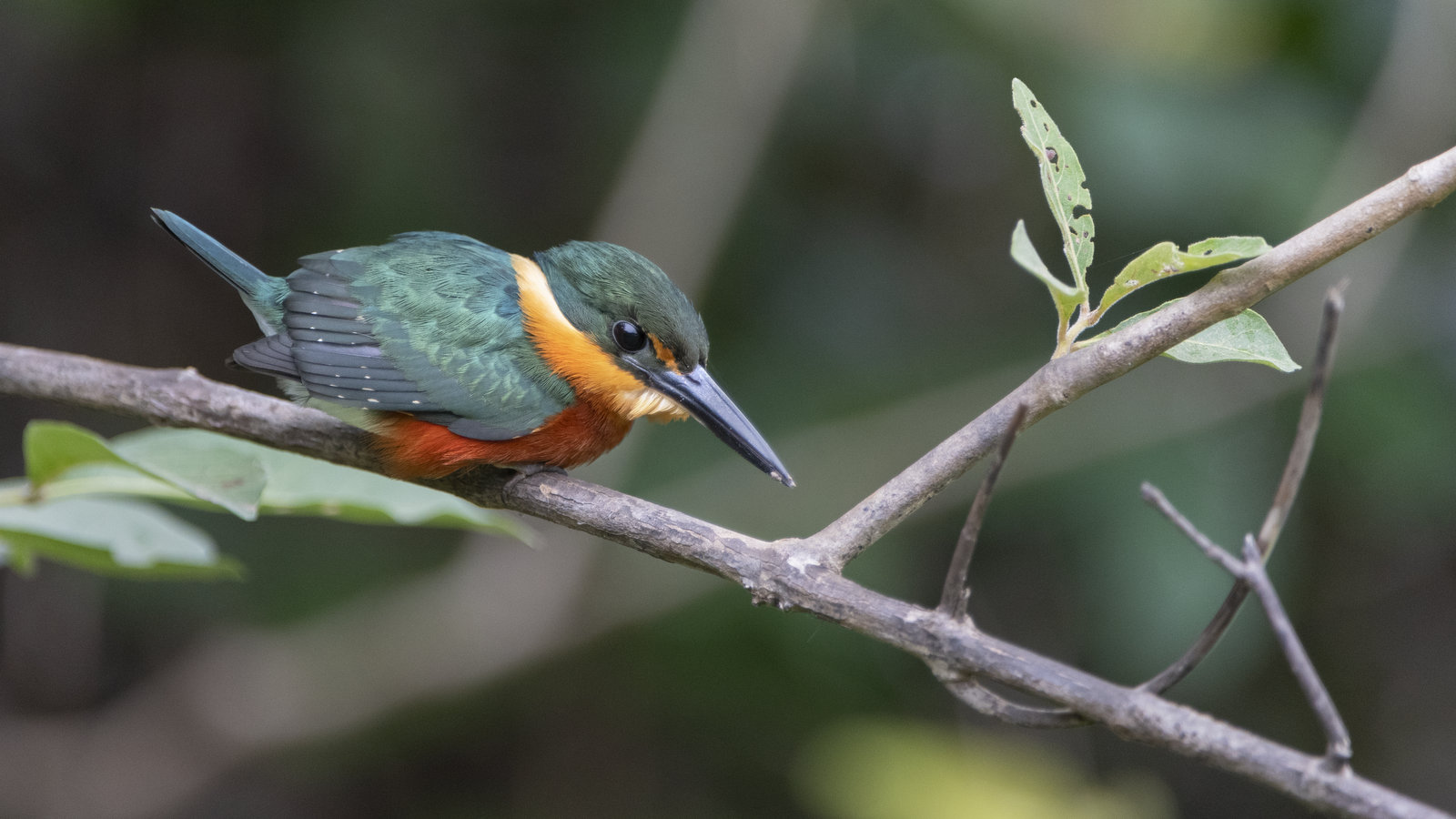
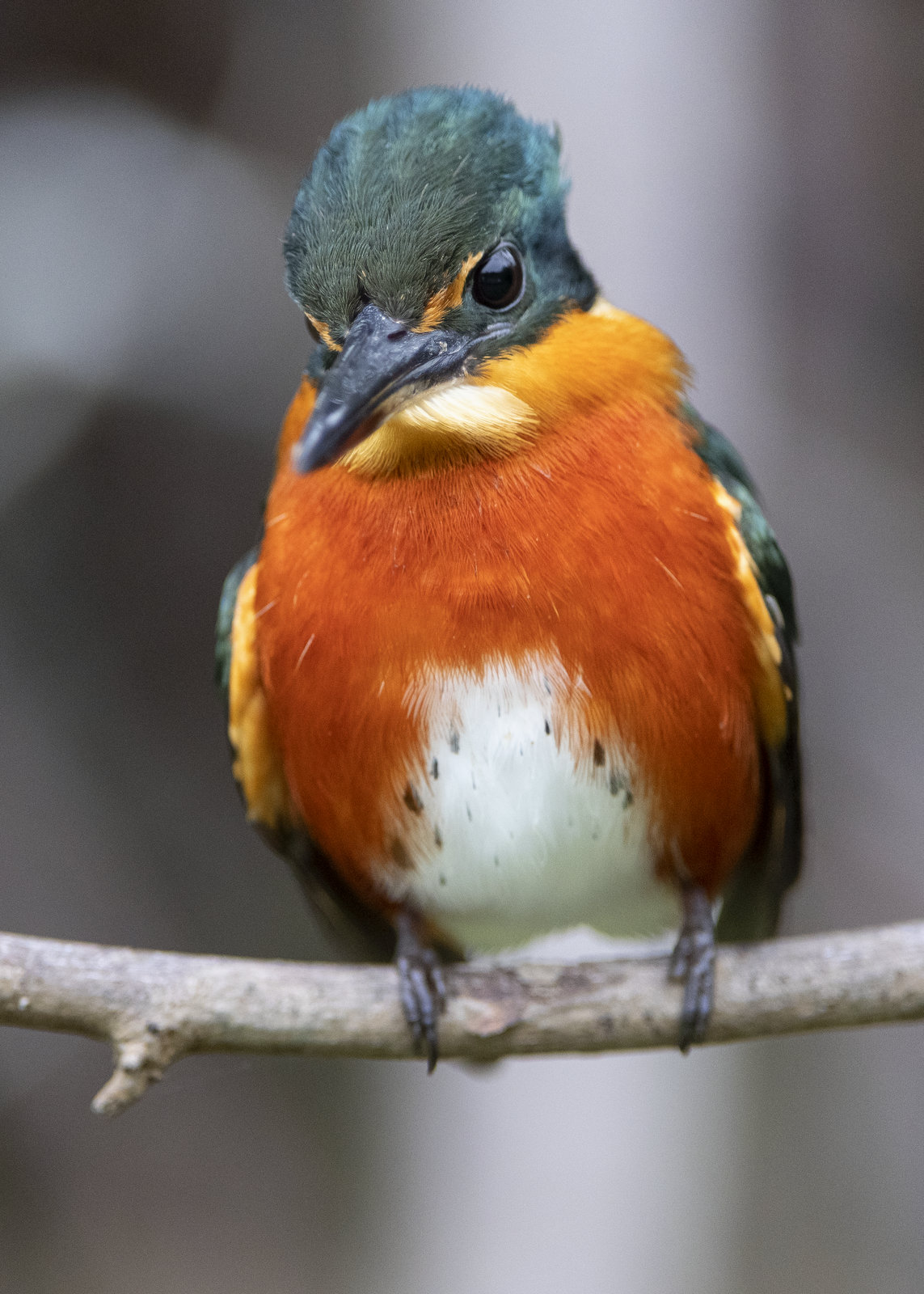
In this image, the American Pygmy Kingfisher (APK) appears to tower over us. Fear not, we are not in danger. The APK is the smallest of all kingfishers and is about 5 inches in length and tips the scales at a mere 18 grams (about the weight of 3 American quarters or about 1/2 an ounce).
The wee bird seems so large because I was floating underneath him in a boat at a close distance with a 400 mm lens when I captured the image. I love this shot as the combination of side lighting and blurred background gives the image an other-worldly, mystical vibe.
APKs can be found in the lowlands of the American Tropics from southern Mexico to central Brazil. They are most commonly seen along small woodland streams, pools, puddles, and small channels in mangroves. You can see their full range here. I photographed this fellow in the Pantanal in Brazil.
The head and wings of the APK are metallic green while its body and neck are deep orange-buff, shading to rich dark rufous on the breast, sides, and flanks. The diminutive kingfisher sits by rivers and will dive headfirst into the water after small fish and tadpoles. He will also dine on insects such as cockroaches, aquatic beetles, and larvae.
Chillin by the river:
Scanning the water below…
Uh, too close!
Smallest of kingfishers = Largest of smiles
Until next month….m
Nikon D500, Nikon 200-400mm (@400mm), f/4, ISO 160, +0.5 EV
Source:
30
Shot of the Month – May 2020
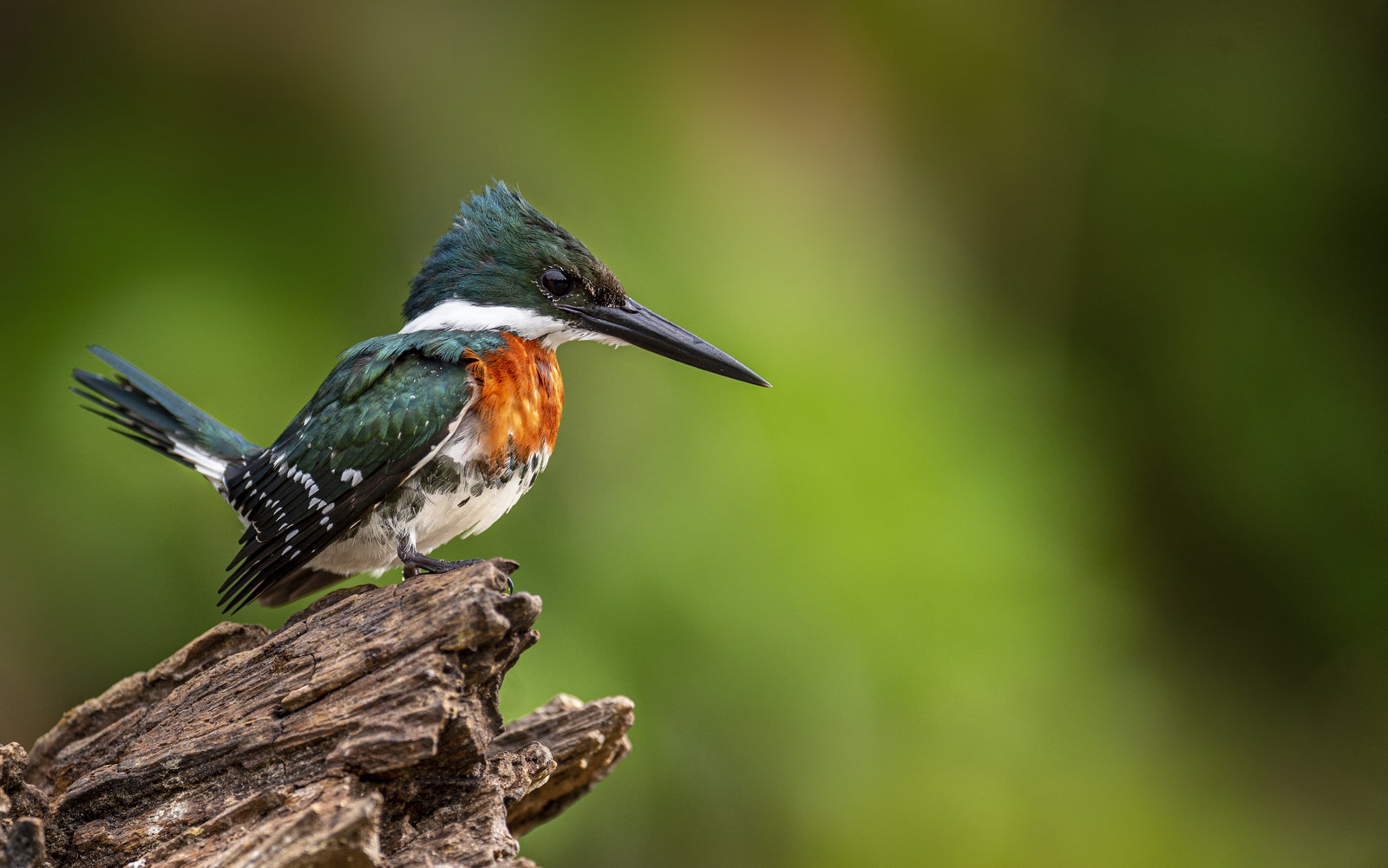
On our first trip to the Pantanal in 2017 we learned that this incredible ecosystem was home to five types of kingfishers. I am a sucker for bold colors so I was hopeful that I might capture a few on “film.” While I was hopeful I was not optimistic, as most kingfishers are tiny and skittish making it very difficult to capture a good image. Seems that they do things differently in the Pantanal. On our first day on the water, during a three-hour boat trip on the Pixaim River we saw ALL five species. And even better, the birds often took no notice of us as we drifted by as they scanned the water below for fish. On our second trip to the Pantanal in 2019 I captured the image above of a male Green Kingfisher (GK). The female GK looks similar though she does not have the rufous colored chest feathers.
Small fish are the mainstay of his diet so you can usually find the GK perched on a low-hanging branch near the water’s edge as the bird looks for fish that swim near the surface. Aquatic insects are also on the menu.
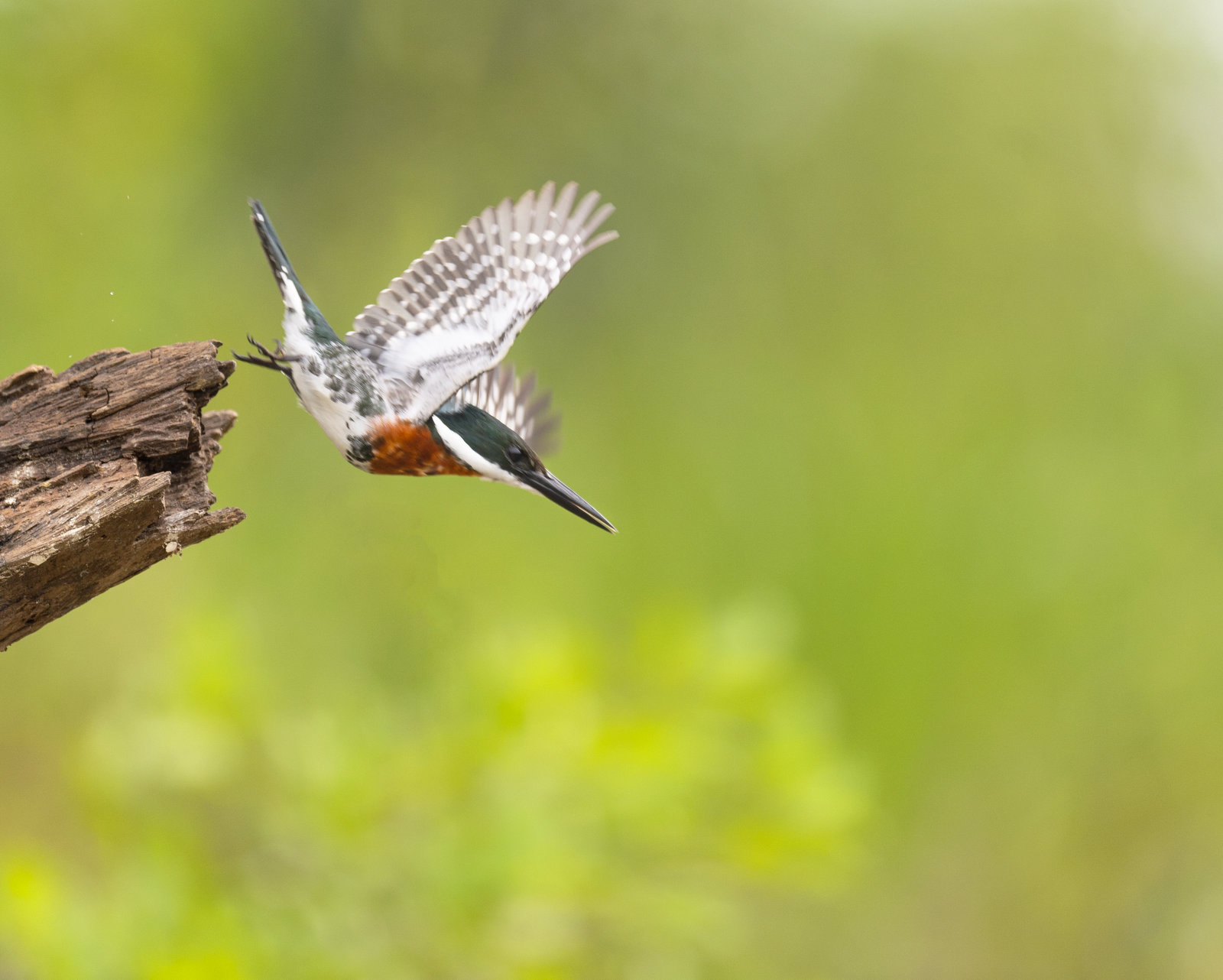
Target acquired, Dive!
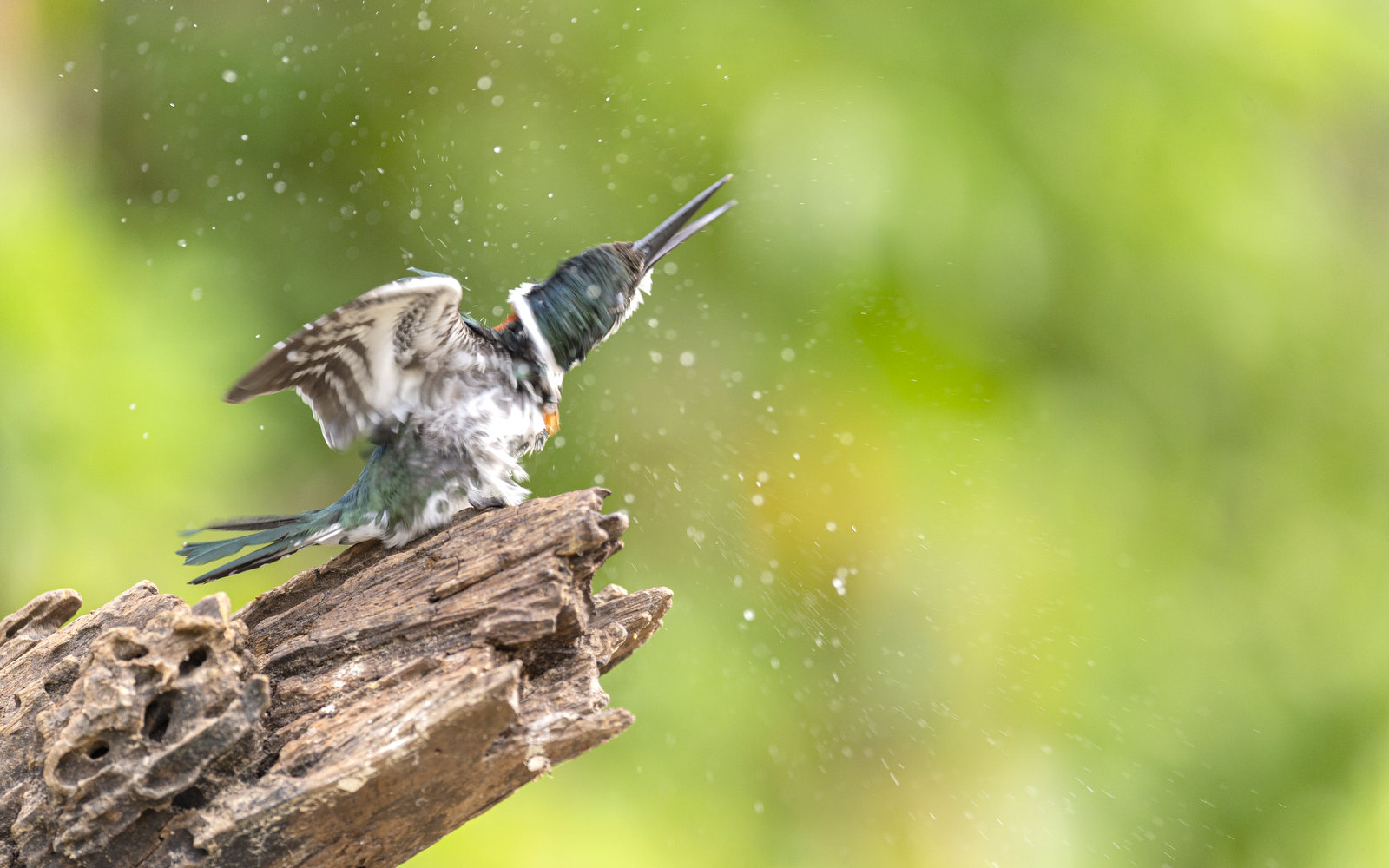
Target missed! Time to shake it off and get back in the game.
