30
Shot of the Month – September 2016
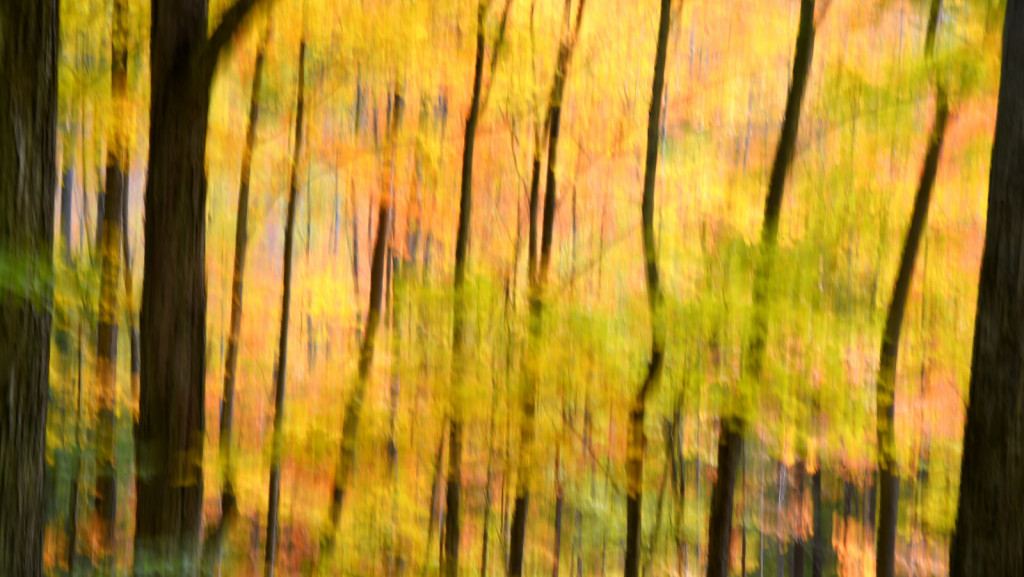
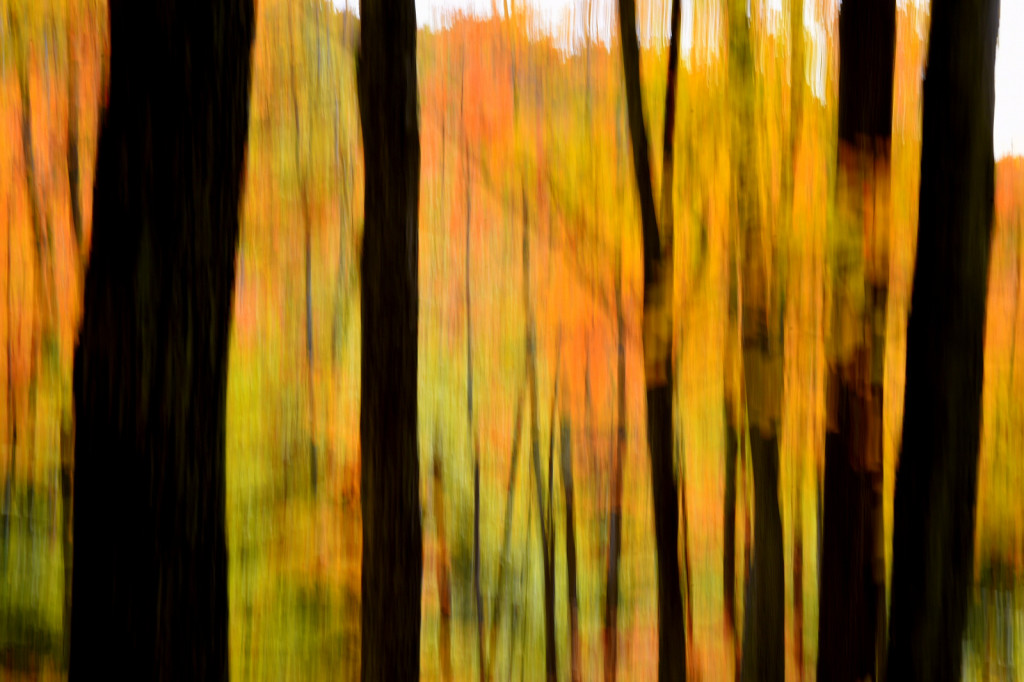
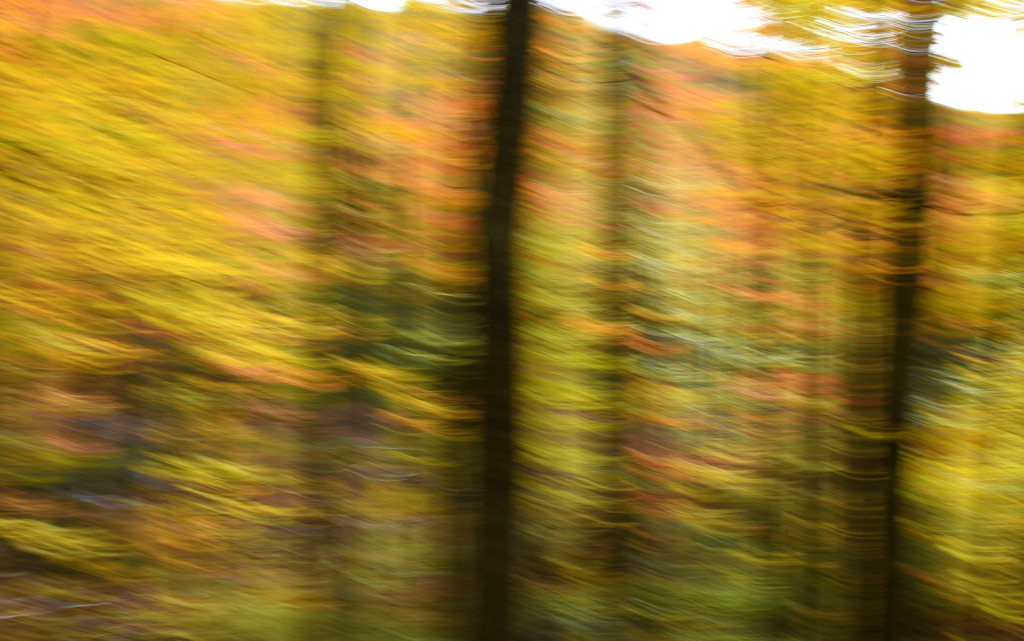
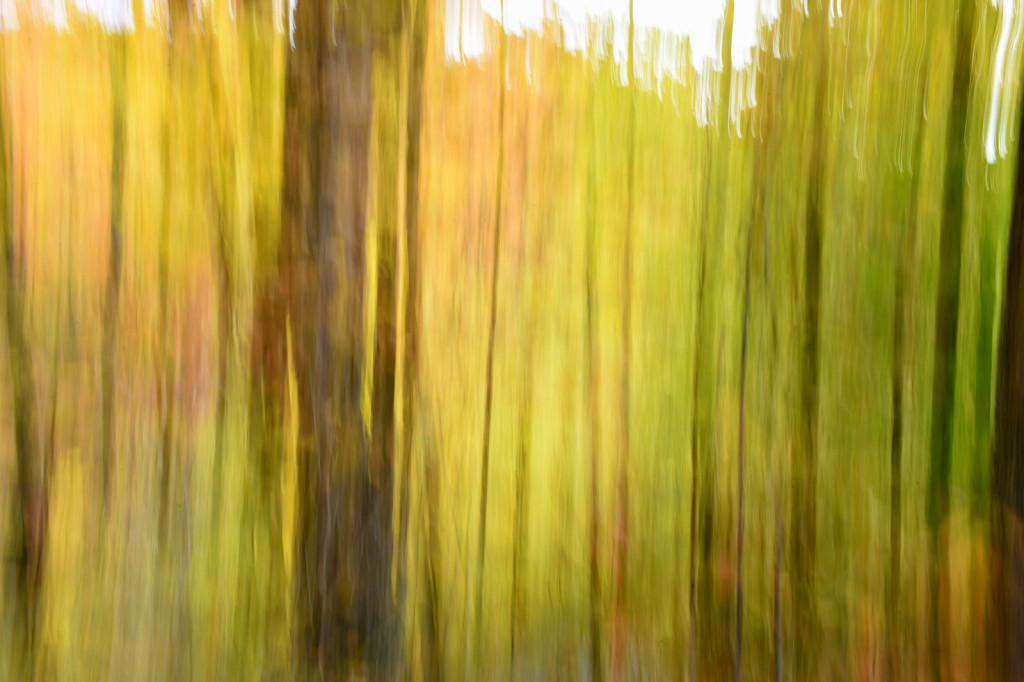
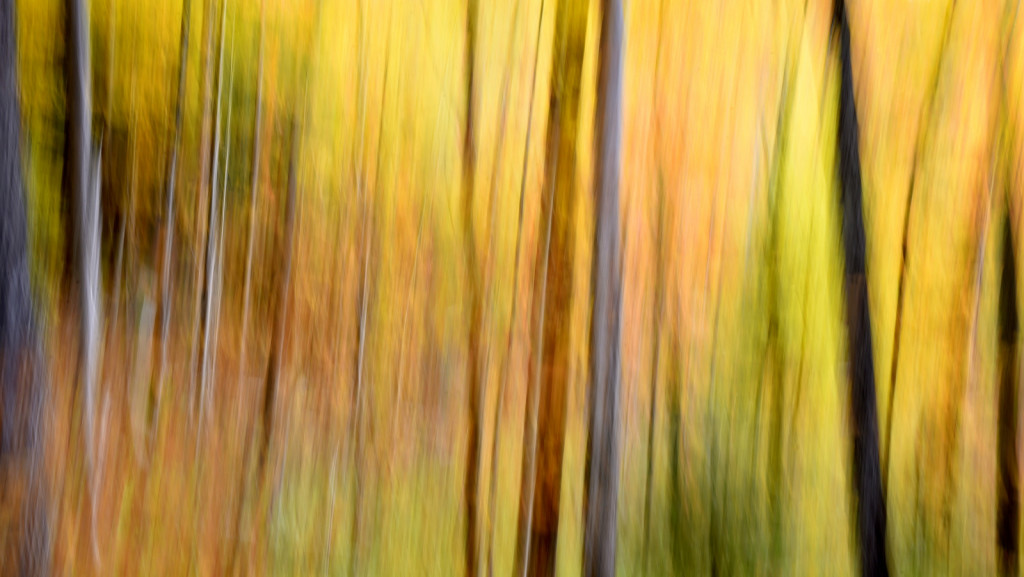
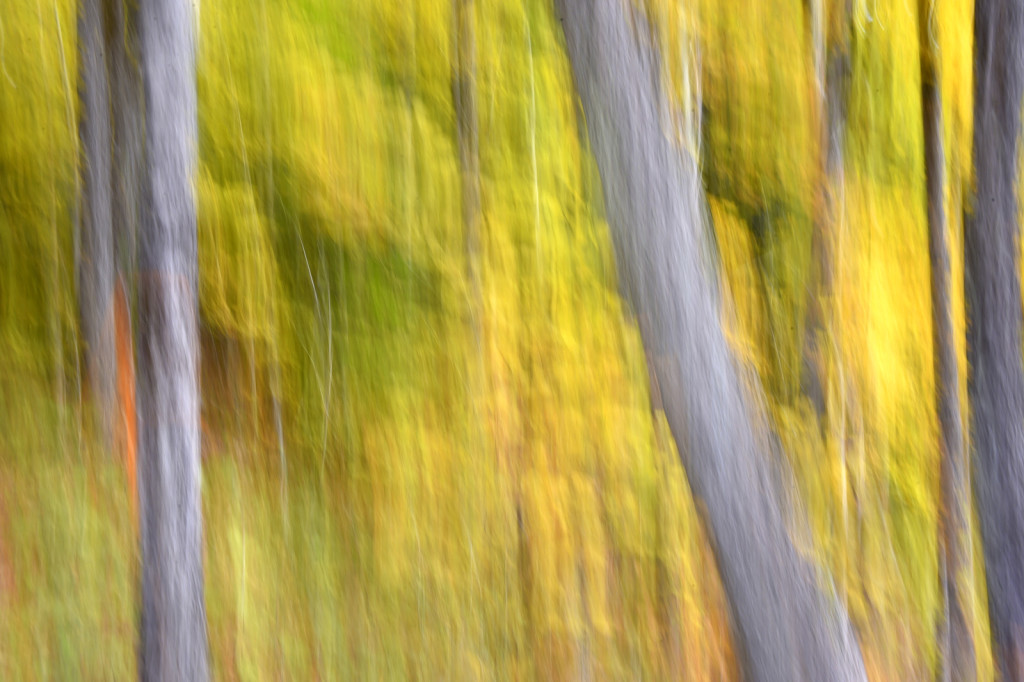
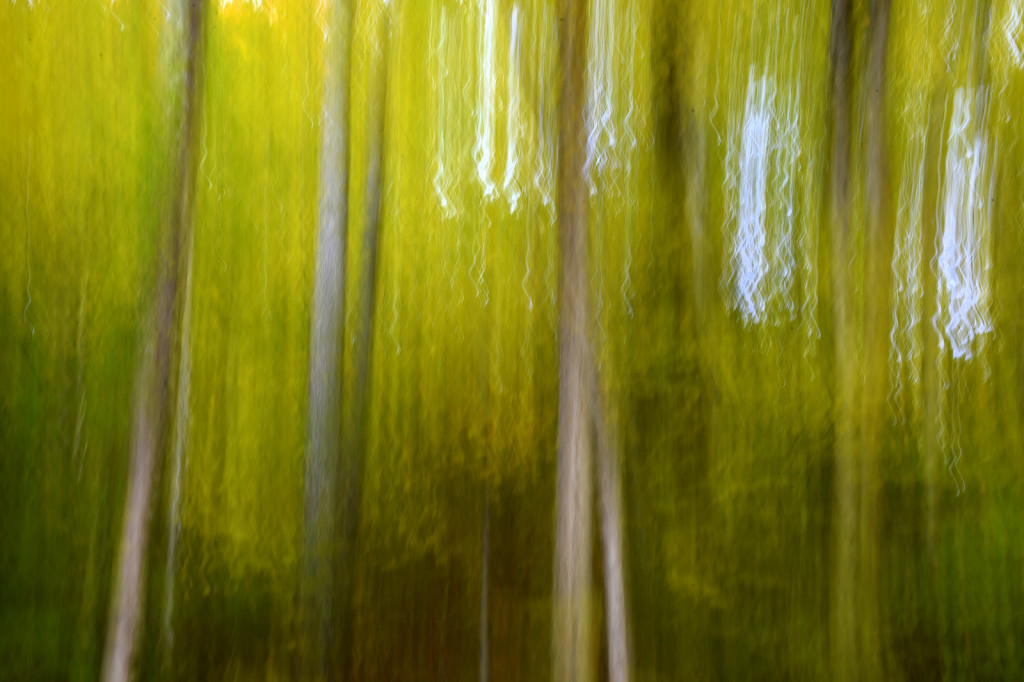
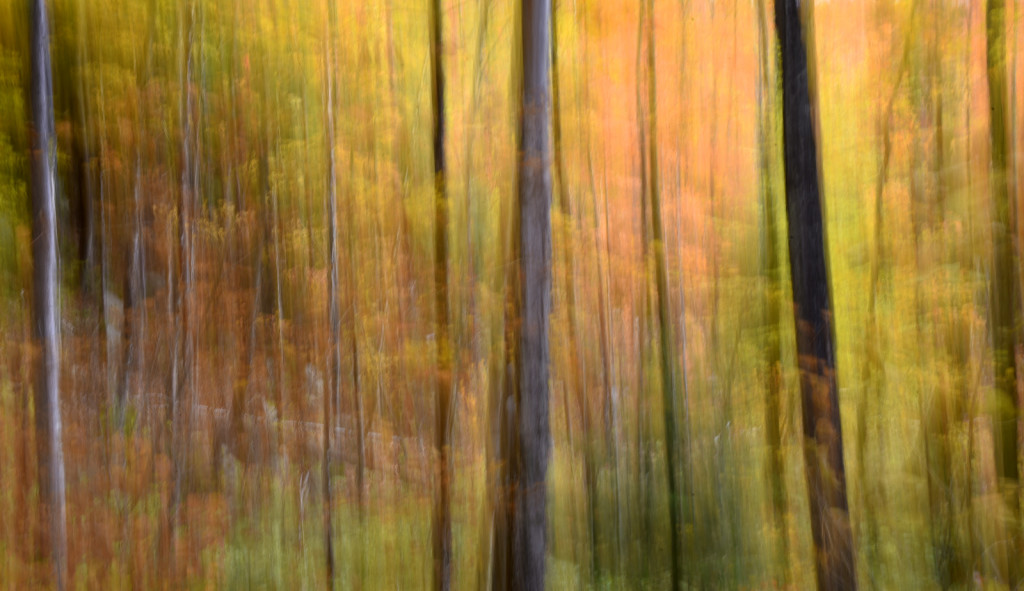