The Green Kingfisher can be found from Southern Texas through most of Central and South America. Their numbers are dropping in Texas due to loss of habitat but they are still plentiful further south. To raise their young GKs build a horizontal tunnel into the side of the river bank. The tunnel is about three long and about two inches wide. (Two inches wide – that gives you a sense of how small these birds are)
This kingfisher, Chloroceryle americana, for you science types, is a real beauty and surely leaves the other birds green with envy.
Until next month…..m
Sources:
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, f/4, 1/1000 sec, ISO 720 (Shot in Manual Mode with Auto ISO)
30
Shot of the Month – April 2020
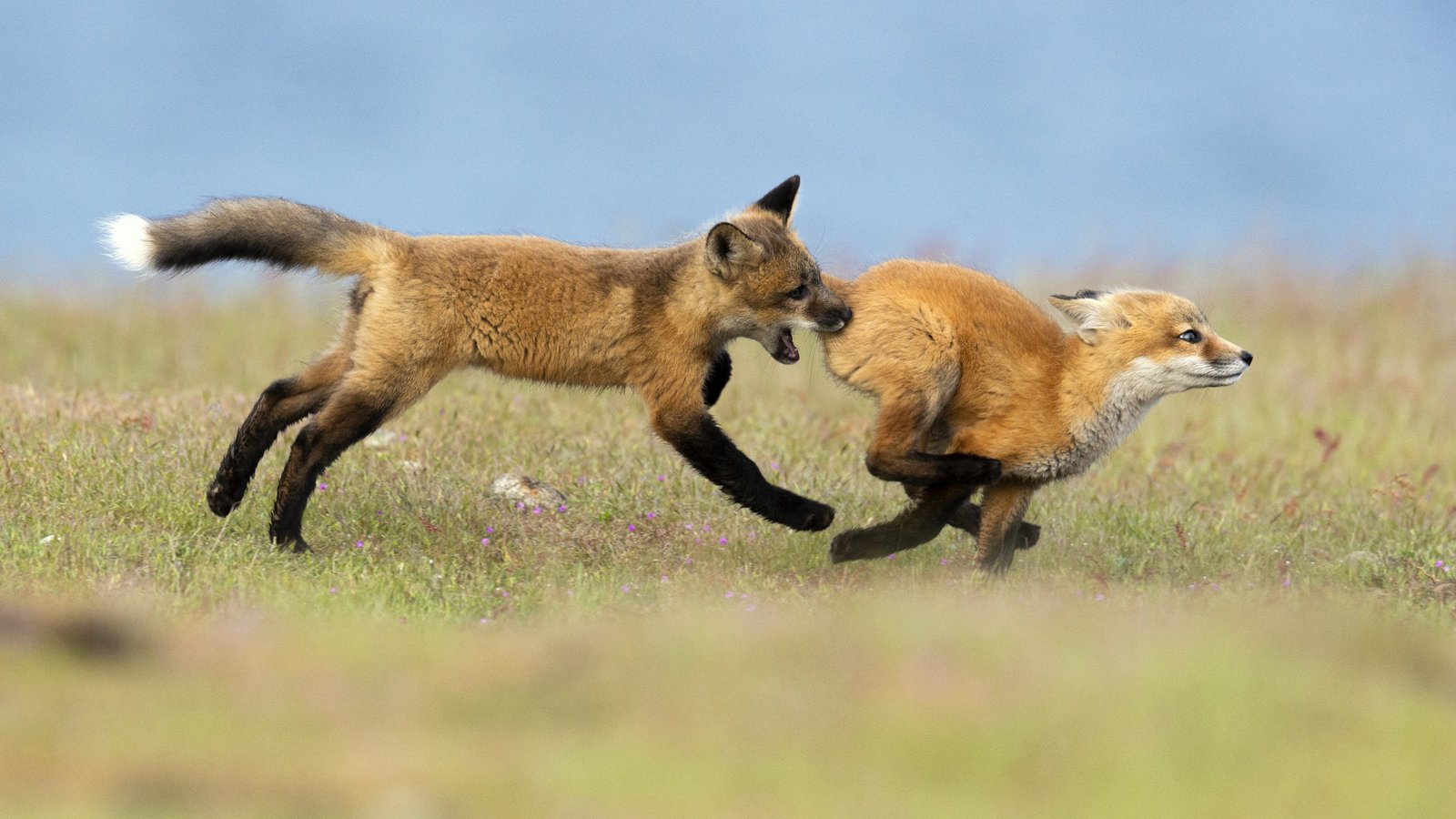
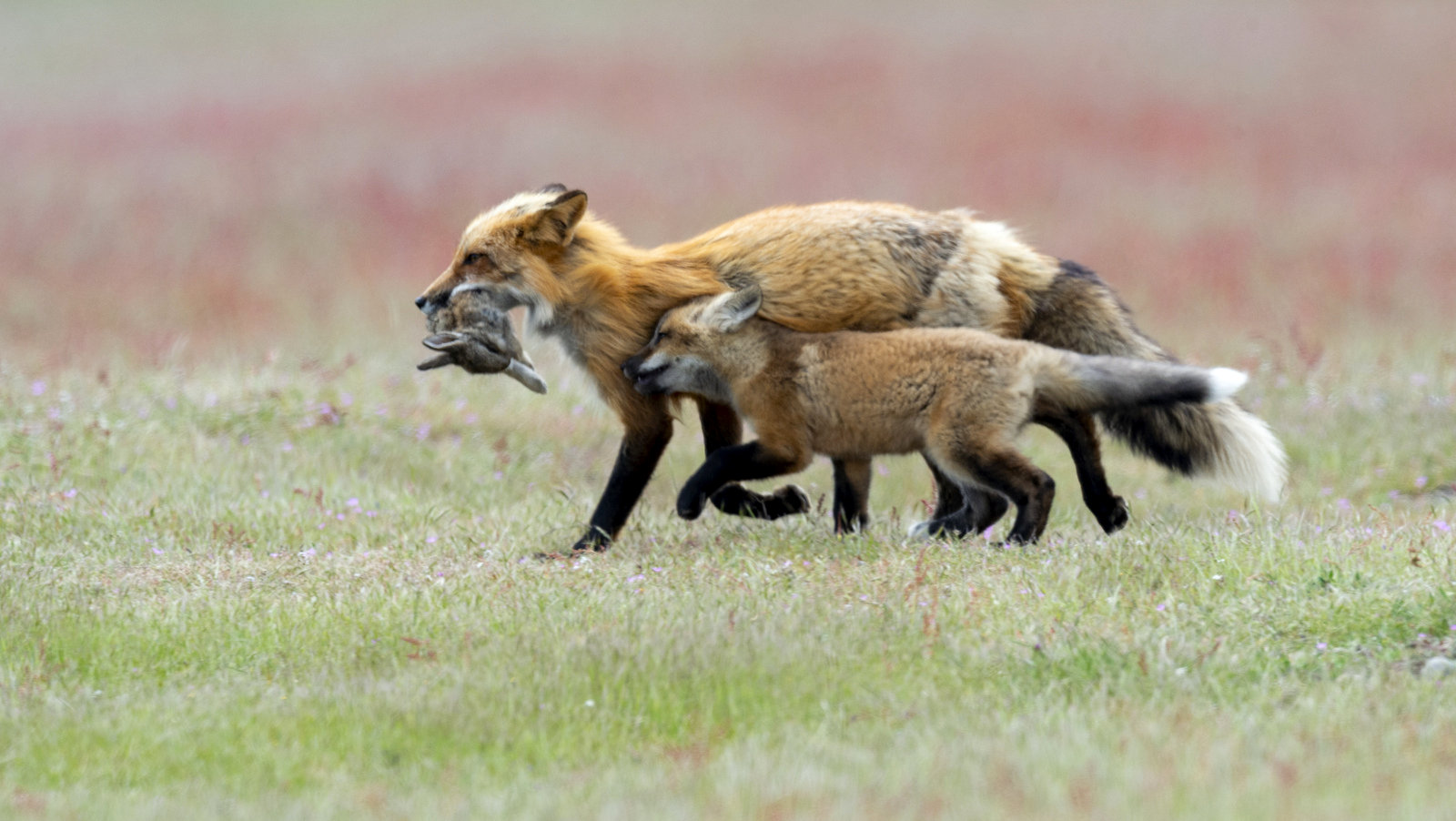
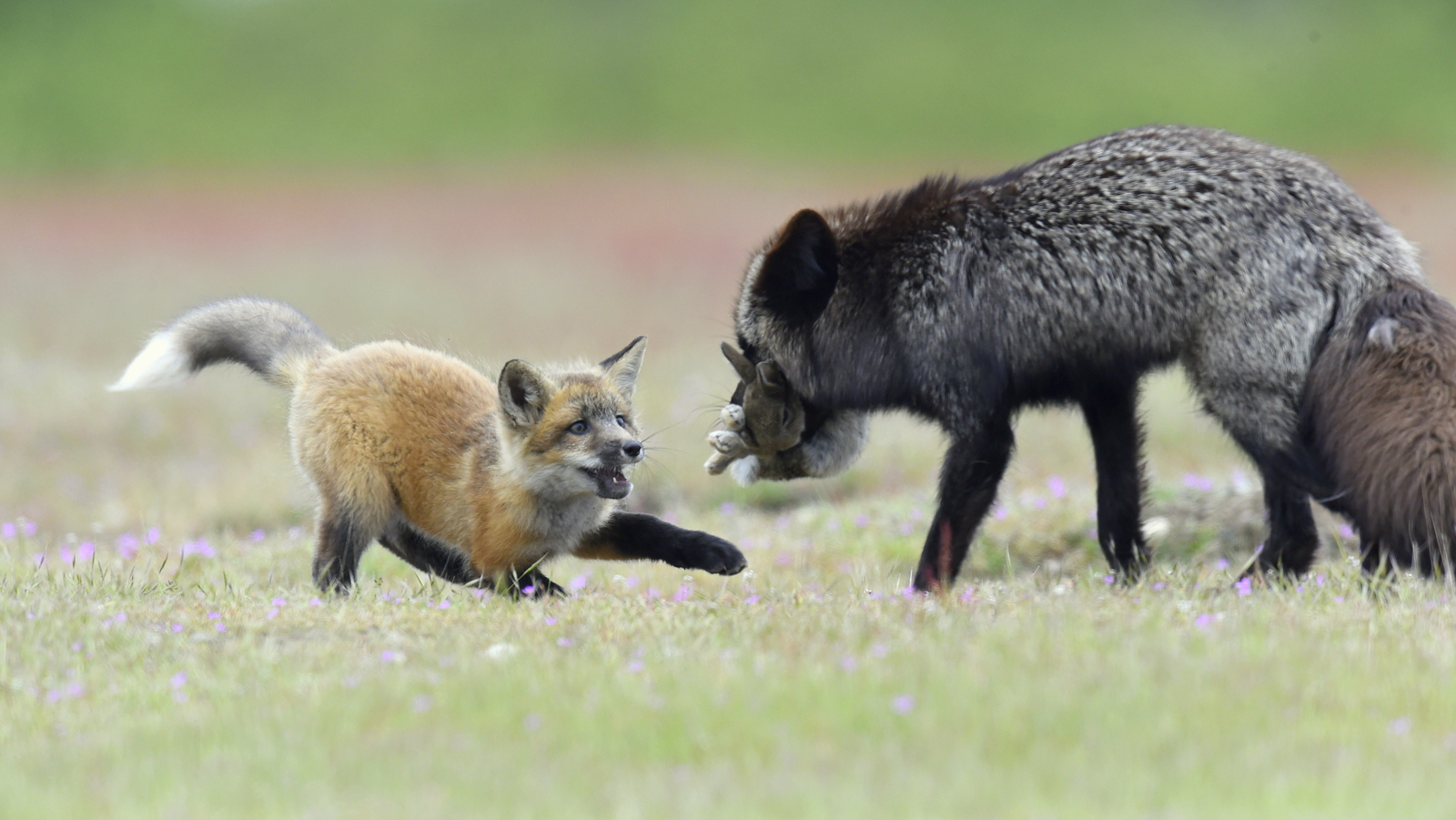
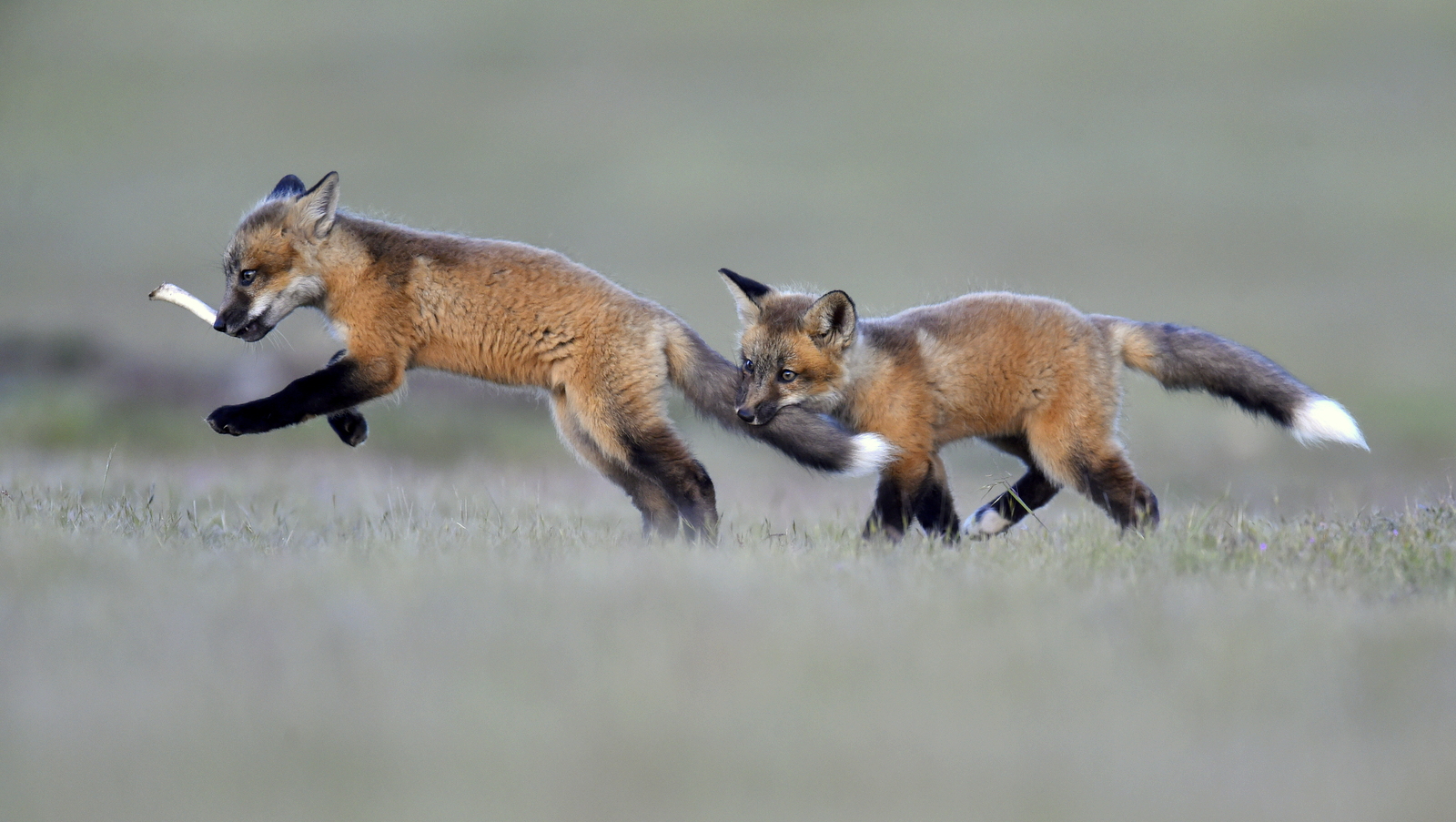
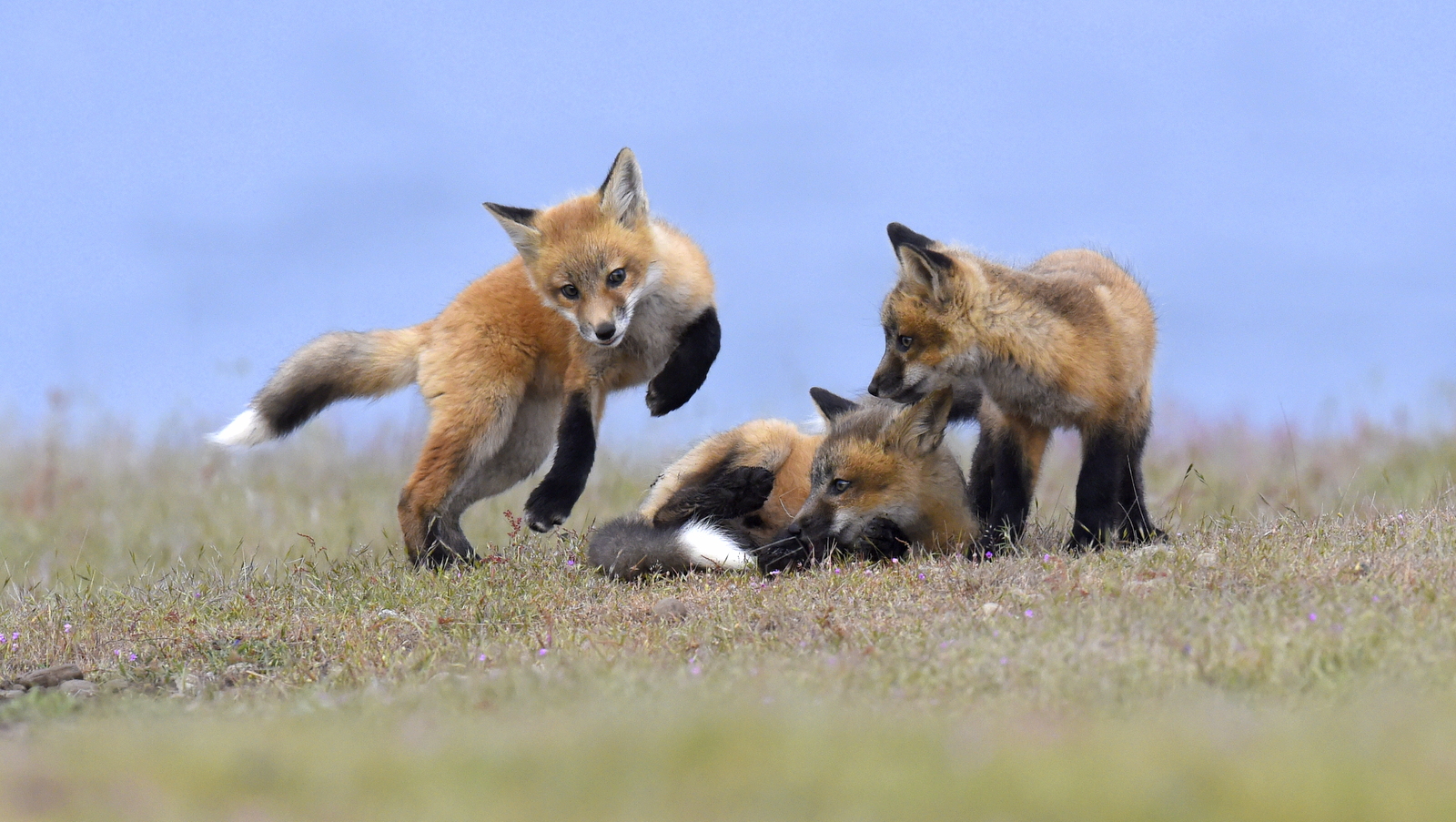
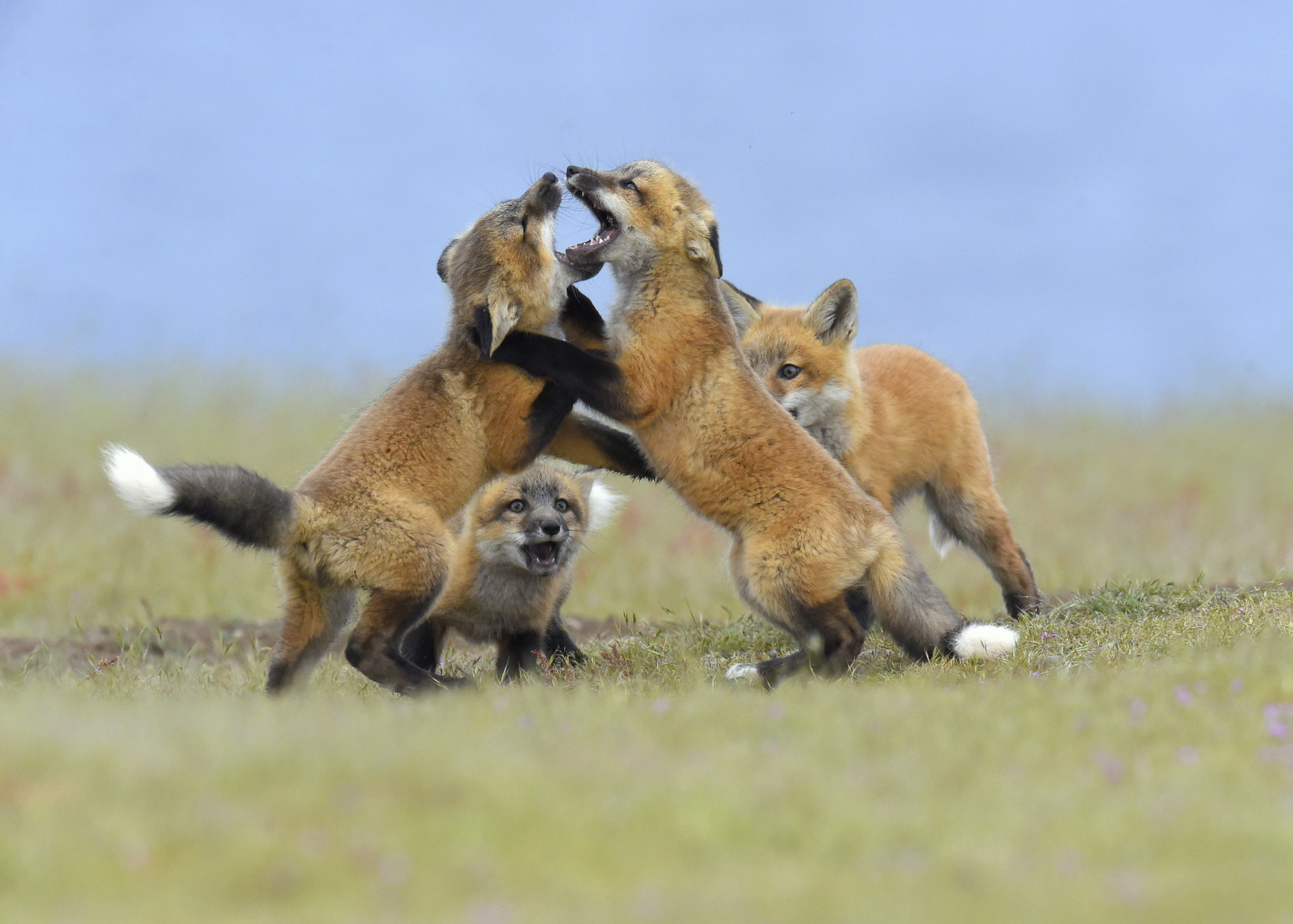
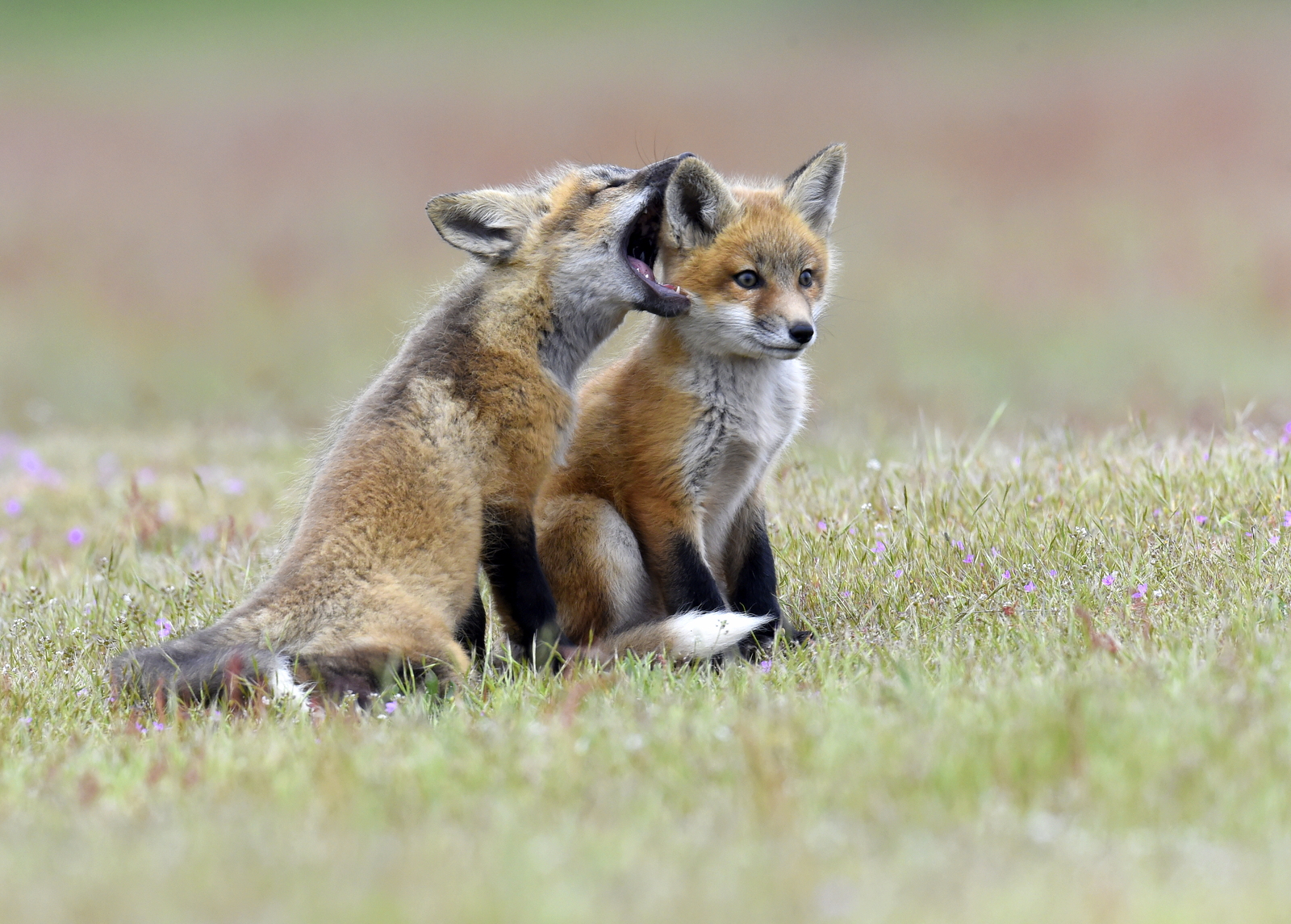
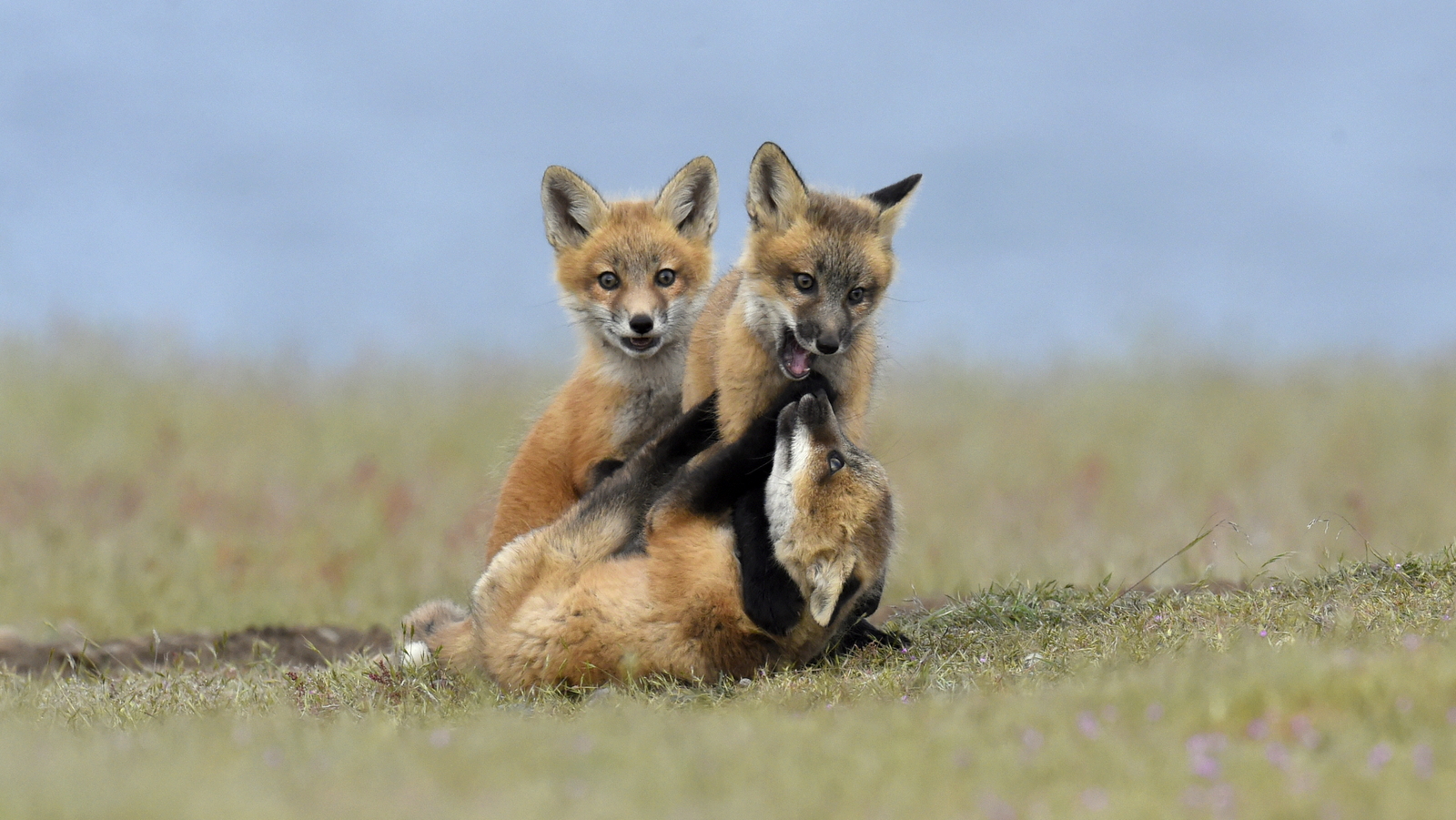
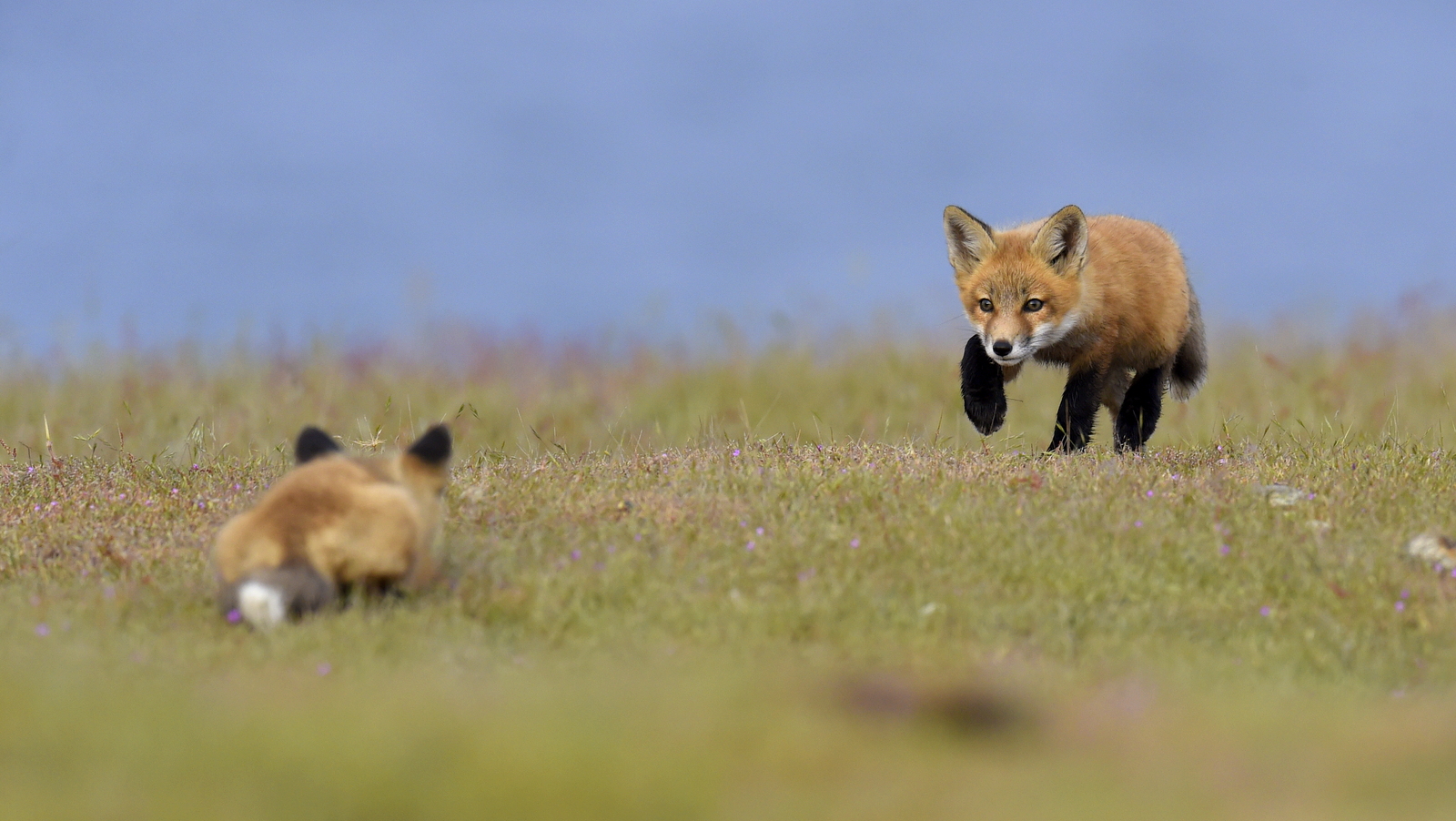
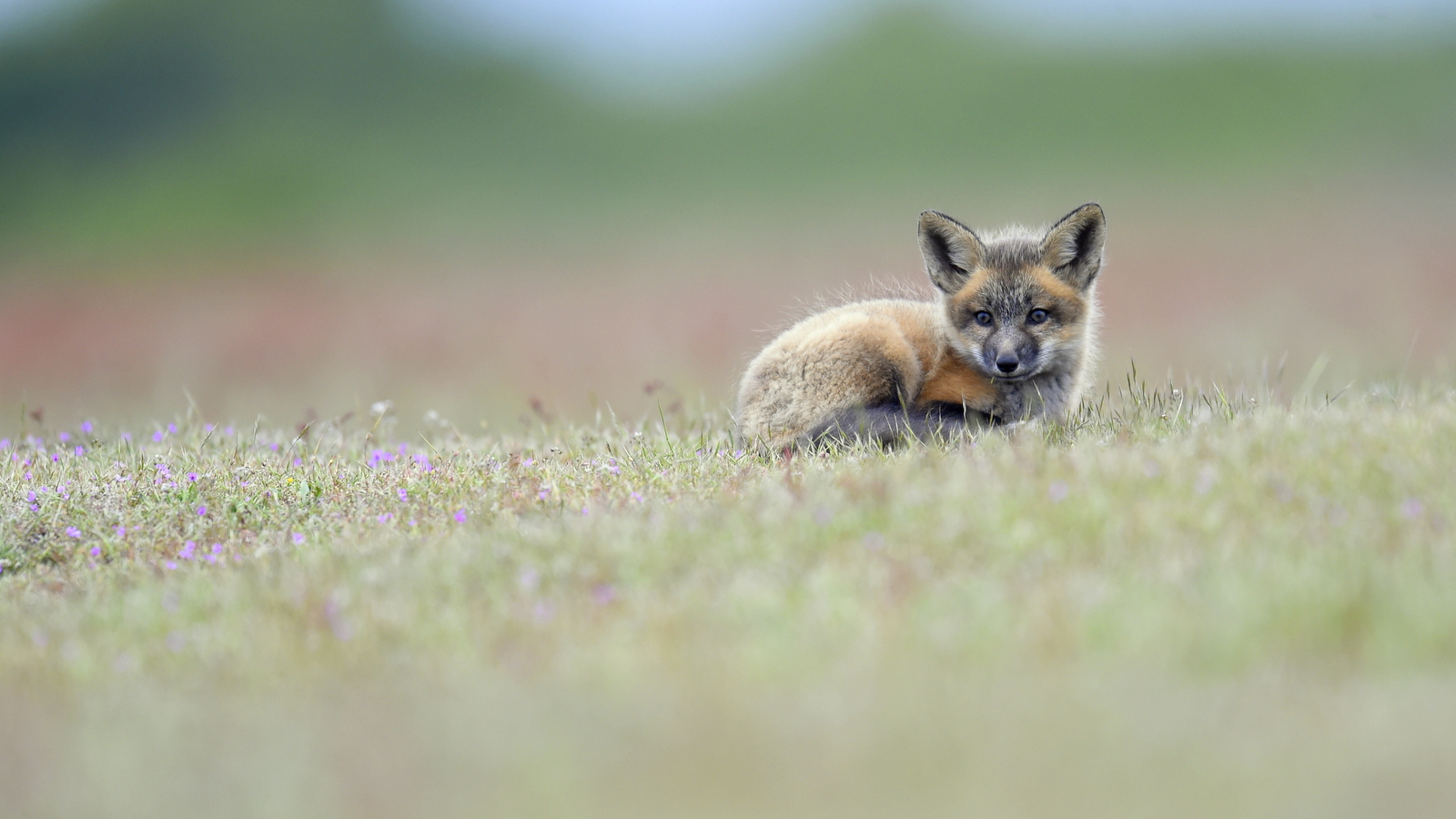
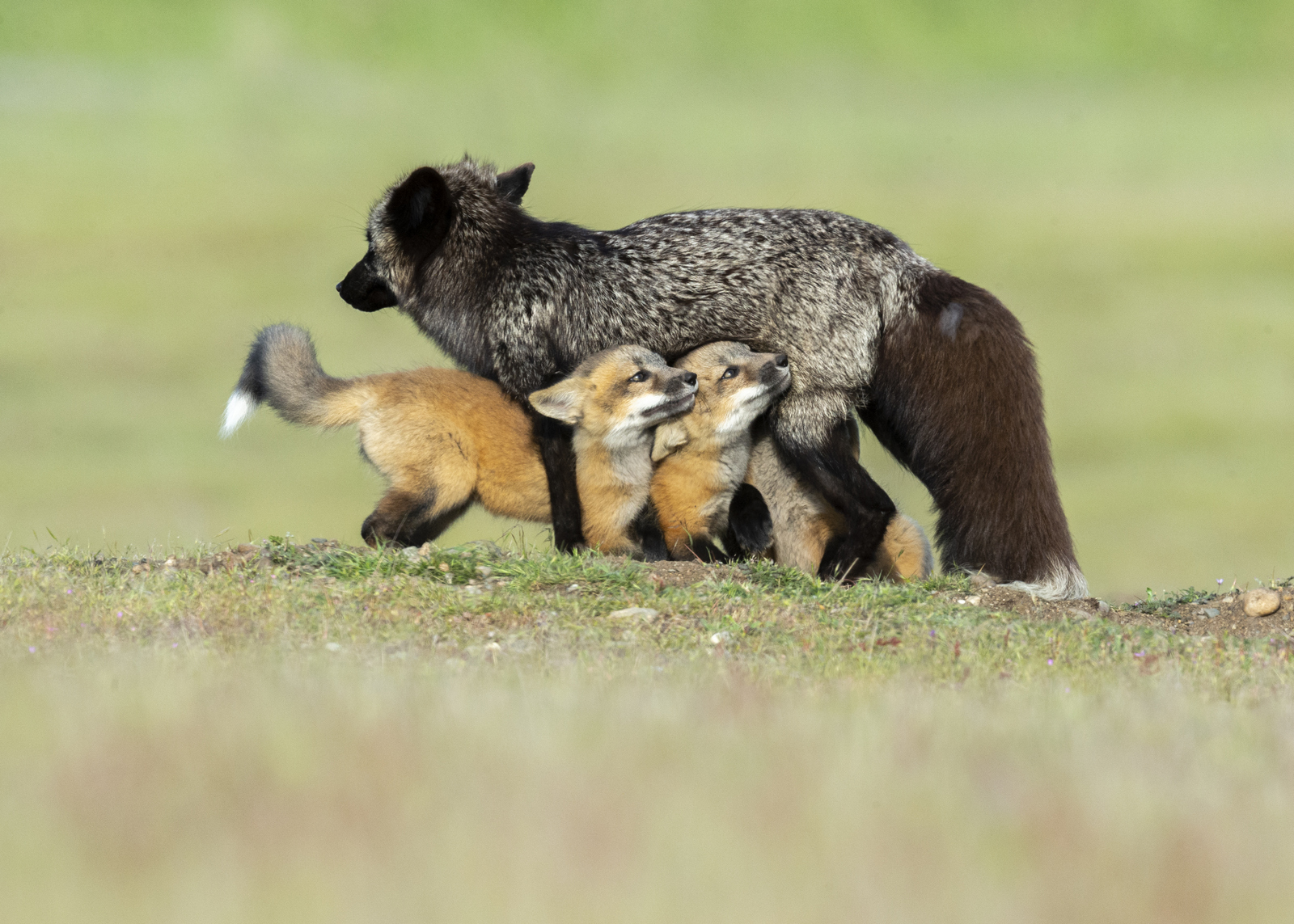
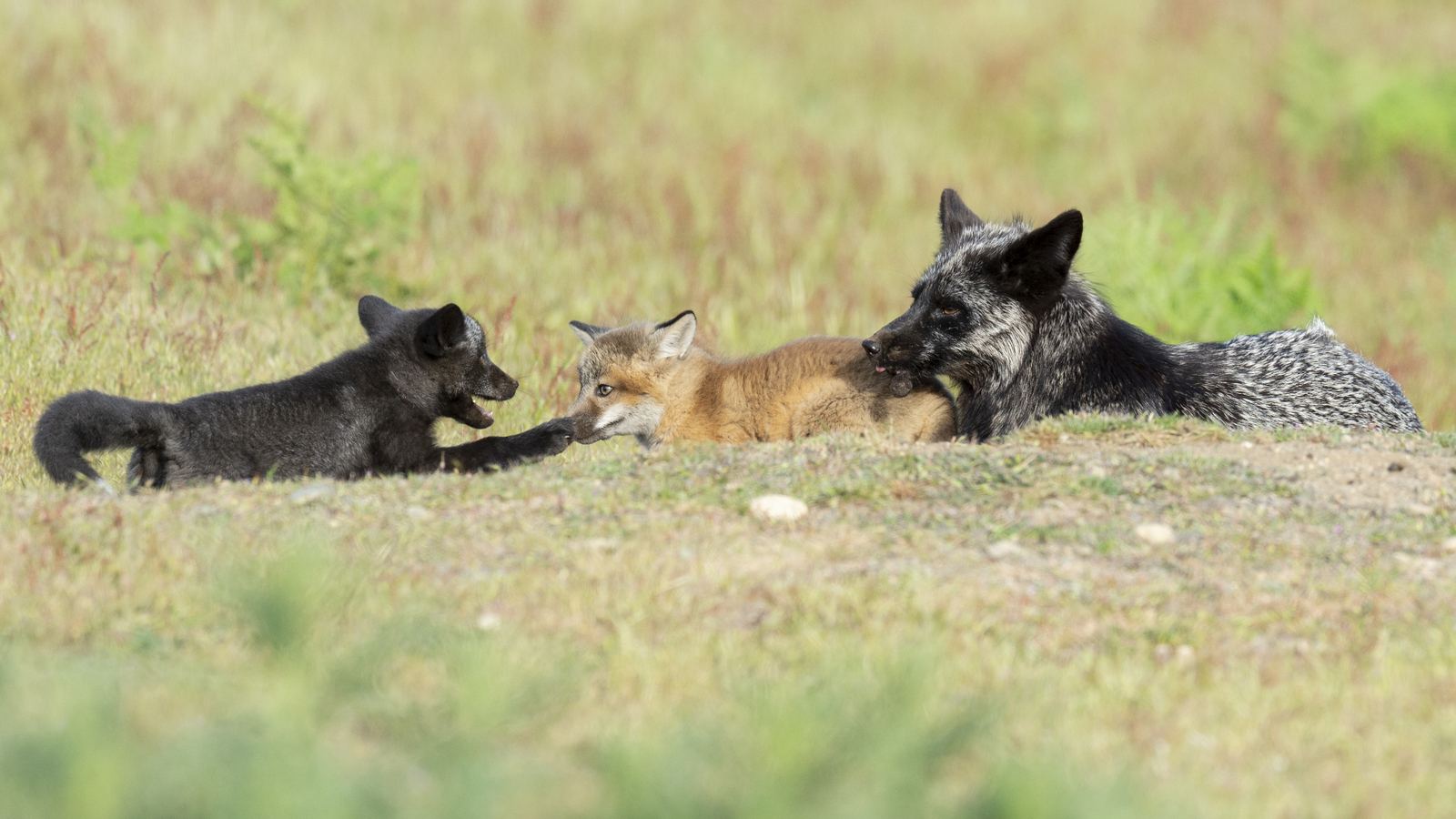