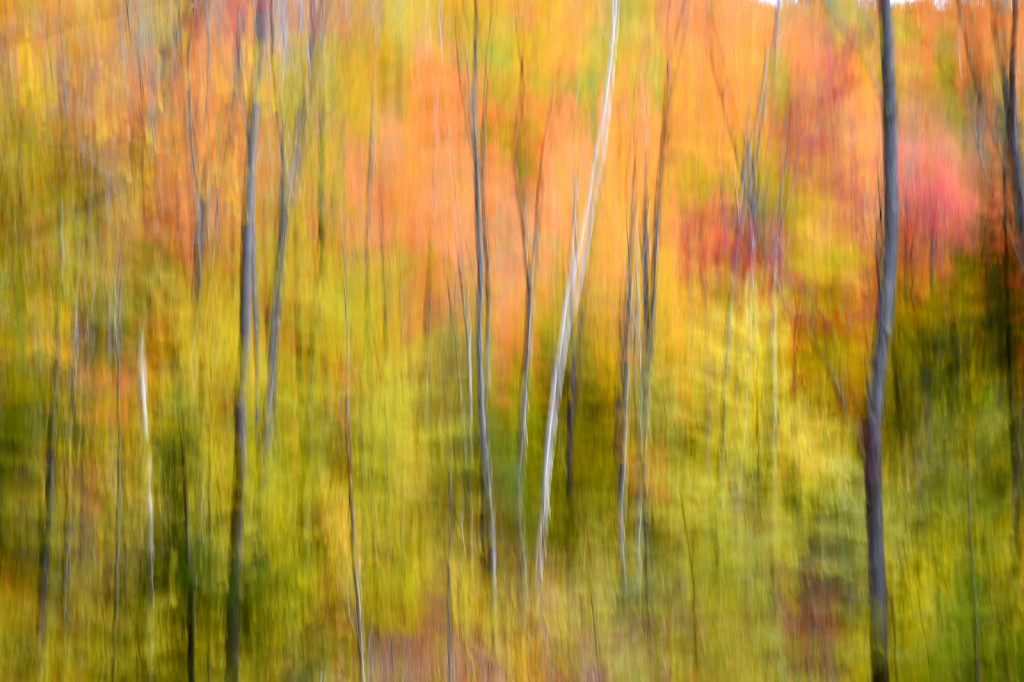
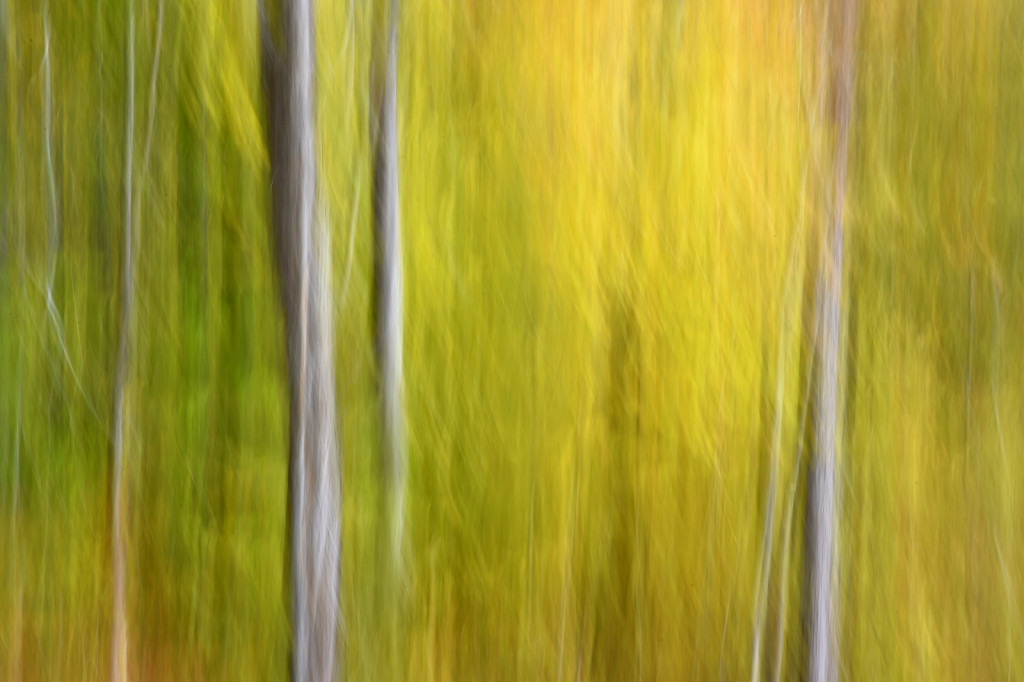
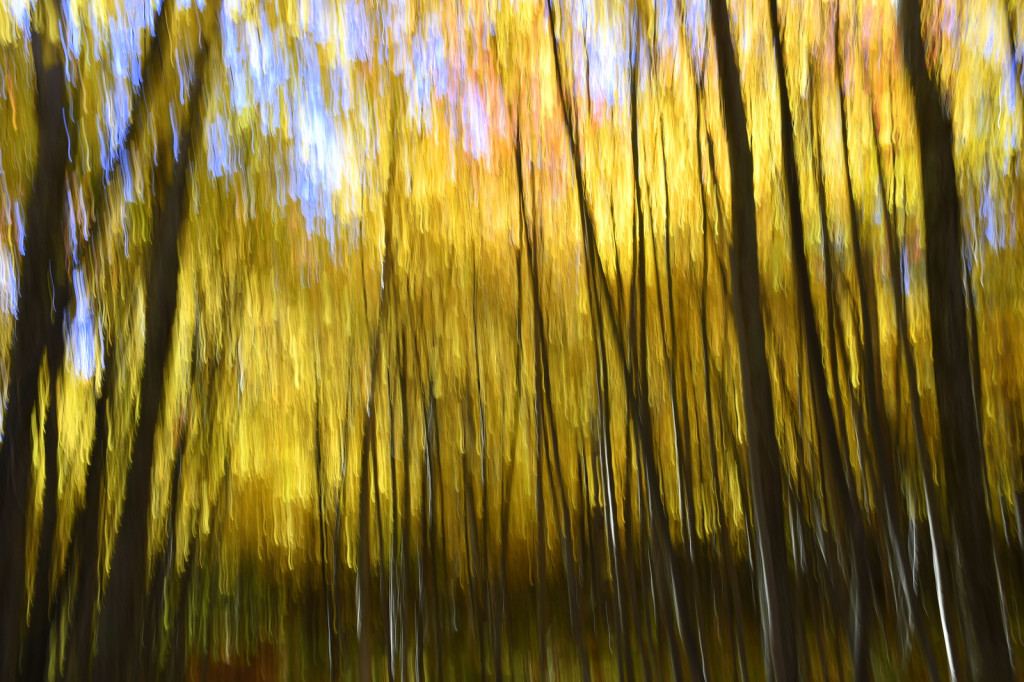
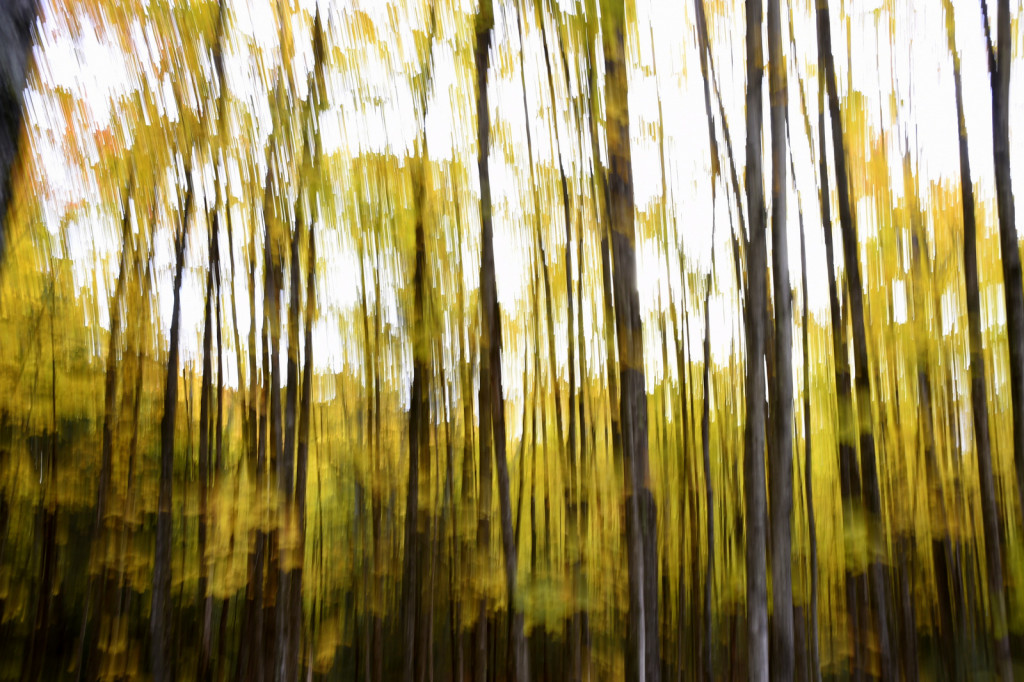
If you dig color then autumn in New England is the place to be. For a few glorious weeks, your entire world becomes a crazed canvas of exploding greens, yellows, oranges, and reds. As a photographer, I have often struggled to capture the scale and audacity of the landscapes that Mother Nature majestically painted each year. The colors in the image never seemed to quite capture the radiance and intensity that assaulted (in the most pleasant manner, mind you) my eye. The scale was always far too pedestrian — either too close, too far, or just never quite right to inspire and capture the sense of awe I felt in the field.
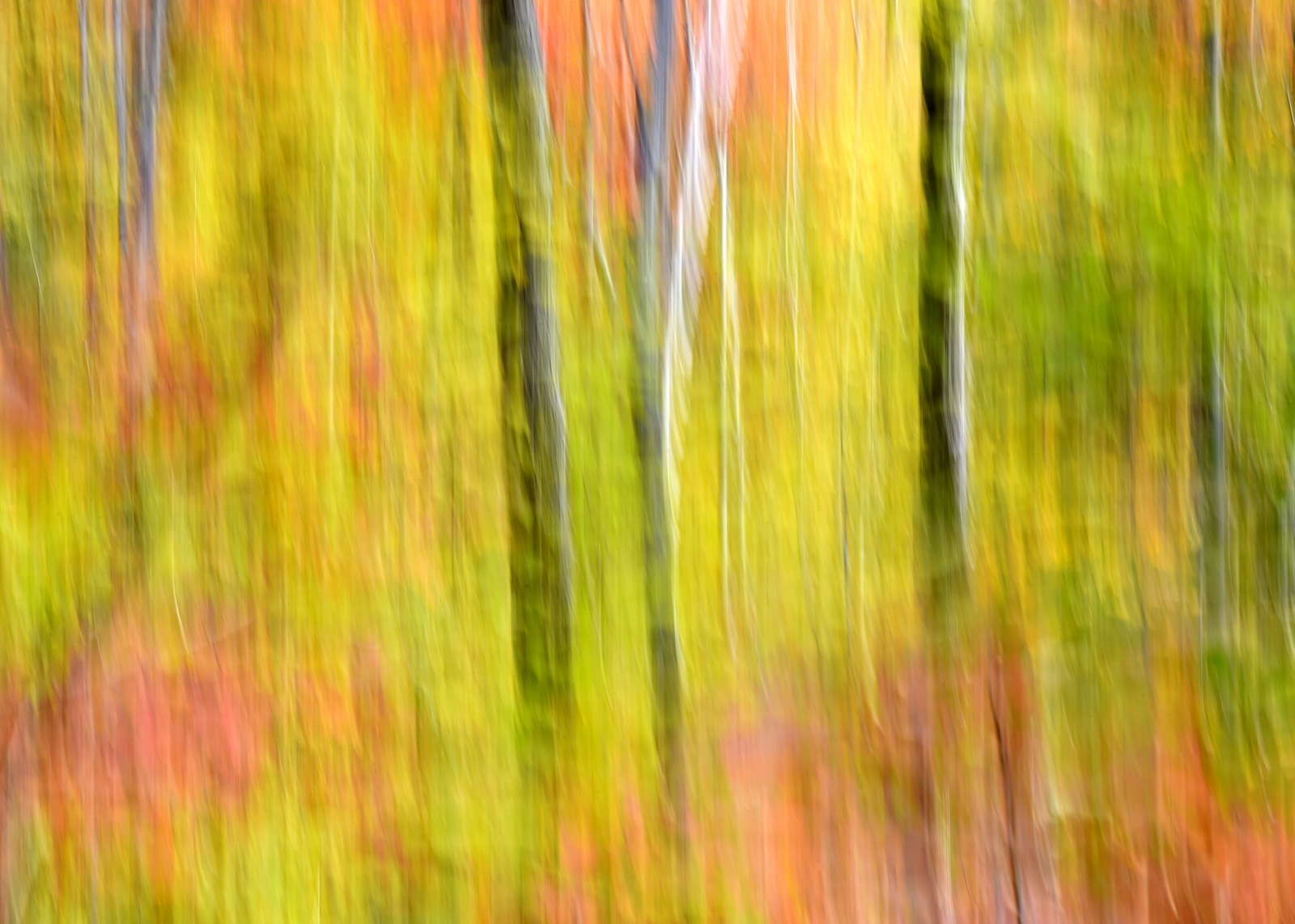
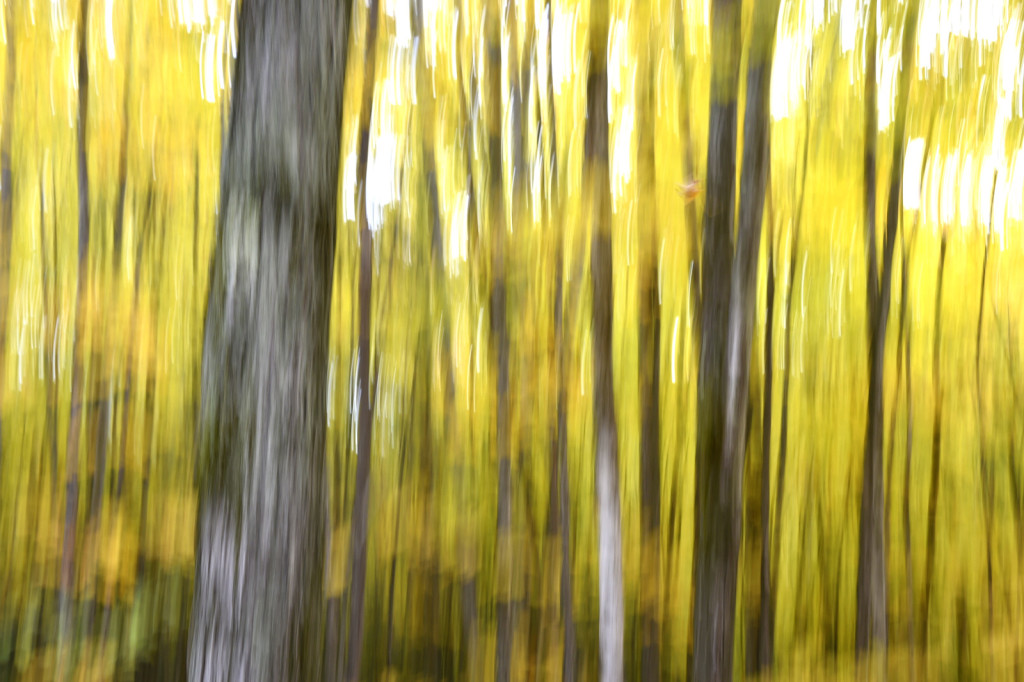
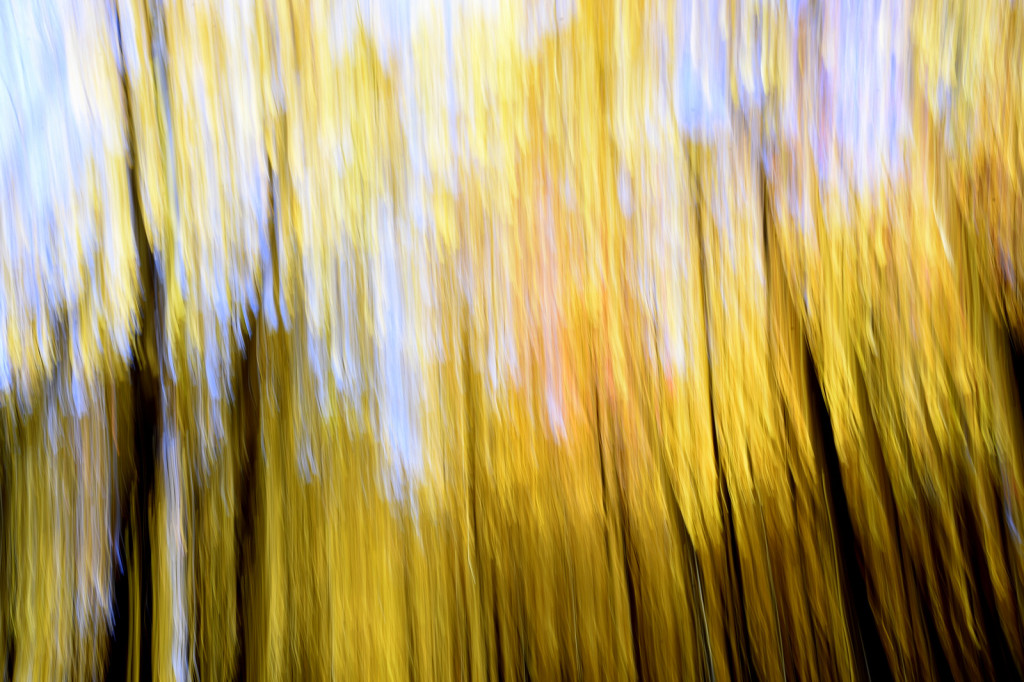