Over the years I have seen a fair number of foxes but the sightings were usually brief and never really produced any good images. In 2019 I hit the jackpot as I was able to spend two full days near a fox den. The den was home to two females who were caring for four kits. A “typical” day would have me show up at sunrise (near 6 am) and sit by the den for about 6 hours. Around noon I would head into town for a quick lunch and then back to the site from around 2 pm till after dark (7 pm-ish). The females would leave the kits at the den as they went off to hunt. The mothers were seemingly tireless in their efforts and would come and go throughout the entire day to ensure enough food for the pups. During these periods the kits did little and often just disappeared into the safety underground. After an hour or so, though sometimes after much longer, a female would return with a rabbit, mouse, or vole. At this point, all hell would break loose. The pups would burst out of the den excited at the opportunity to feed. Mom would give the prey to one of the kits who would then run off with their “kill.” The others might chase it to try and steal the meal. Mom would then allow the kits to nurse for a few minutes. After feeding the young’ins would be in high spirits and run around like sugared-up toddlers and engage in all sorts of hi-jinks, roughhousing, assorted shenanigans, and general mischief. This chaos could last for ten to thirty minutes. Mom might leave fairly quickly to head off on the next hunt leaving the kits to their antics. Eventually, the kits would tire out or get bored and head down into the den.
And just like that, poof, an empty field. And then we waited for the return of one of the females with the next meal. So my day was made up of long waits of nothingness and then frantic shooting once the females appeared. As the day drew on the periods of nothingness seemed to get longer and longer. Pick at the grass. Pace around a bit. Lie on your back and look at the sky. Review some images. Pick at the grass…And then boom! Foxes are running everywhere and me trying to figure out which act of this three-ring circus to focus on.
It was a blast.
Here are the two moms – both are red foxes. Check last month’s post to understand how this is possible.
Moms heading off to hunt
Mom’s Back!
And now that we are fat and happy, let the games begin
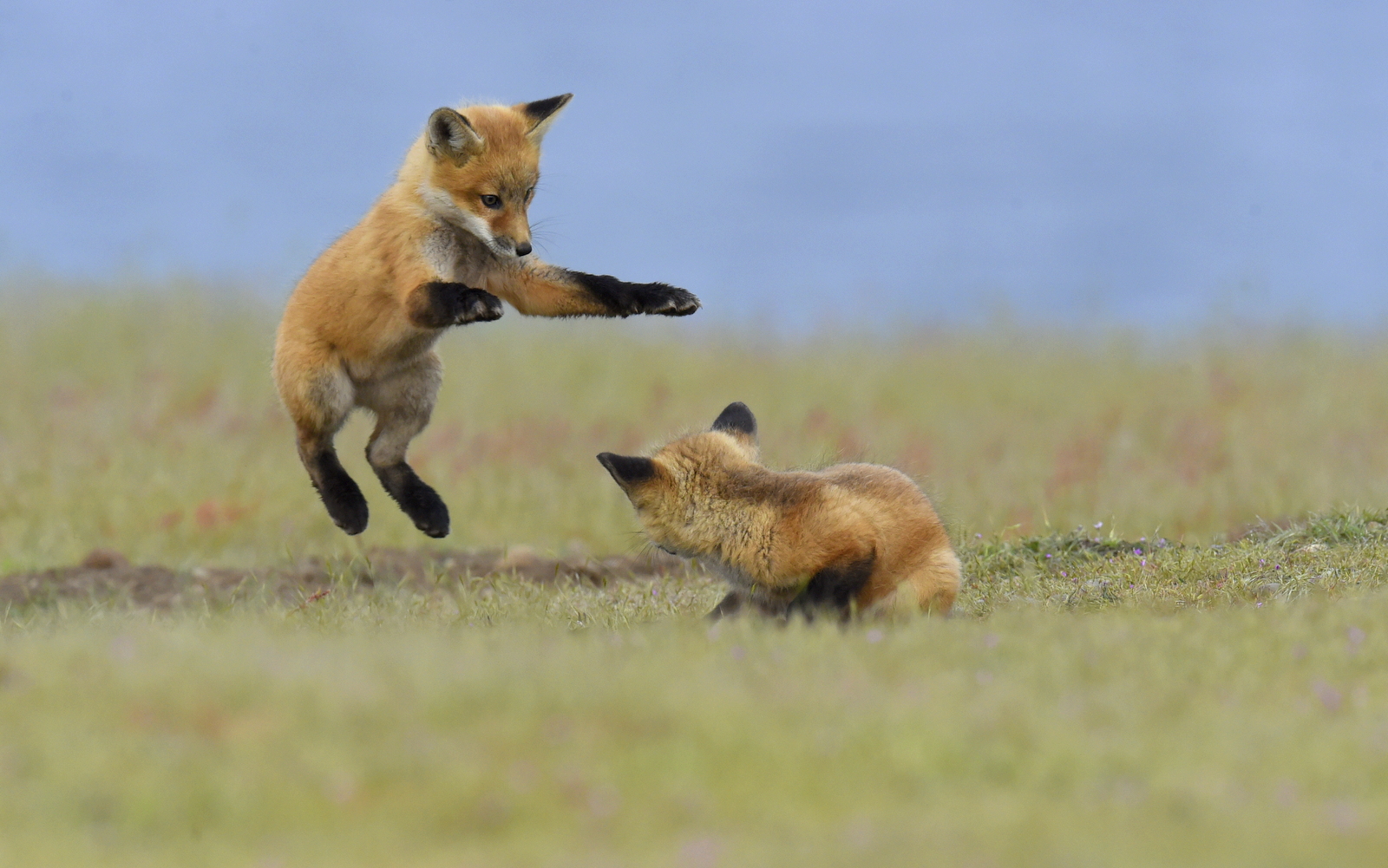

Finally running out of steam
Who knew that kaos could be so kute and kuddly?
And in case you missed it, here is another adorable family moment.
Until next month…..m
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm,, 1.4x TC (effective 850mm), f/7.1, 1/1000 sec, ISO 1600
31
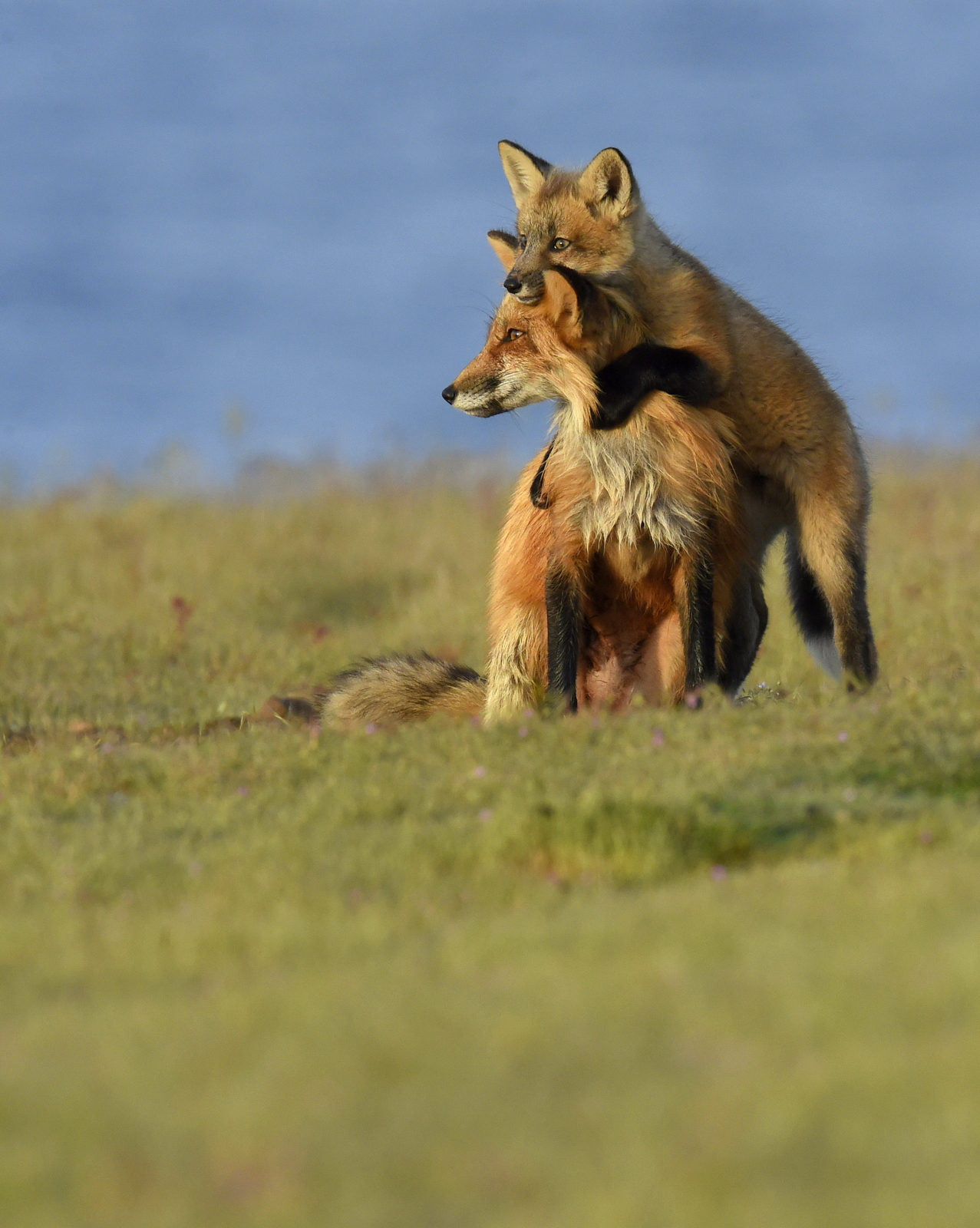
Shot of the Month – March 2020
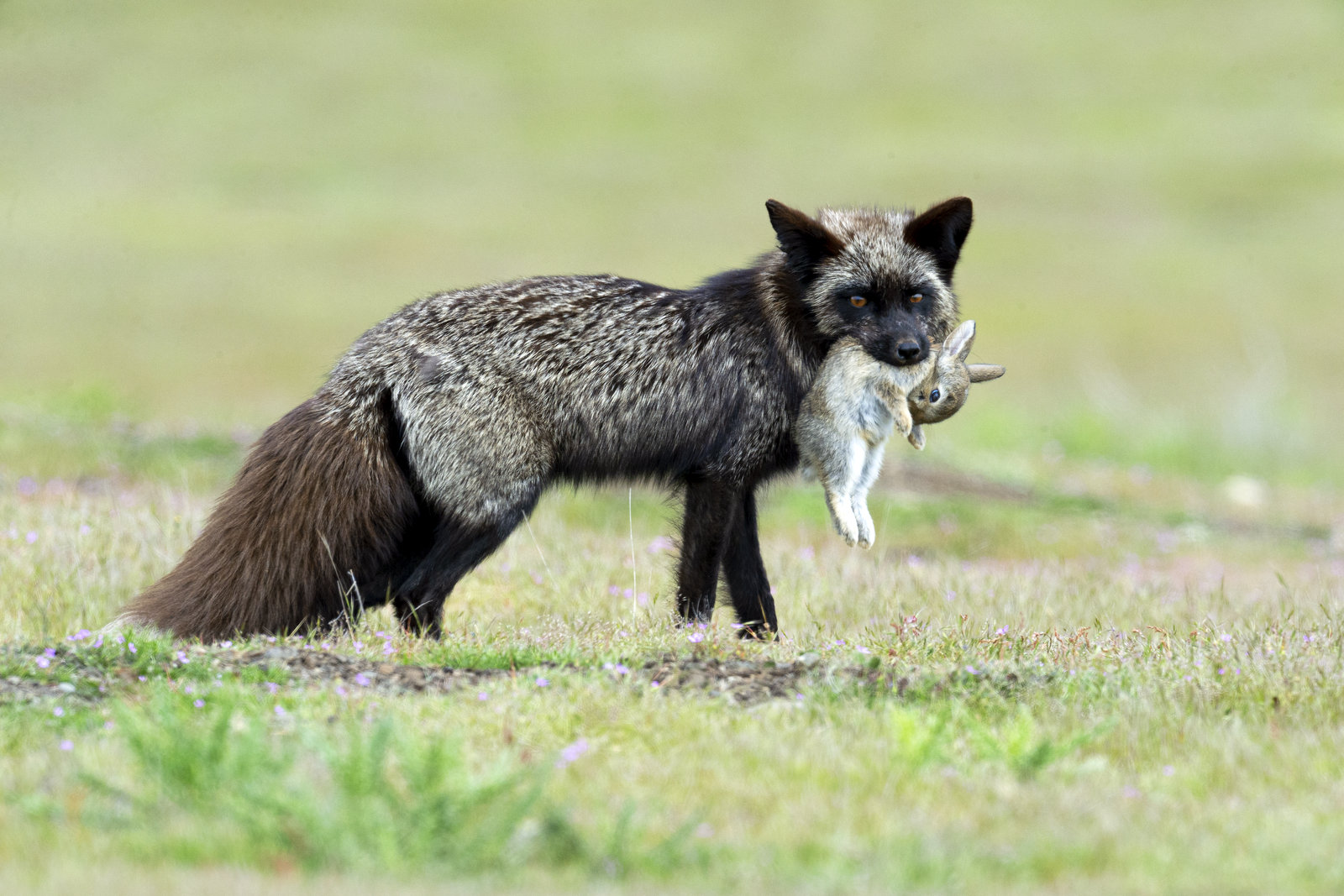
Here we have a lovely female red fox bringing a meal back to her kits. Please do not adjust your set (old person reference). Nor is that a typo. You might want to sit down for this, but, red foxes are not always red. I know, I know, it is a crazy, topsy-turvy world out there…
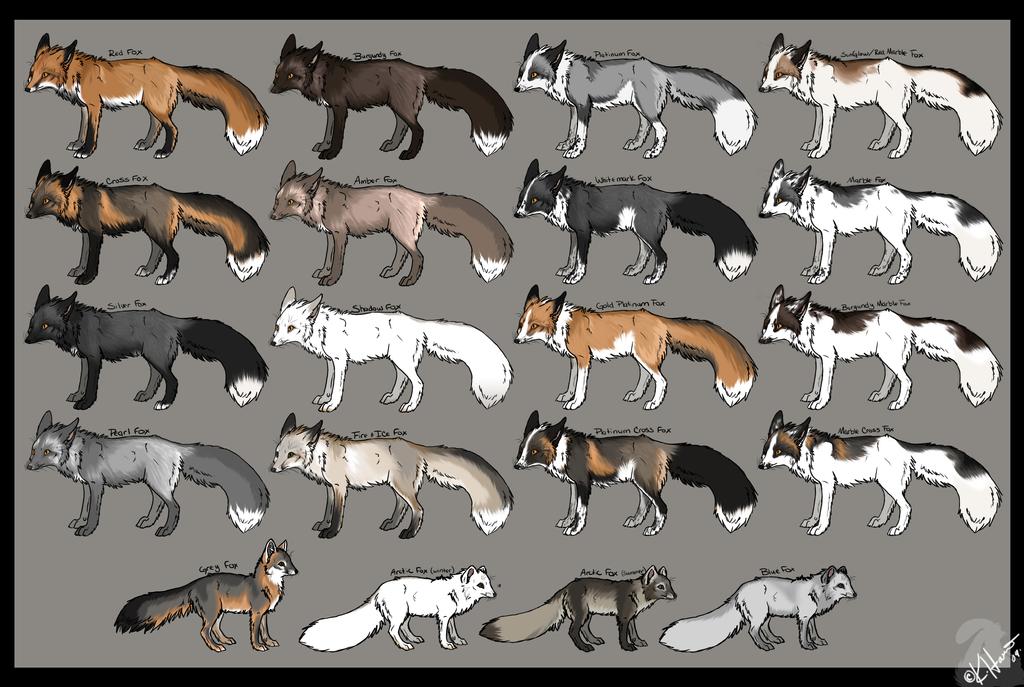
Despite the very firm, very unambiguous sounding name, red foxes come in a surprisingly large variety of colors. Most are categorized under three main color variations or morphs (if you want to sound all zoological and whatnot).
Red Morph
The red morph red fox is primarily red/orange in color and is the most common type of red fox.
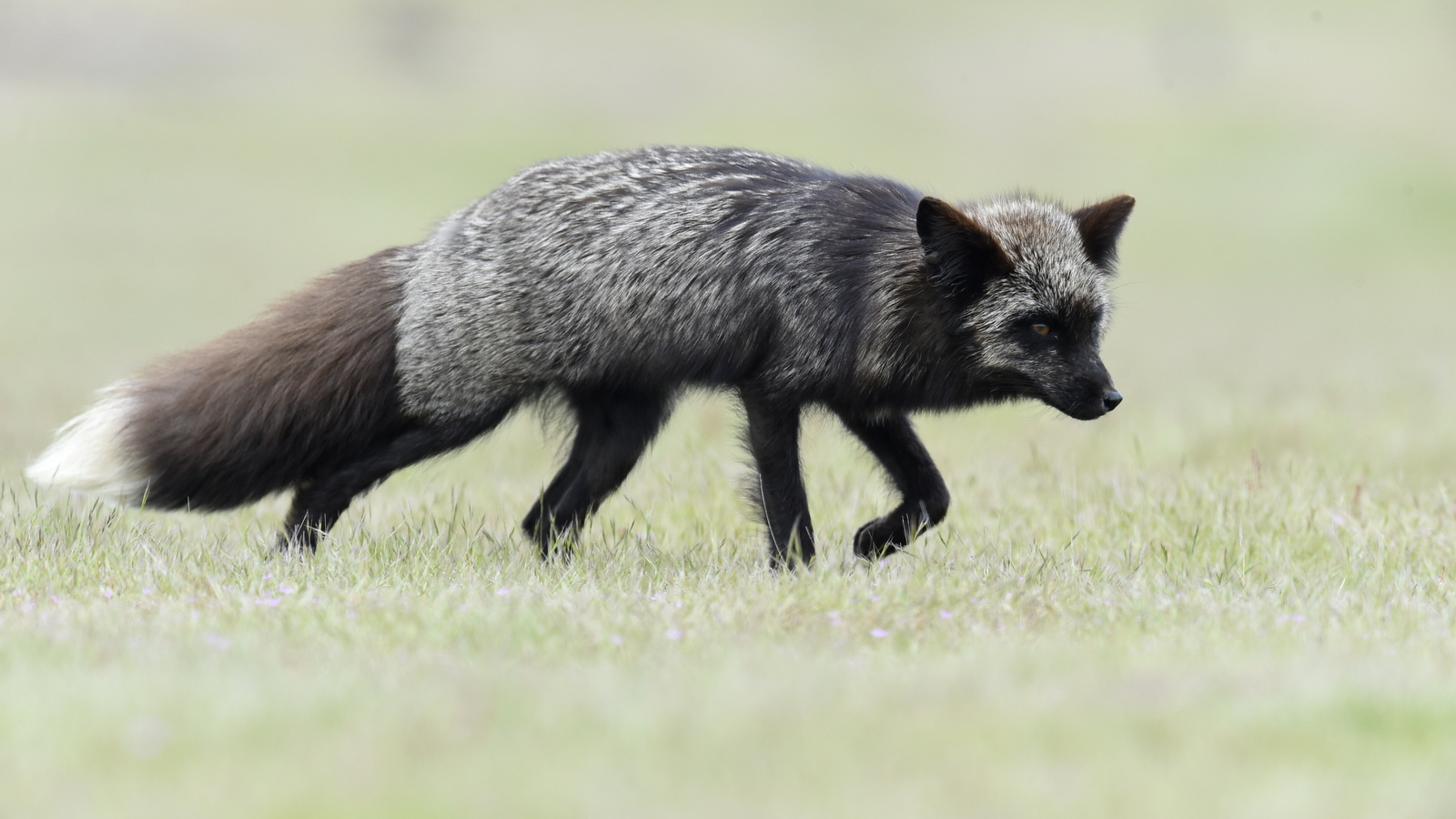
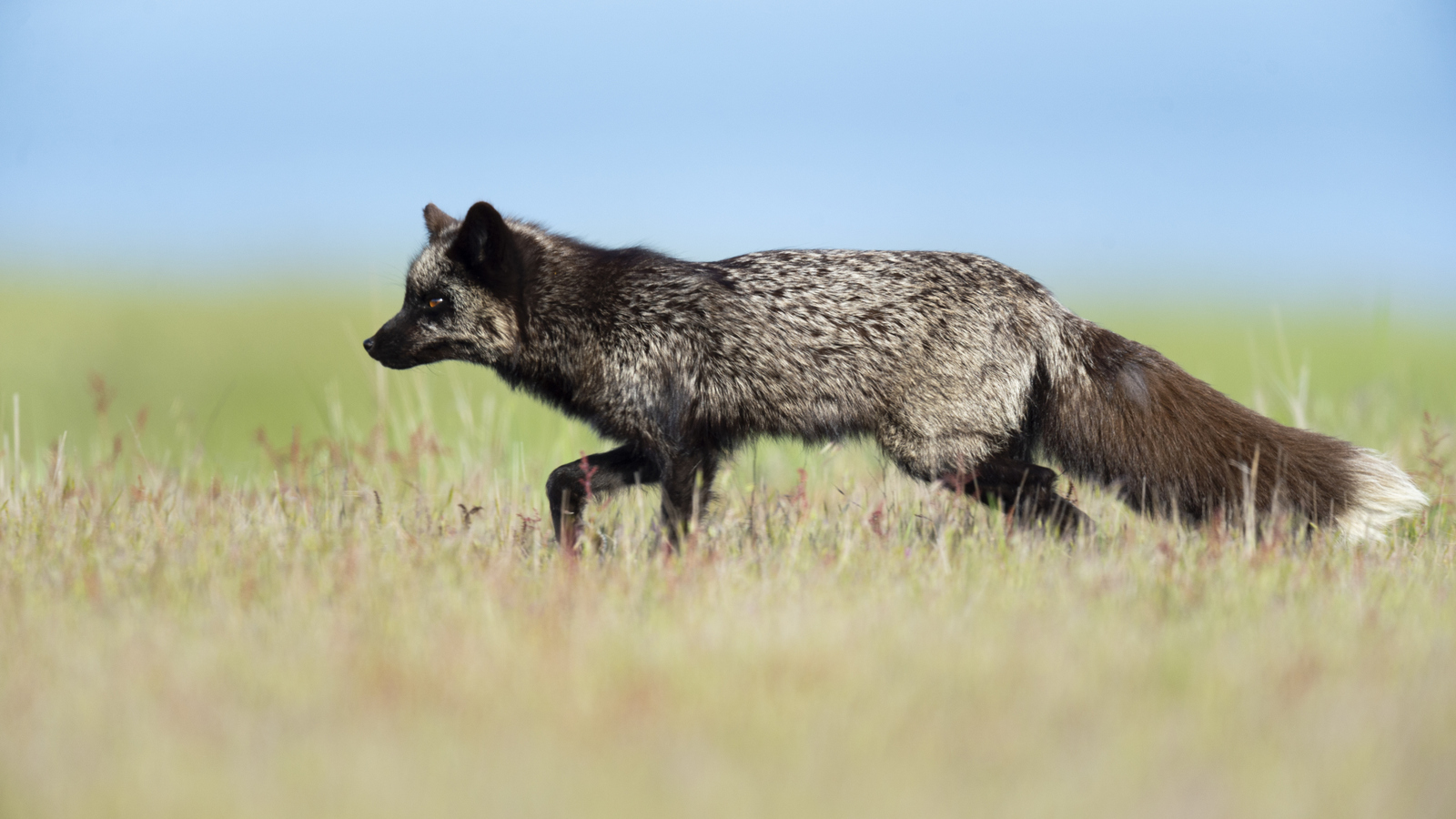
Silver/Black
Silver foxes are a melanistic morph of the Red Fox that have a range of colors from bold silver to almost complete black. The silver version has silver-tipped hairs interspersed among the black fur. Black foxes vary in color and may have some brown fur also.
This whole naming thing is starting to sound pretty bogus, but ok, let’s carry on.
Cross Morph
Cross foxes are red foxes with a prominent black stripe along the spine and a stripe along the shoulders at a right angle which gives the appearance of a cross – hence the name of this morph. This color variation is only found in North America.
Regardless of the color mix all Red Foxes have one thing in common — that white-tipped paint brush of a tail. How’s that for a handy identification tip?
So, a Red Fox can be any color mix of red, orange, white, black, grey, silver, and brown as you can see in this graphic below. (Note: The four morphs shown at the bottom of the graphic are not found in the wild but are the result of selective breeding)
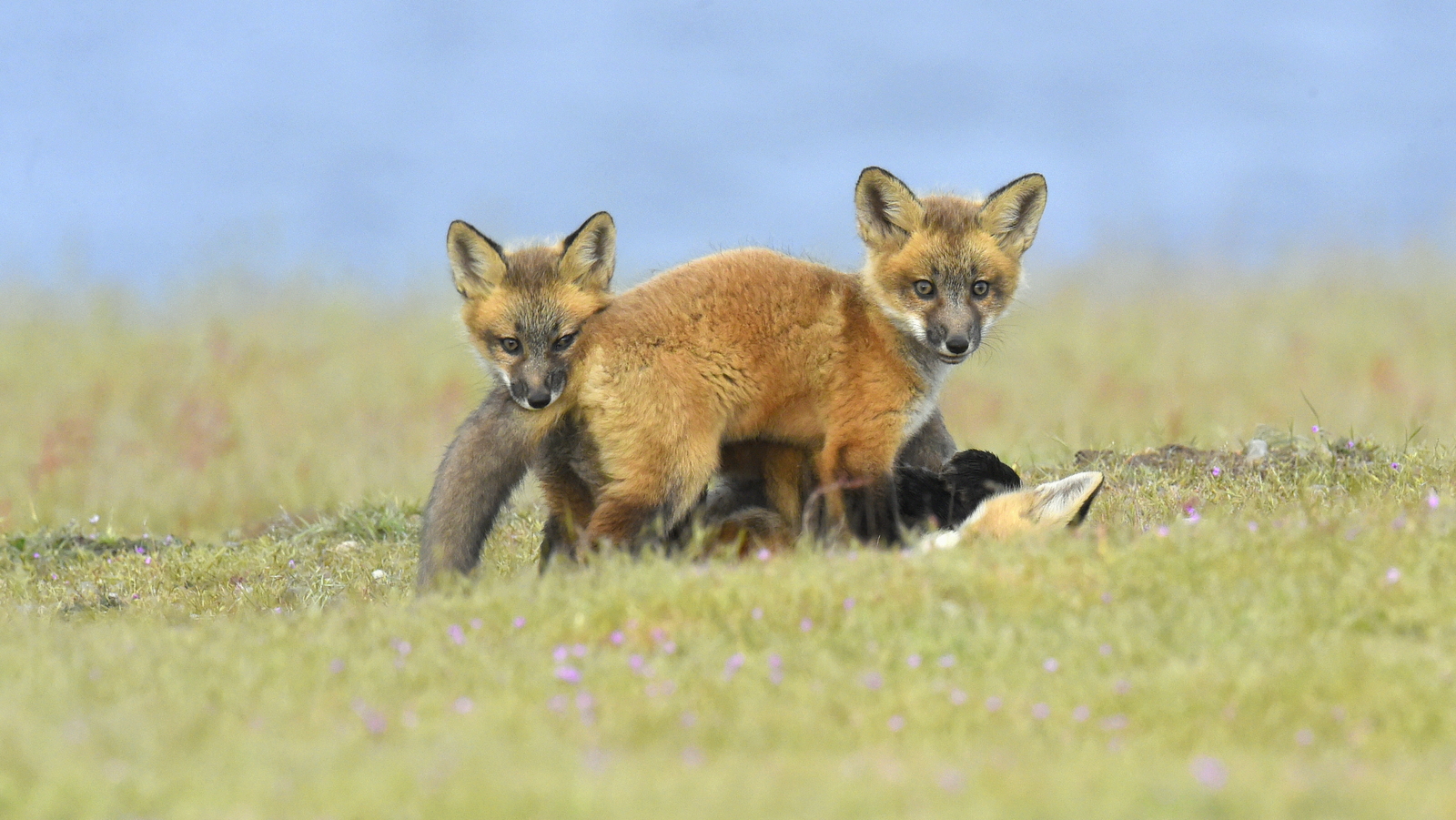
In the image below we see the same female silver fox waiting patiently as her kits jostle for an opportunity to nurse.
Here is the same female as she heads off to hunt for more food for her family:
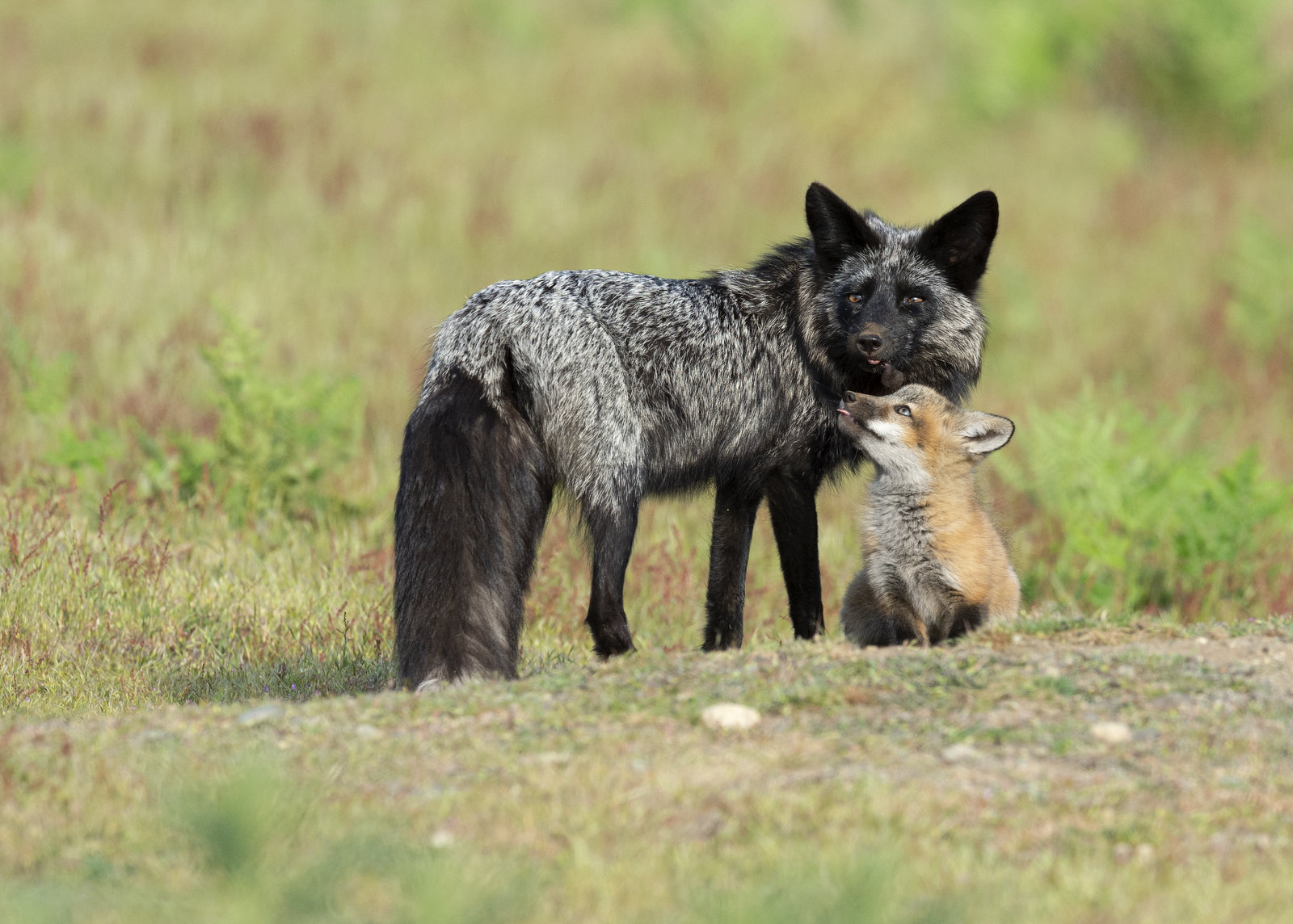
And here is a male silver fox that I found at a different den site with one of his kits:
And here he is with two of his kits:
Wasn’t life easier when you just needed the “Red” crayon to color in the fox drawing? Well, now there is no going back. Next time you will have to break out the BIG box of crayons. You know, that big box of 64 crayons with the sharpener in the back? Yeah, that one. Let the games begin…
no going back. Next time you will have to break out the BIG box of crayons. You know, that big box of 64 crayons with the sharpener in the back? Yeah, that one. Let the games begin…
Until next month…..m
Sources
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, 1.4x TC (850mm effective), 1/1000 sec, f/11
29
Shot of the Month – February 2020
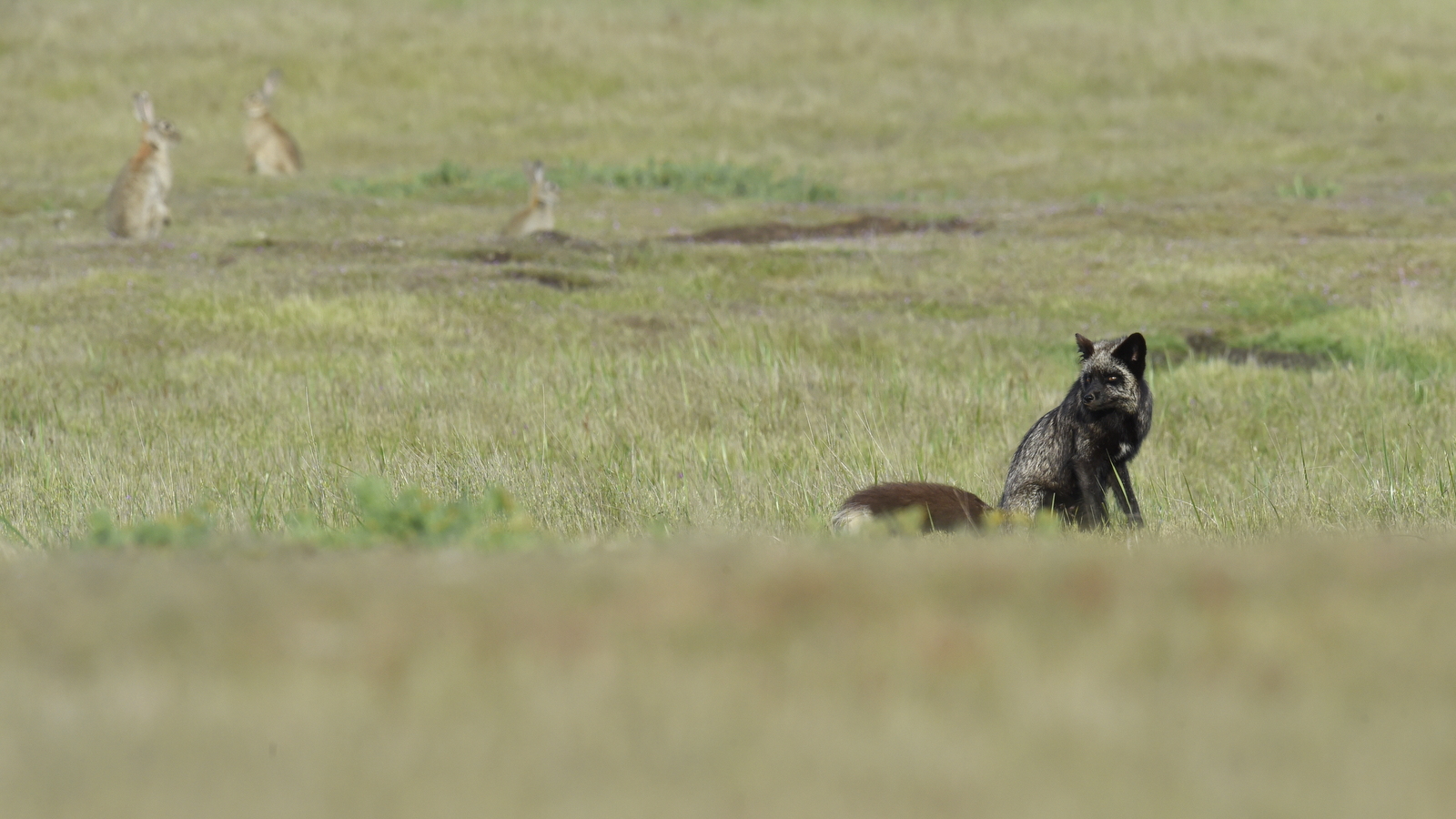
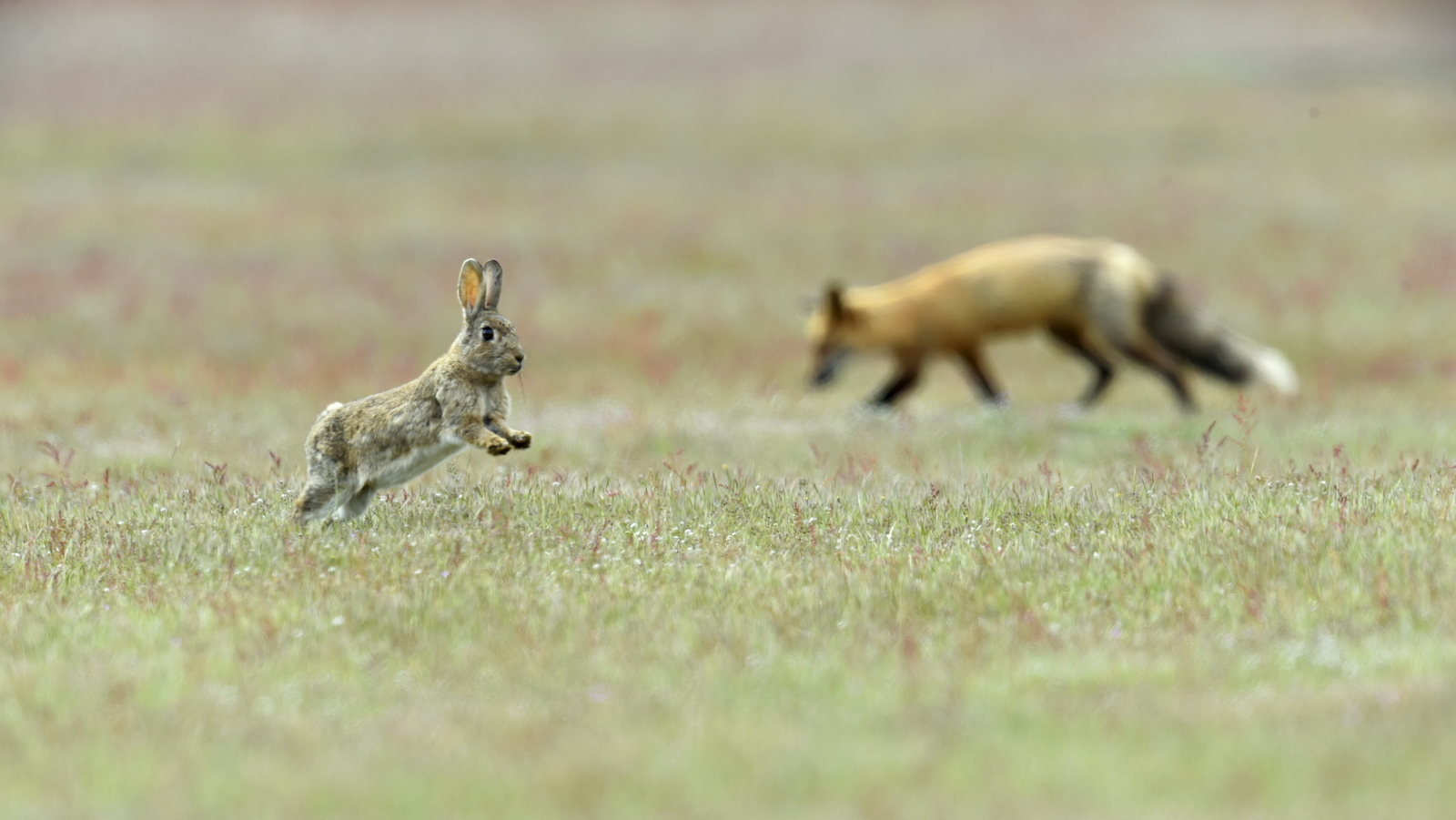
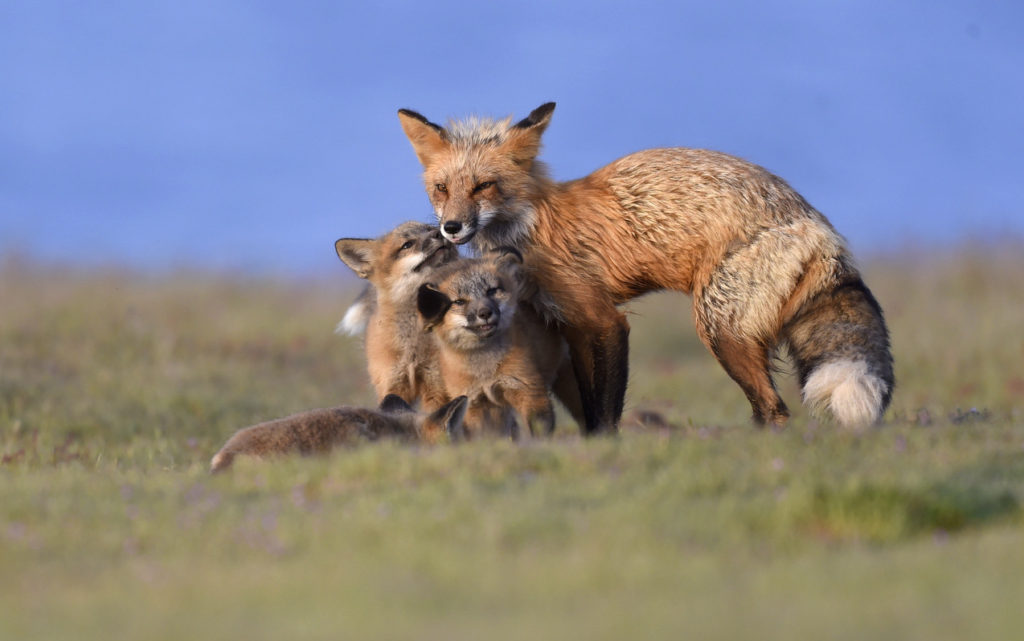
This month an installment from the “Awwwwl Collection.” In this image I captured an adorable Maternal Mammal Moment (MMM) — a mother Red Fox (RF) with one of her kits as they look into the warm light of the morning sun. Mom is actually looking at rabbits off in the distance and the kit is, well, just being a goofball.
If you spend much time in nature you are going to see a red fox or twenty. The wily Red Fox is a survivor and exceptionally 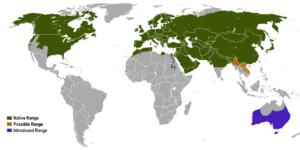 skilled at adapting to almost any environment. How successful? The RF is the most wide-spread carnivore in the world and she can be found across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America (except southwestern US and Mexico) Europe, Asia and parts of Northern Africa. Red Foxes were introduced into Australia which has caused all sorts of problems…sigh. Humans….
skilled at adapting to almost any environment. How successful? The RF is the most wide-spread carnivore in the world and she can be found across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America (except southwestern US and Mexico) Europe, Asia and parts of Northern Africa. Red Foxes were introduced into Australia which has caused all sorts of problems…sigh. Humans….
Foxes are the smaller members of the dog family (Canidae) but you can clearly see their kinship with jackals, wolves and other other dogs. There are about 30 species of foxes though only 12 of these, in the “vulpus” genus, are considered “true foxes.” Of this group of diminutive dogs the RF is the largest and most common of the group.
Is that like being a jumbo shrimp?
The Red Fox is about the size of a medium size dog and typically weighs around 25 pounds. For comparison the dessert dwelling fennec fox is about the size of a chihuahua and the arctic fox only weighs about seven pounds and most of that is fur!
Although RFs are listed as a carnivore they are really omnivores and can eat just about anything. Red Foxes feed primarily on small rodents (mice, rats, voles, squirrels, woodchucks, pocket gophers, deer mice) though they will also hunt rabbits, game birds, reptiles and other small animals. They will also eat fruit, bugs, worms, vegetables and if they live near the ocean they dine on fish and crabs. As you can see their diet can vary widely depending on what is available. In some areas, in the autumn RFs will dine exclusively on fruit including blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, cherries, persimmons, mulberries, apples, plums, grapes and acorns. They will also munch on grasses, sedges, and tubers. Whew, who’s hungry??
The family/social life of the Red Fox is also quite varied and hard to fit into any one category. Foxes are definitely less “pack” oriented than wolves and other dogs. RF’s may live in small groups of related individuals or may live on their own depending on their environment and temperament. I feel ya. Foxes are solitary hunters and only dominant females will give birth to kits. Foxes form monogamous life pairs with their mates. Alas these life pairings are rather short – the life expectancy for foxes, for some unknown reason, is only about 4 years in the wild!
For those playing at home:
Male Fox = Reynard
Female Fox = Vixen
Young Fox = Kit
A group of Foxes = Skulk, Earth, Leash
Us humans have a complicated relationship with foxes. On the one hand our mythologies and folklore are full of tales of the wiley fox and their supernatural powers. I wrote about some of these tales here. On the other hand foxes are considered pests and killed at every other opportunity in many countries. Germany kills about half a million foxes each year, while England kills about 25,000 annually to highlight a few kill zones. And let’s not forget the whole fox hunting controversy in England. The fur of Red Foxes is one of the mostly highly sought after and results in fox farms with millions of foxes suffering in cages under terrible conditions. Wild foxes are likewise trapped for the fur trade and suffer painful deaths for fashion.
Despite this onslaught Red Foxes continue to thrive and even expand their range. The crafty creature has learned how to live in cities and now populates many an urban landscape – it is estimated that 10,000 Red Foxes now live in London alone.
Stick it to the Man. Well done, mate.
Until next month….m
A few other images from the “Awwwwl collection”:
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, 1.4x TC (effective 850mm), f/11, 1/1000 sec, ISO 2500
Sources:
31
Shot of the Month – January 2020
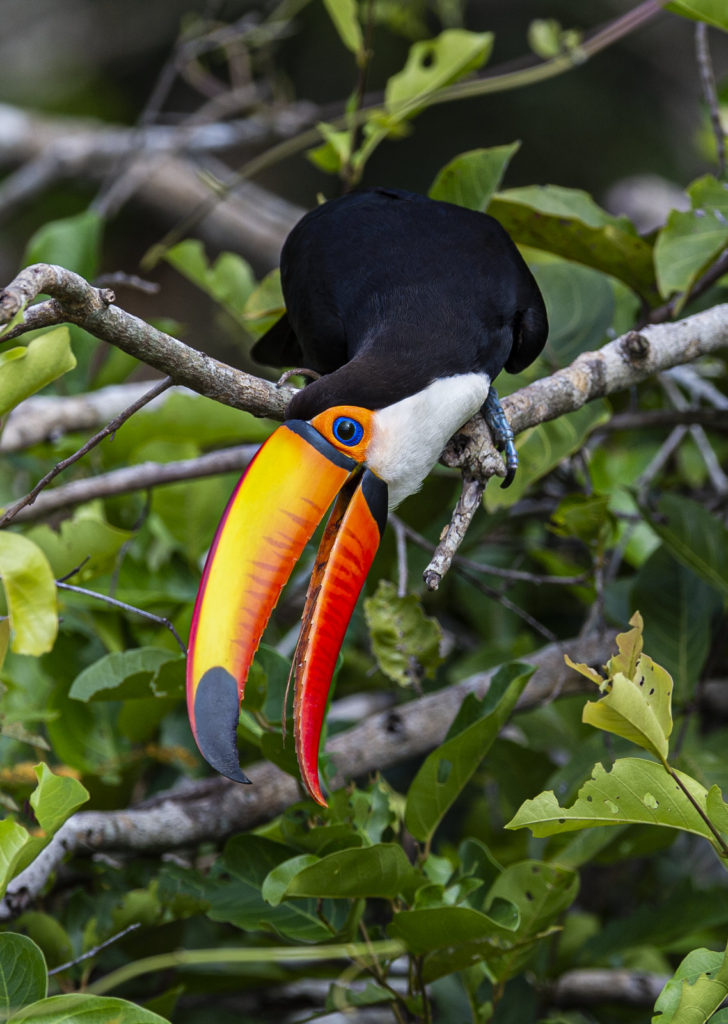
I find it impossible to look at this image and not smile and shake my head in amazement. How does mother nature come up these incredible combinations of sizes, shapes and colors? This particular combination gives us the glorious Toco Toucan (TT). I photographed this fine chap in the Pantanal in Brazil. It is pretty obvious to see why Mr. TT is one of the world’s most popular birds.
I was first introduced to TTs as a child as the mascot for my favorite cereal, Froot Loops (hey, this is a judgement-free zone!), was based on this bird. Toucan Sam became the cereal’s mascot in 1963, hence he is just slightly older than me, and for some reason he had an English accent.
Toucans have been used to sell stuff for quite awhile – they were recommending Guinness Beer back in 1935. In Brazil they get political as they hawk the Social Democratic Party (see what I did there?). In popular culture, Senor Tucan provided Dora the Explorer occasional advice. In the world of Pokemon you can find Toucannon who is likewise crafted after Mr. TT.
On a more etheral plane TT’s can be found on many South American tribal totem poles as an incarnation to fly to the spiritual world. The ancient Aztecs believed that the Toucan’s beak was created from rainbows as a reward for being the messenger of the gods. Nice.
Yes, let’s talk a bit about that glorious beak. But, before we dive in, a quick reminder:
Bill = Beak. Although many people refer to beaks as pointed bills, like what raptors have, in modern ornithology (the science of studying birds) there is no recognized difference in the terms. Beak, bill, all the same. Just saying…
Size
Typically 1/3rd of the total length of a Toco Toucan is all beak. The beak is 8 inches long while the total length of the bird is about 25 inches. Although the beak looks heavy it is actually very light as it is mostly hollow and is made up of a honeycomb of keratin (the same protein that makes up fingernails and horn). The TT is the largest of the 40 species of toucans in the world, but even with that large beak it only weighs less than 2 pounds!! Birds are light!!
Function
So why the massive beak? Scientists are not sure but there are many theories. Many people assume it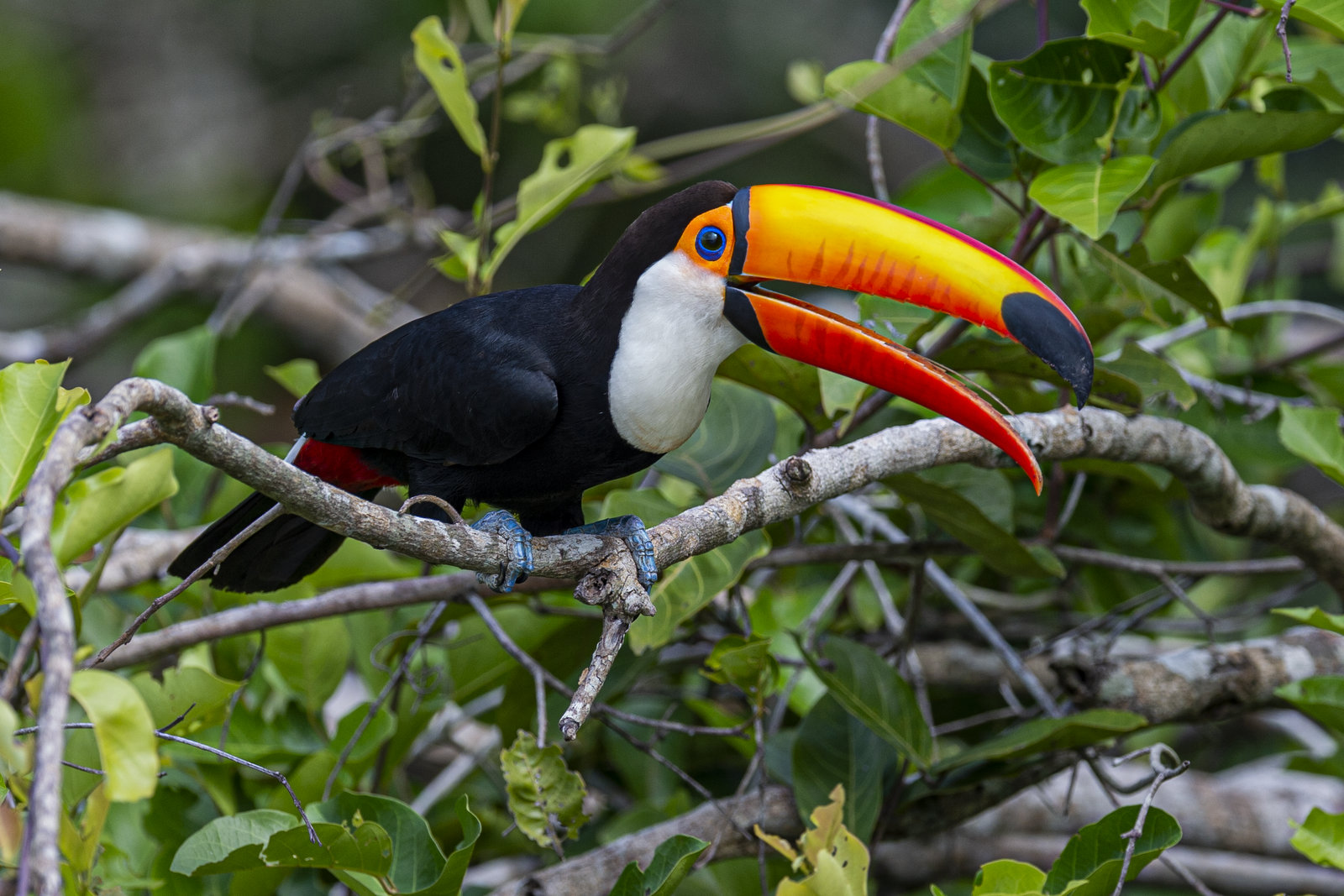  plays a role in attracting a mate, though no evidence has been found yet to support that idea. It does seem however that the bill is an effective tool for regulating the bird’s body heat. Toco Toucans are found in the tropical forests, savannas, and shrublands of South America. Living in such hot, humid climates where evaporation is slow, it can be difficult for an animal to cool off. The TT’s bill represents 30-50% of the bird’s body surface area making it the largest bill relative to body size of all birds. If the TT gets too hot he can direct more blood to pass through the beak and depending on conditions it can dissipate 25% to 4x the heat produced by the bird’s body! That is incredibly efficient and effective. For comparison, elephants use the massive surface area of their big ears to regulate body heat in the same way but they can only shed about 10% of the heat that their body produces.
plays a role in attracting a mate, though no evidence has been found yet to support that idea. It does seem however that the bill is an effective tool for regulating the bird’s body heat. Toco Toucans are found in the tropical forests, savannas, and shrublands of South America. Living in such hot, humid climates where evaporation is slow, it can be difficult for an animal to cool off. The TT’s bill represents 30-50% of the bird’s body surface area making it the largest bill relative to body size of all birds. If the TT gets too hot he can direct more blood to pass through the beak and depending on conditions it can dissipate 25% to 4x the heat produced by the bird’s body! That is incredibly efficient and effective. For comparison, elephants use the massive surface area of their big ears to regulate body heat in the same way but they can only shed about 10% of the heat that their body produces.
The big bill is also useful for feeding. The TT eats primarily fruit and that long bill allows the bird to reach distant fruit that may otherwise be too far away. Fruit on a branch that is too small to support the bird’s weight? No problem, just leeeean over and snatch it with that uber long bill. The long bill also allows the bird to sit in one place and still reach a lot of fruit – not having to move around as much saves energy. Speaking of fruit, did you notice that the beak is serrated? You can really see the notched edges of the bill in the upper image. The serrations allow the bird to peel fruit. Although these birds primarily eat figs, oranges, guavas and other fruit the long beak is also useful for catching insects and for reaching into tree cavities to catch young birds and eggs — a vital source of protein.
Ahhh, the Toco Toucan — a bird of the tropics with that Technicolor, swiss-army knife of a beak made from rainbows that acts as tool, knife, radiator and portal to other realms.
Cool bird.
Until next month…..m
Nikon D4s, Nikon 600 mm, f/4, 1/1000 sec, ISO 200
Source
31
Shot of the Month – December 2019
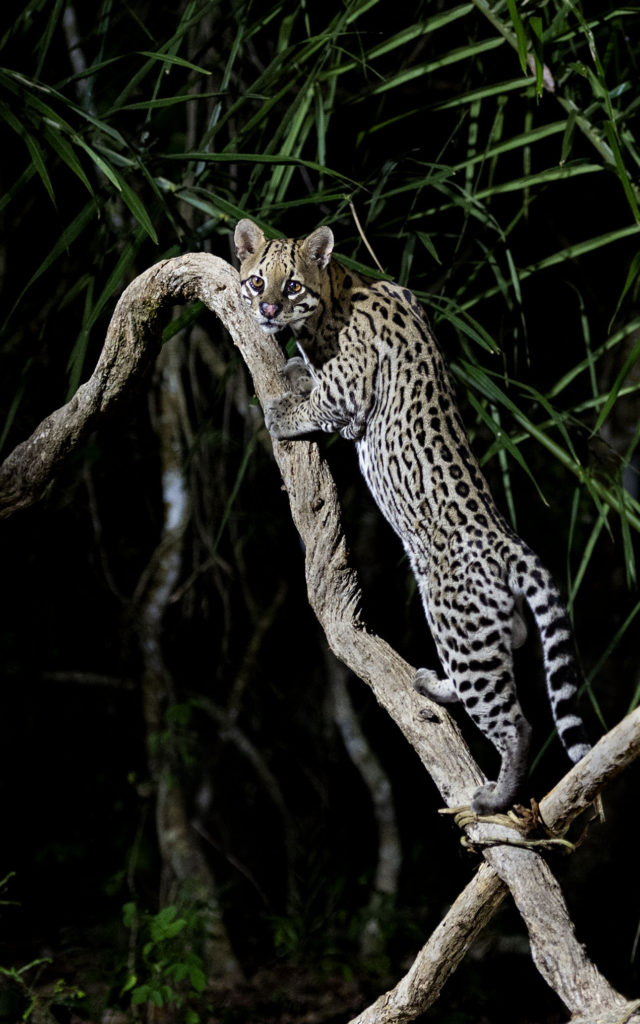
In 2019 I visited the Pantanal in Brazil to photograph jaguars and other wildlife – you can see the highlights in this video. En route to the prime jaguar location we spent one night at small lodge where we saw another wild cat of the region – the Ocelot. Each night the lodge puts out chicken to attract this rarely seen cat. I am not a fan of baiting wildlife as it can diminish their survival skills and promote dangerous human – wildlife interaction. For what it is worth this cat does not show up every night and it seems that he is not dependent on this food supply but only drops in when he wants a supplement. Or perhaps only when he is in the mood for a bit of chicken….
As you can see Ocelots are fairly small, coming in at about twice the size of an average house cat or roughly the same size as a bobcat. The males can grow to about four feet in length while the females are usually about two and half feet long. Ocelots tend to weigh between 28-35 pounds.
These solitary cats are highly nocturnal and use their exceptional eyesight to hunt rabbits, rodents, snakes, fish, frogs, young deer, peccaries, iguanas and other lizards. They are good swimmers and good climbers so they will hunt for fish in nearby streams while also stalking monkeys and birds in the trees. Ocelots hunt by walking slowly along game trails hoping to ambush their prey. They are also “sit and wait” predators, sitting motionless for 30-60 minutes at a den or burrow site. If no luck they move quickly to another site and sit and wait again.
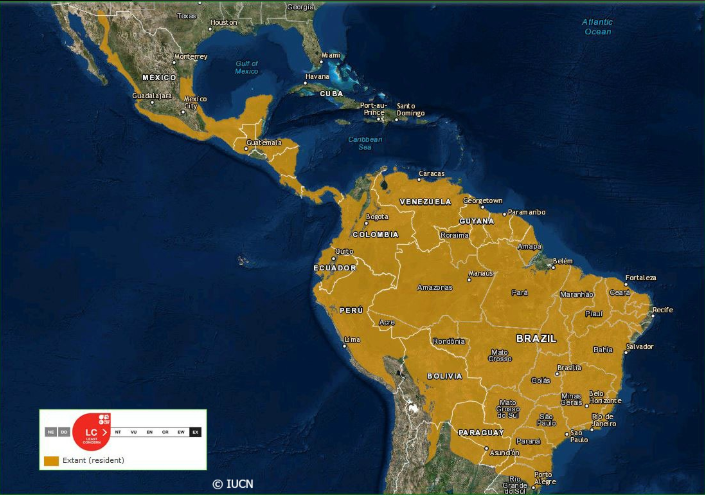
Ocelot Range Map (Source)
Ocelots can be found from southwestern United States to northern Argentina. These cats thrive where plant life is dense and can be found in tropical forests, thorn forests, mangrove swamps and savannas. There are about 800,000 to 1.5 million Ocelots remaining in the Western Hemisphere but their numbers are declining. In the US Ocelots were once found in southern Arizona and throughout much of Texas, and even reaching Arkansas and Louisiana. Alas, human development in these areas has caused Ocelot numbers to plummet and they are now at risk for extinction in the US. Today they can only be found in southern Texas with only about 40 individuals remaining. In Colombia, Argentina and parts of Brazil the cat is listed as vulnerable.
The fur trade in the 1960s and 1970s was devastating to the Ocelot population – in 1970 alone over 140,000 Ocelot skins were traded in the United States. Fortunately most countries now ban the trade of Ocelot skins. While the threats from the fur trade, hunting, and the pet trade have reduced other threats are growing. The loss of habitat and fragmentation of habitat is a major threat as us humans continue to expand our footprint across the planet. Traffic accidents are a growing threat as Ocelots are increasingly hit by cars as new roads crisscross their shrinking habitat. Logging and poaching of their prey species are additional threats to their survival.
Although these lovely cats are rarely seen our world would be much poorer without their nightly jaunts through the jungles of our dreams and fables. Let’s hope that we can find a way to allow the Ocelot to roam our jungles for many years to come.
Until next month….m
And for your easy viewing pleasure, our Pantanal Highlight Video (includes images of the Ocelot):
Sources:
Nikon D4S, Nikon 70-200mm (@ 95mm), f/2.8, 1/125 sec, ISO 6400
30
Shot of the Month – November 2019
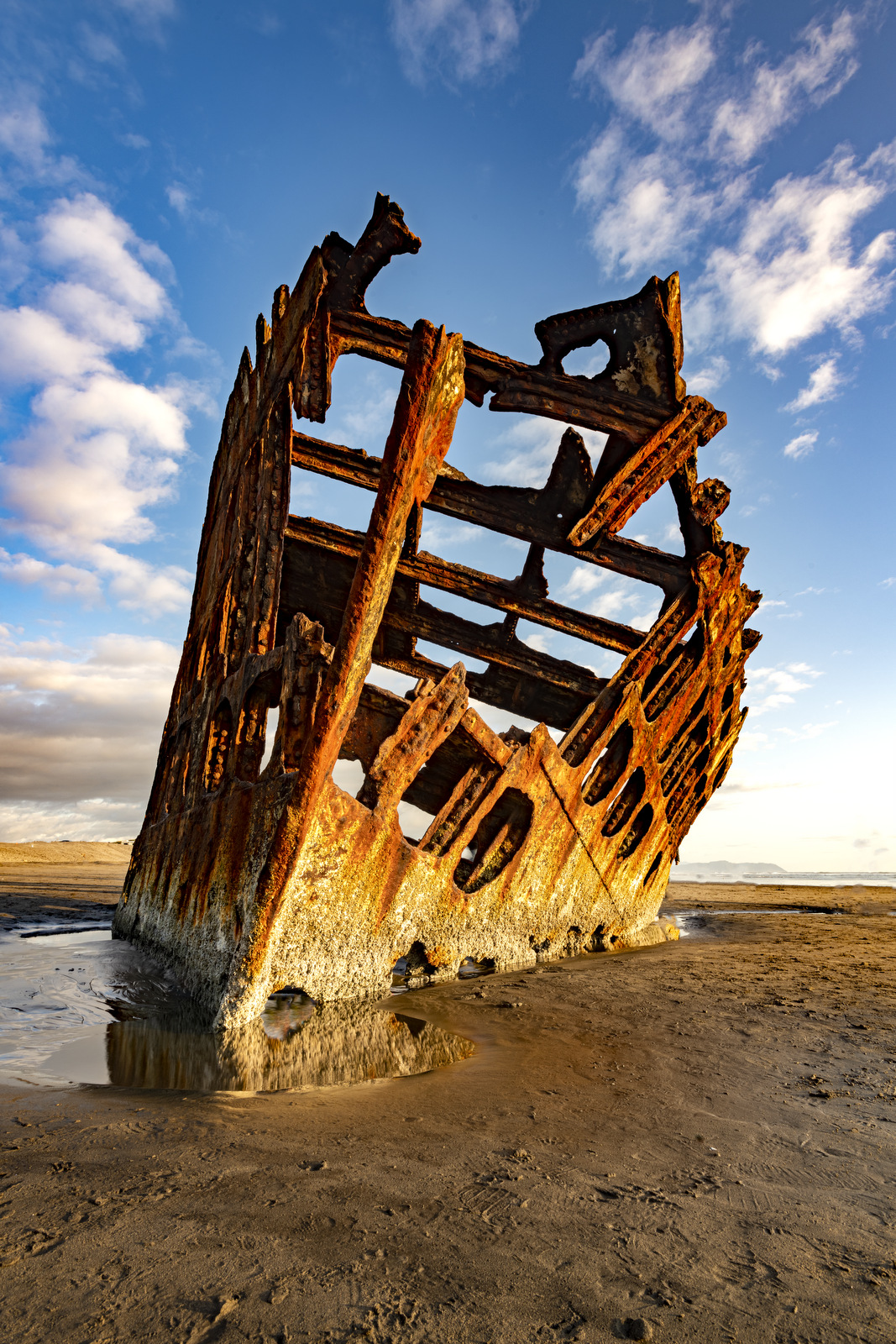
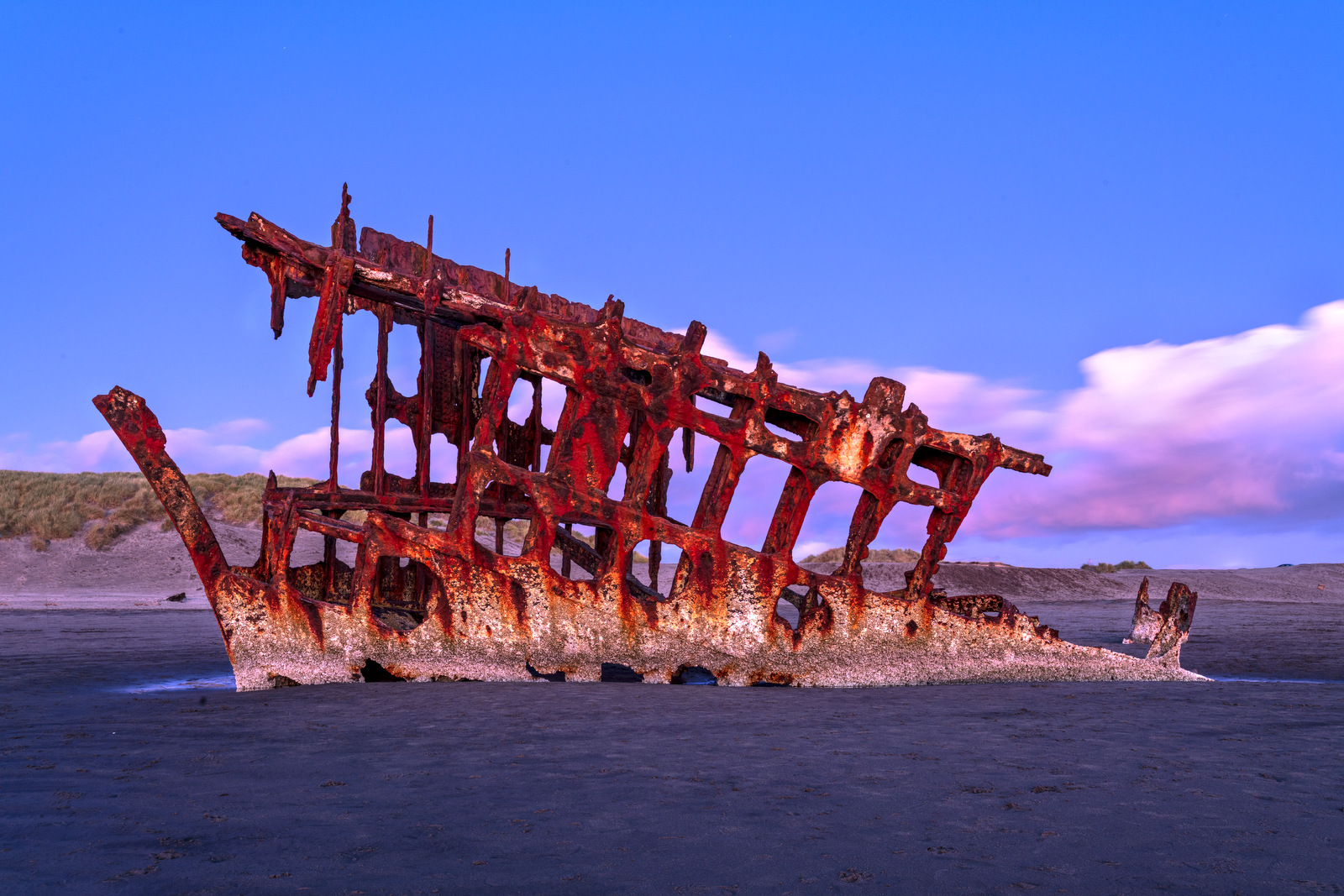
While this ship is clearly no longer sea worthy its rusting hull can, at least for a few more years, take our imagination on a journey back in time. The hull, located on the beach at Fort Stevens Park, is all that is left of the Peter Iredale, a four-masted steel barque that ran aground on the Oregon coast on October 25, 1906. The ship had departed from Salina Cruz, Mexico (about 60 miles south of San Diego) a month earlier bound for Portland, Oregon with 1,000 tons of ballast and a crew of 27. Nearing the end of its journey the ship encountered a fierce storm just four miles south of the Columbia River channel and was driven onto the beach in the driving winds. The force of the impact was so great that 3 of the 4 masts of the ship snapped when it hit the sand. All crew were rescued from the ship and there were no casualties.
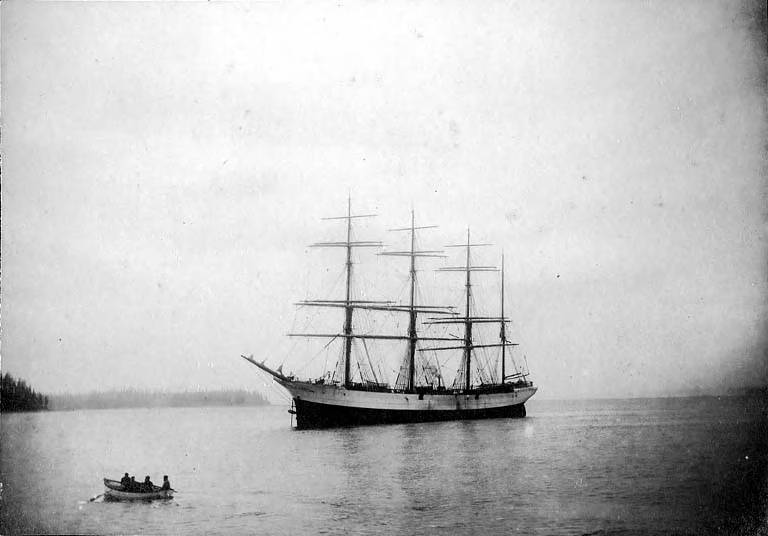
Above we can see the Peter Iredale in all his glory — the steel ship was built in 1890 in Maryport, England and was 285 feet long. The ship was sent to Portland to pick up a cargo of wheat that would be sailed to England. Below we can see the ship not long after it ran aground.
There was little damage to the hull so initially the plan was to tow the ship back to sea. However, the recovery team had to wait a few weeks for favorable weather and during this time the ship sank deeply into the sand and it was impossible to move it. And so there it has stayed for the last 113 years.
And, in case you were wondering:
Who the heck is Peter Iredale?
He is the bloke that owned the ship. He had a shipping firm called Iredale & Porter and was a business big shot in Liverpool, England.
Did the crew screw up and cause this mess?
Well, a naval inquiry was held by the British Vice-Consulate to determine the cause of the wreck. The British Naval Court ruled that the sudden wind shift and the strong current were responsible for the stranding of the ship, and that the captain and his officers were “in no wise to blame” and in fact the captain (Captain H. Lawrence) and the crew were commended for their attempts to save the ship.
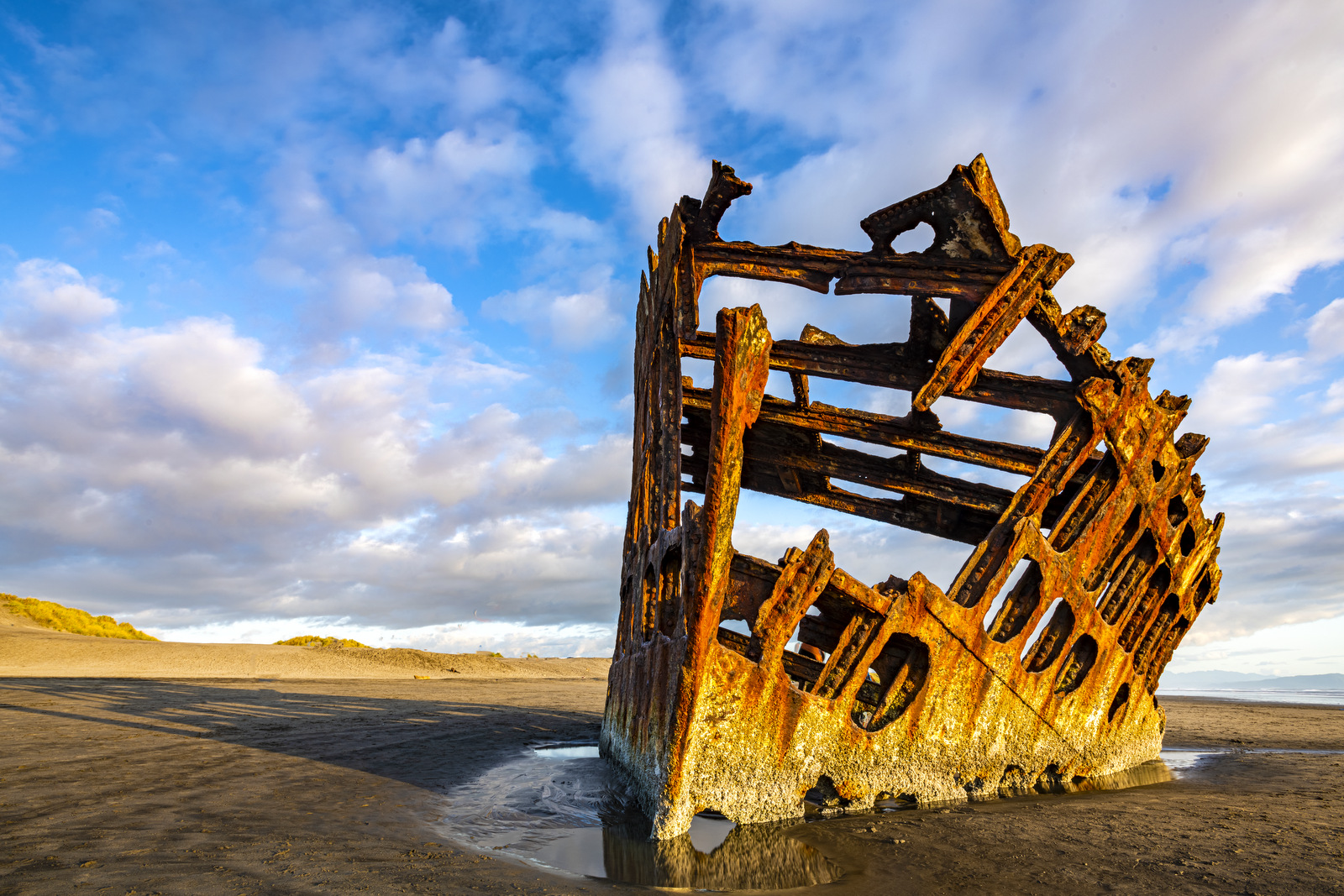
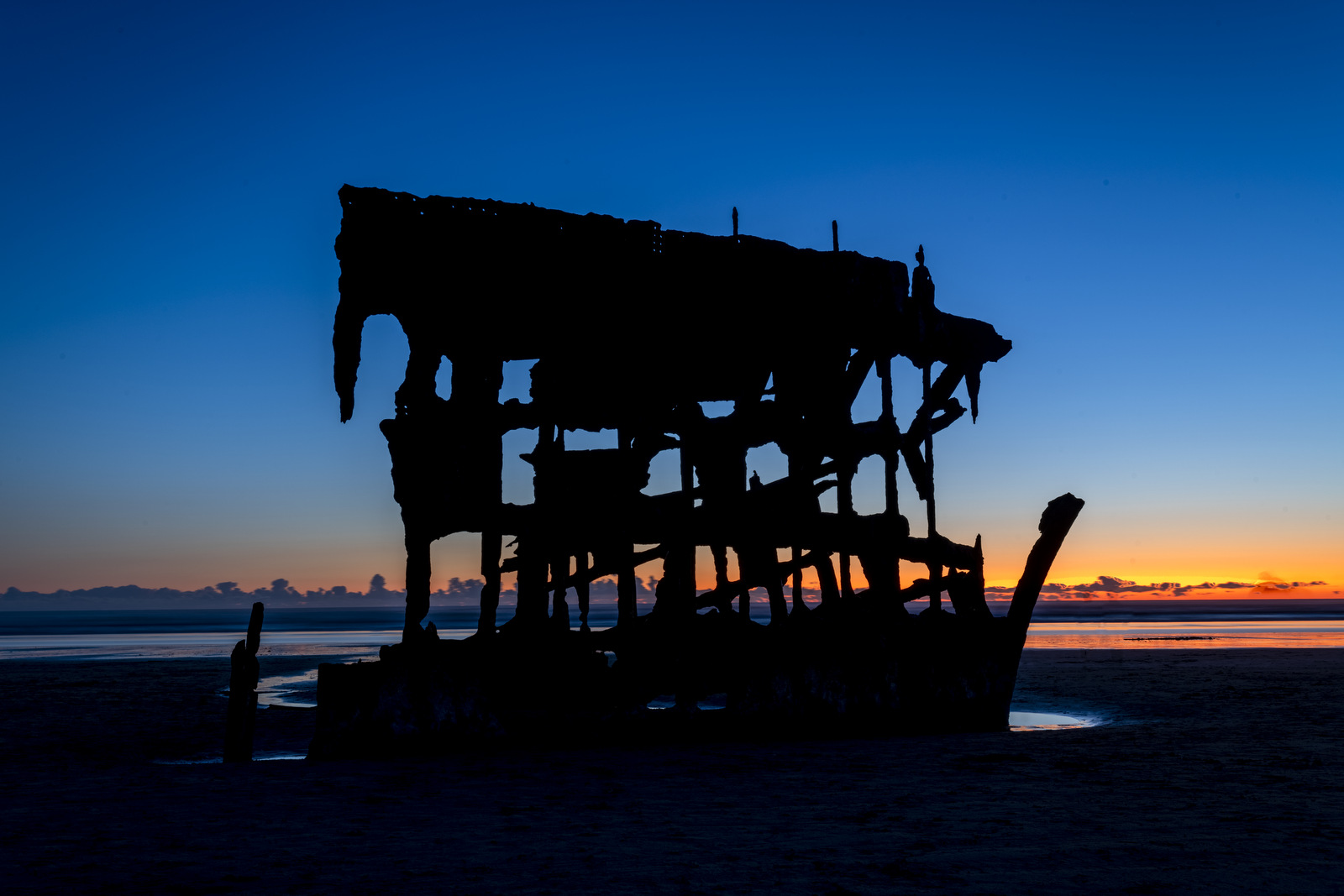
I only spent one afternoon at the wreck site and as luck would have it, there was a low tide near sunset allowing me to walk right up to the hull. Here a few images from different perspectives and as the light transformed as the sun went down.
Here is a landscape orientation as some clouds rolled in:
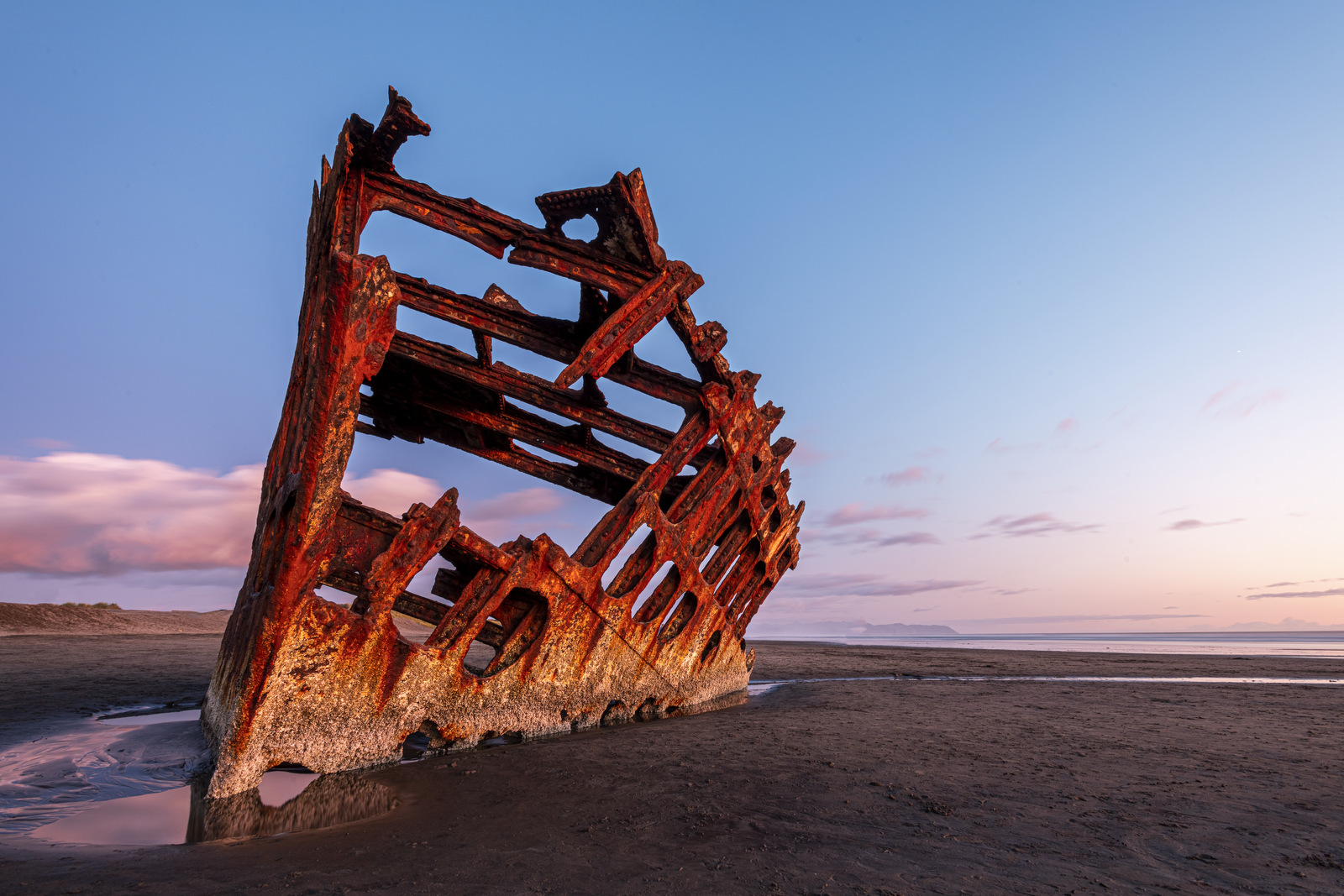
As the sun nears the horizon the light weakens but there is a soft pink hue (alas, we lost most of those lovely clouds):
Here we can see the full side of the remaining hull in the last light:
On that fateful day, just before leaving the beach, it is reported that the red-bearded captain stood stiffly at attention, saluted his ship, and said:
May God bless you and may your bones bleach in these sands”
He then turned and addressed his men with a bottle of whisky in his hand. “Boys,” he said, “have a drink.”
I don’t know if this salty tale is all true, but I like to believe that it is.
Ayyye! Until next month….m
Sources:
Here is a fun video on the shipwreck:
And here you can see historic images of the wreck over the last 100 years:
https://www.oregonlive.com/travel/2018/03/watch_oregons_iconic_shipwreck.html
Nikon D850, Nikon 17-35mm (@ 17 mm), f/8, 1 sec, ISO 64. HDR composite of 5 exposures (-2,-1,0,+1,+2 EV).
31
Shot of the Month – October 2019
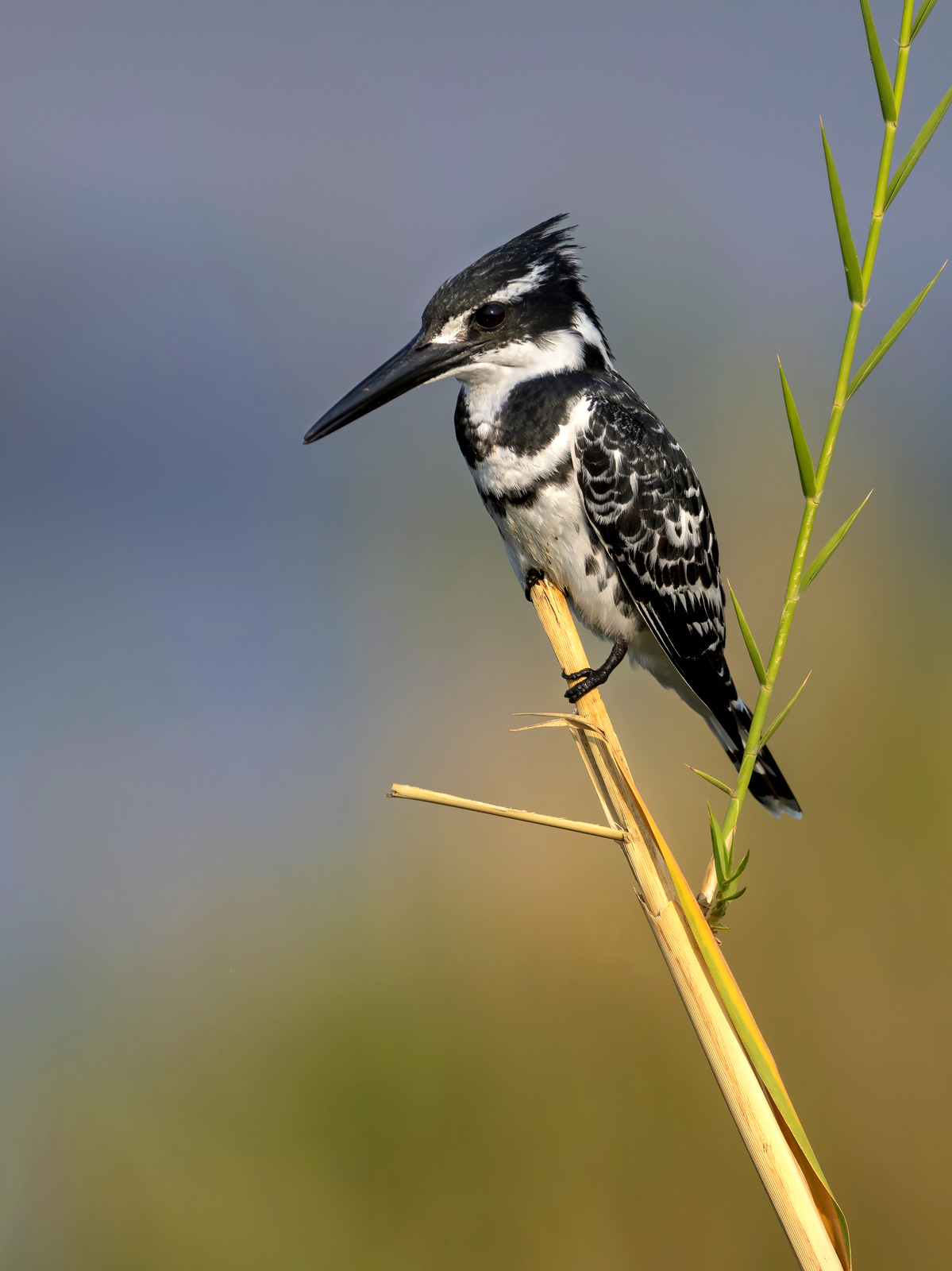
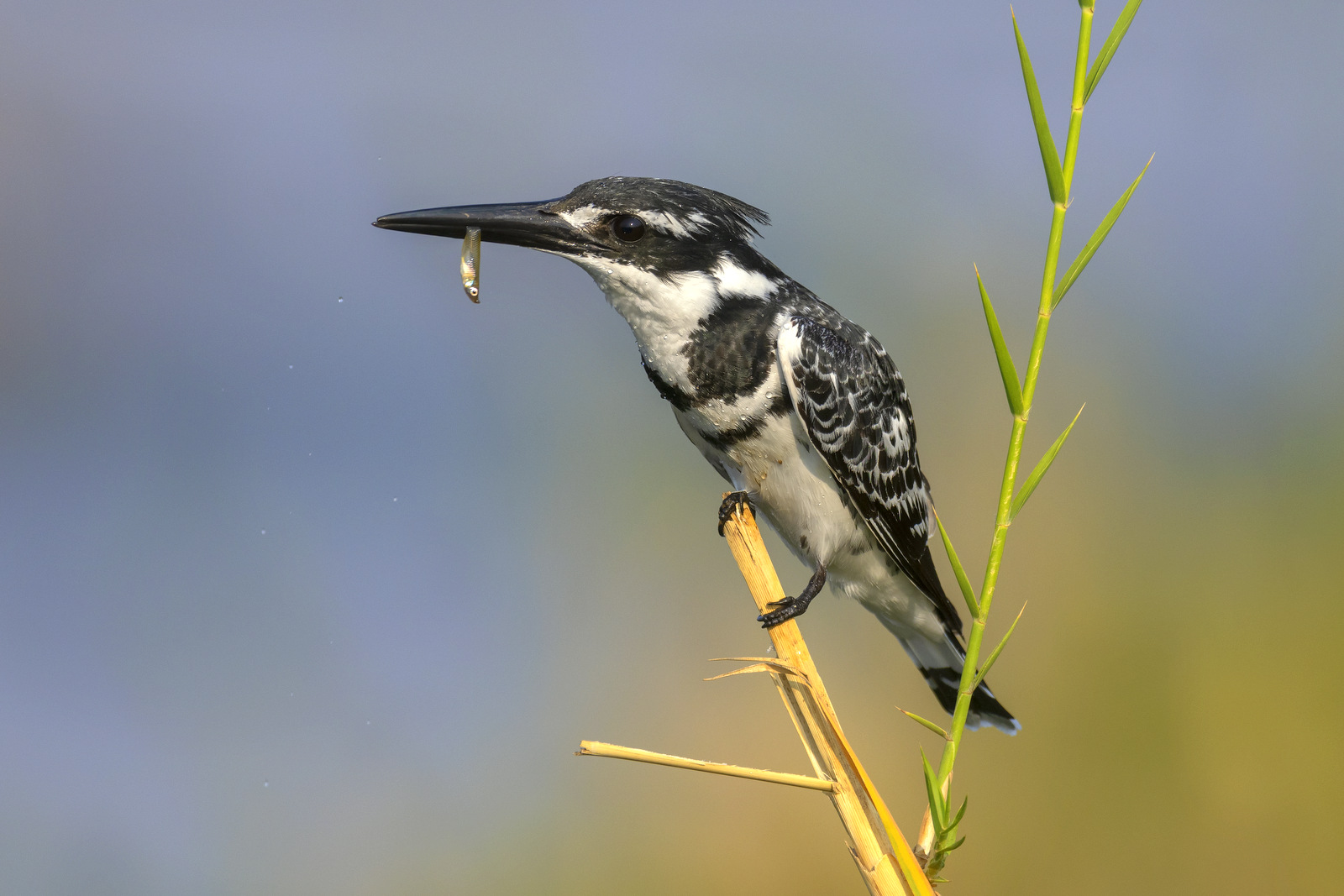
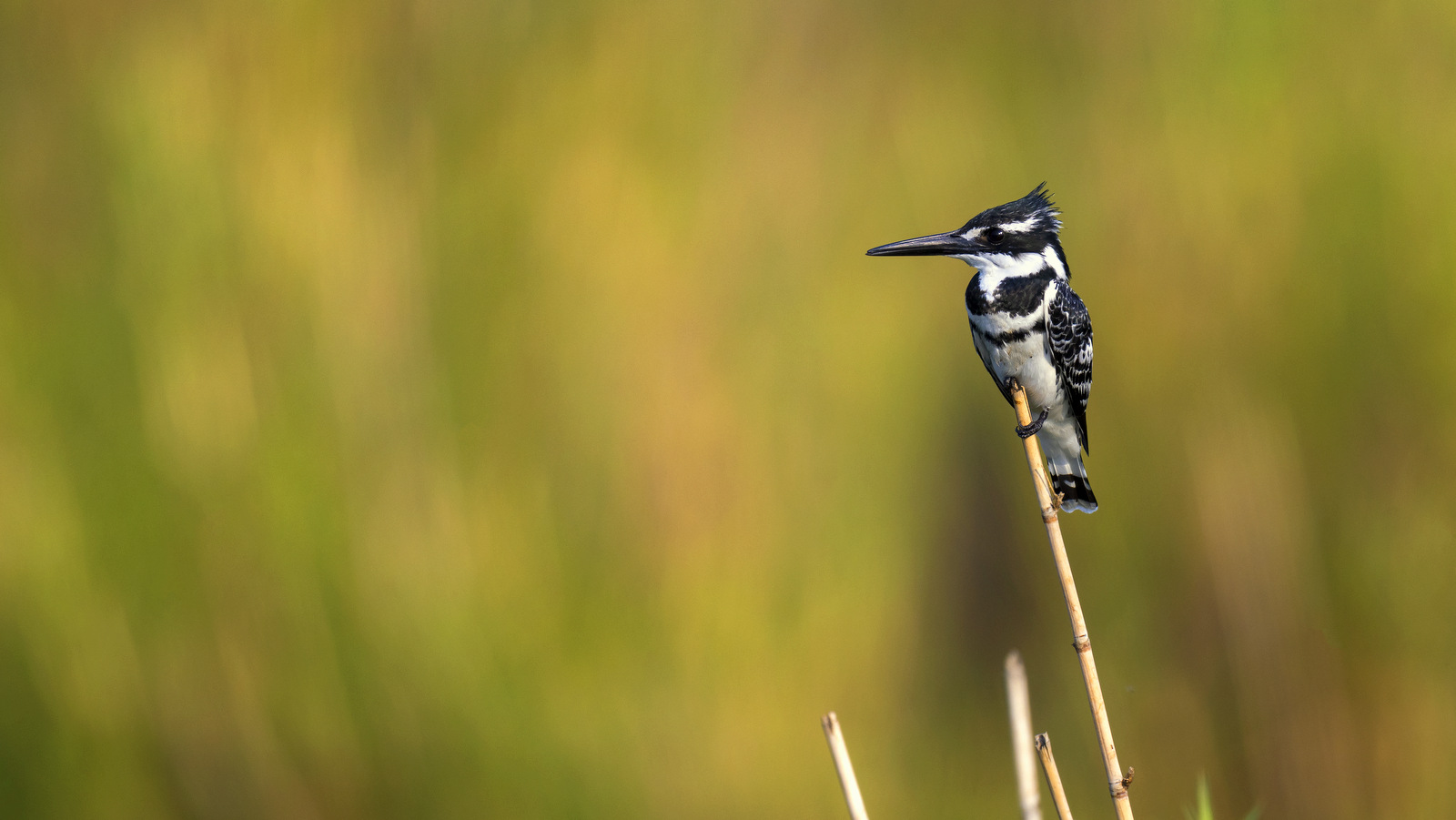
There are 114 species of kingfishers around the world and most are bright splashes of color with wings. These small to medium size birds tend to specialize in catching fish though a few prefer insects. All tend to have large heads, long, sharp pointed bills, short legs and stubby tails. One of the most common kingfishers is the Pied Kingfisher as seen above. Bright splash of color?? It seems that the Pied Kingfishers were at the back of the line when the colors were given out as they are rather penguin-esque decked out in their monochromatic black-and-white color scheme. Click here to see a more colorful variety.
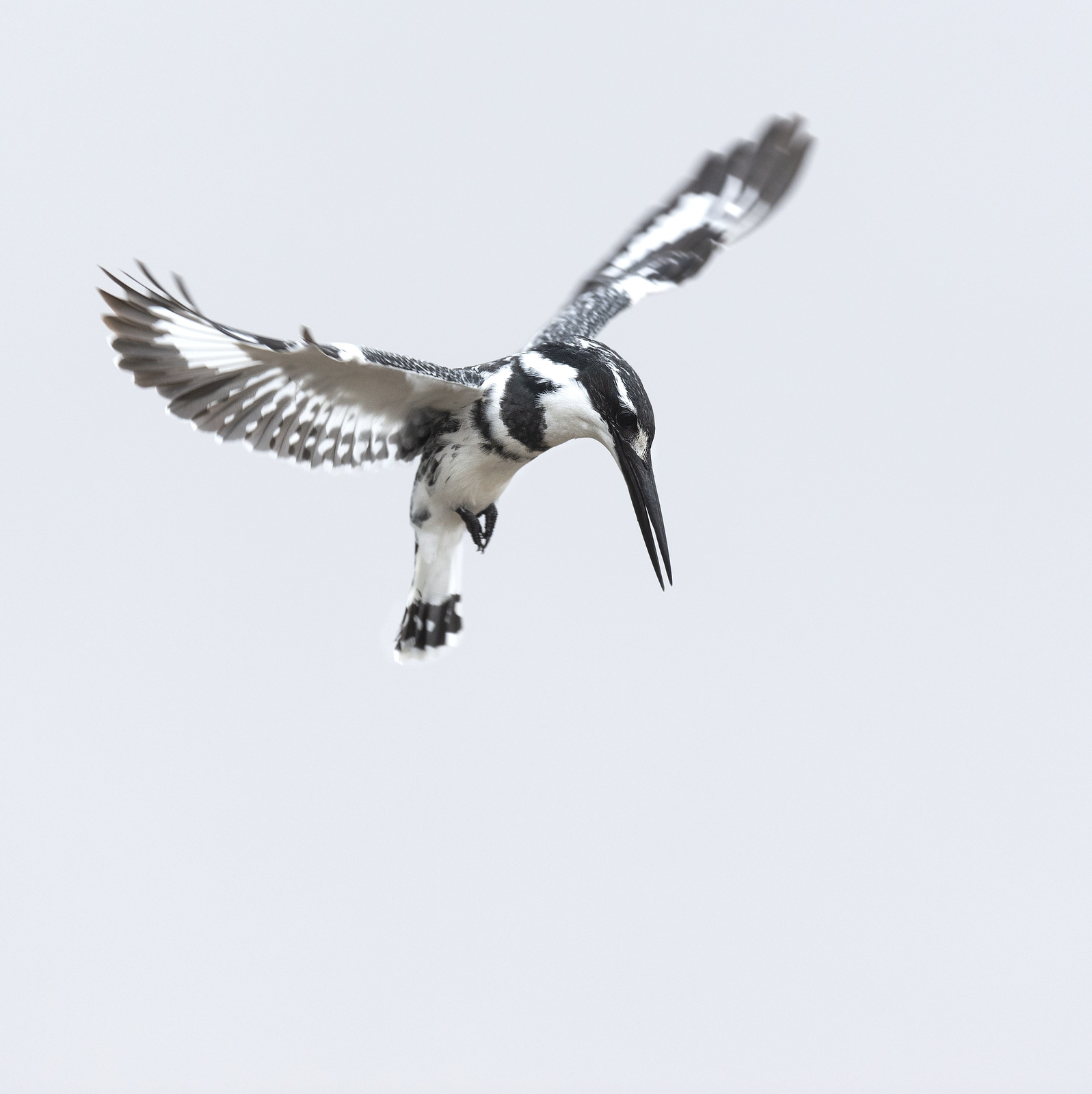
As shown below, Pied Kingfishers are exceptional hoverers — by flapping their wings rapidly they can stay in one place for an extended period time as they scan below looking for fish in the water. They are actually the largest bird that can truly hover. While hovering they have to keep their head perfectly still to judge the location of the fish below. Here is a great video that explains the hunting technique of these skilled fliers. And another good video here.
A fresh kill captured on film….Definitely will NOT need a bigger boat for this one.
The Pied Kingfisher can be found throughout sub-Saharan Africa and southern Asia from Turkey to India to China. I photographed this lovely chap in Kruger National Park in South Africa.
The Pied Kingfisher – what they lack in color they make up for it with true acrobatic talent and classic formal style and grace.
Until next month….m
Sources:
Nikon D500, Nikon 600 mm f/4 (@ f/5.6), 1/1500 sec, ISO 200, EV -0.5
























