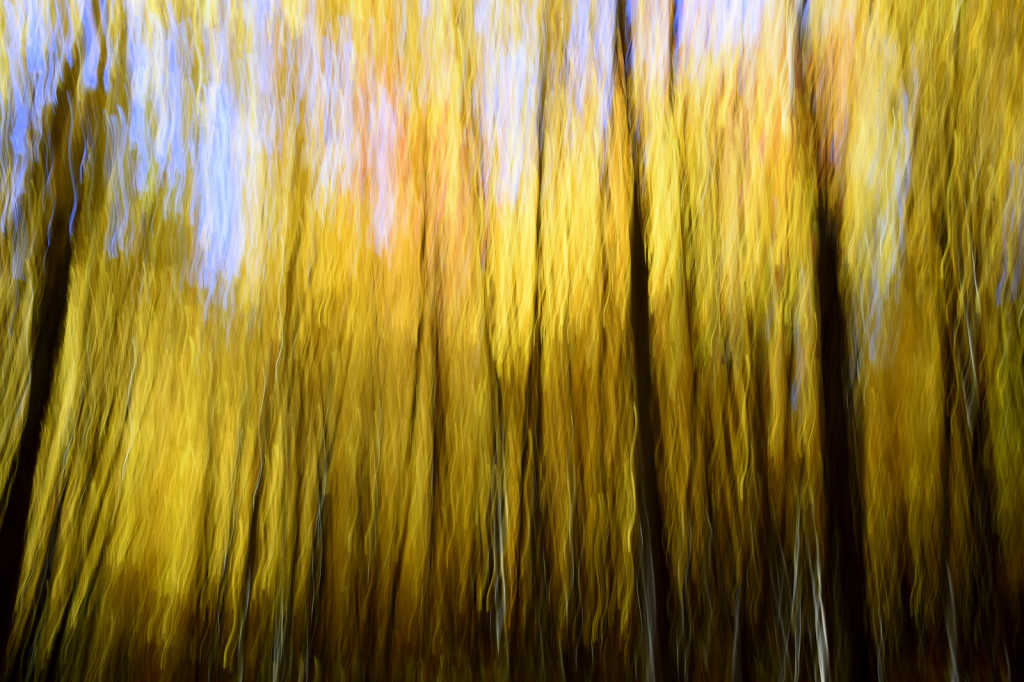
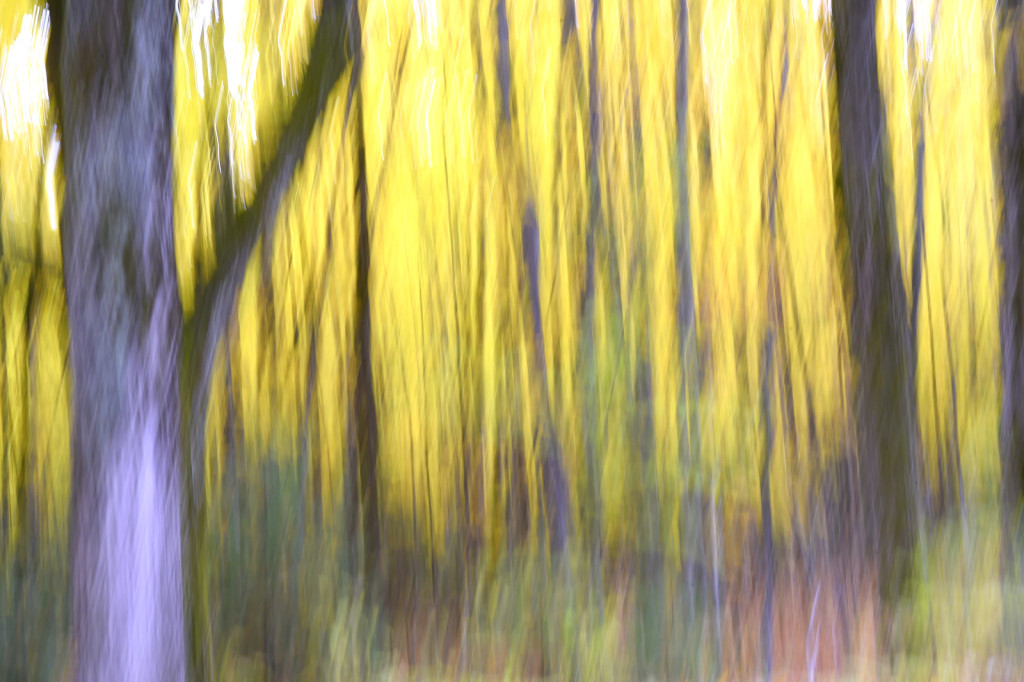
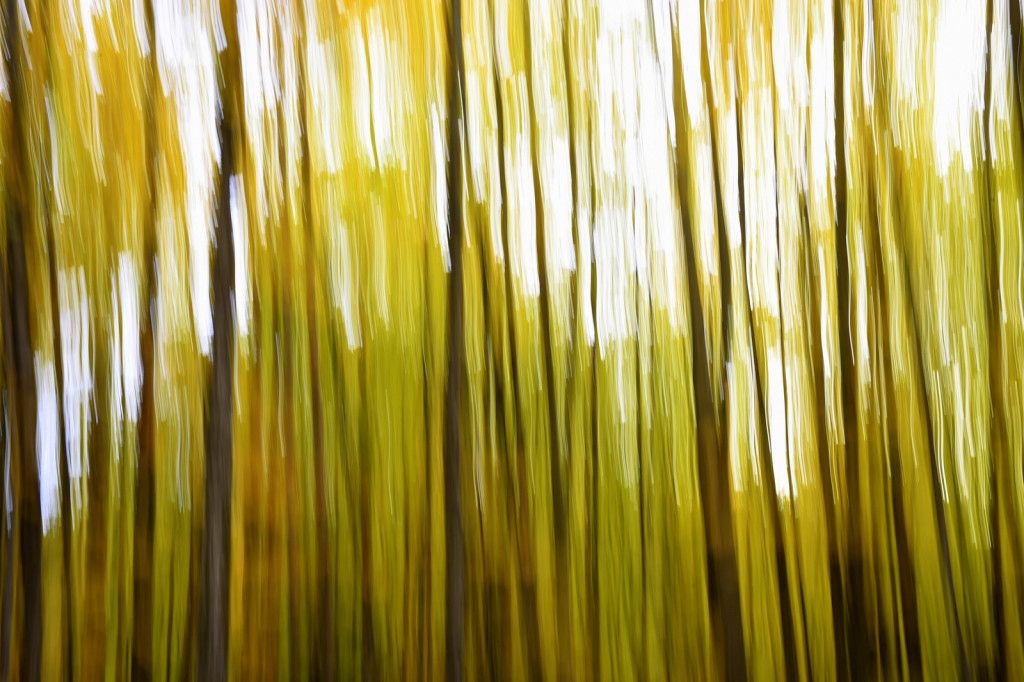
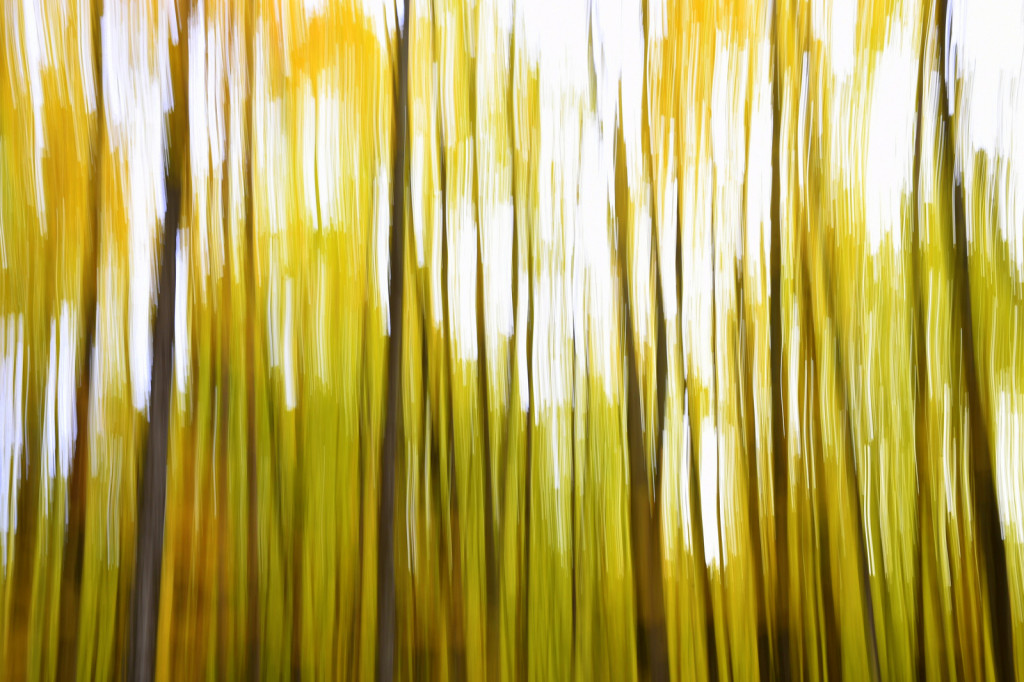
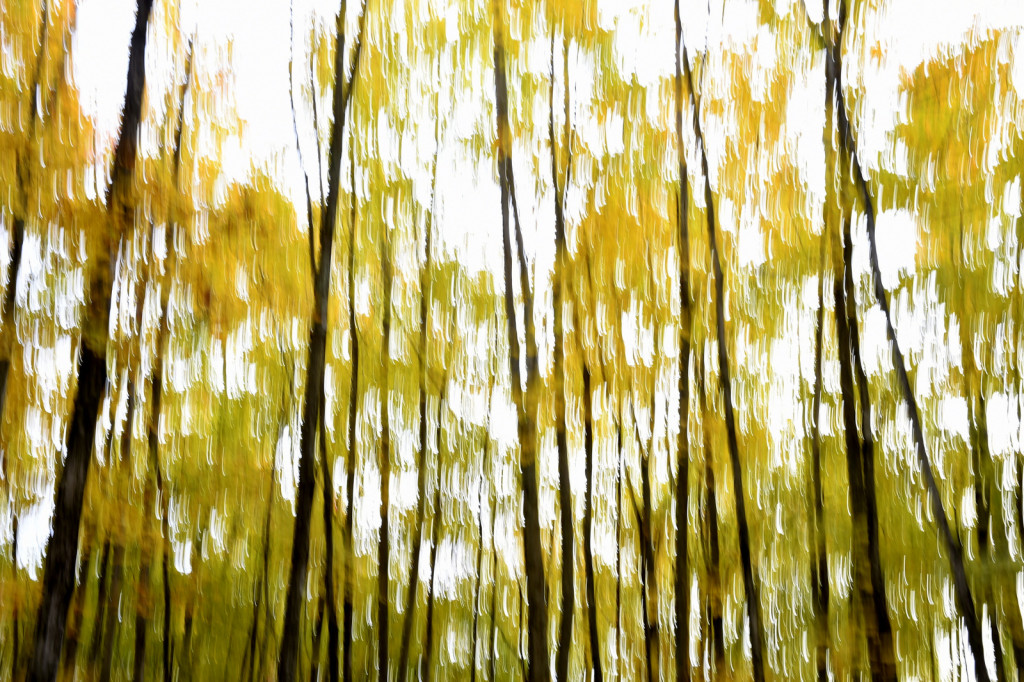
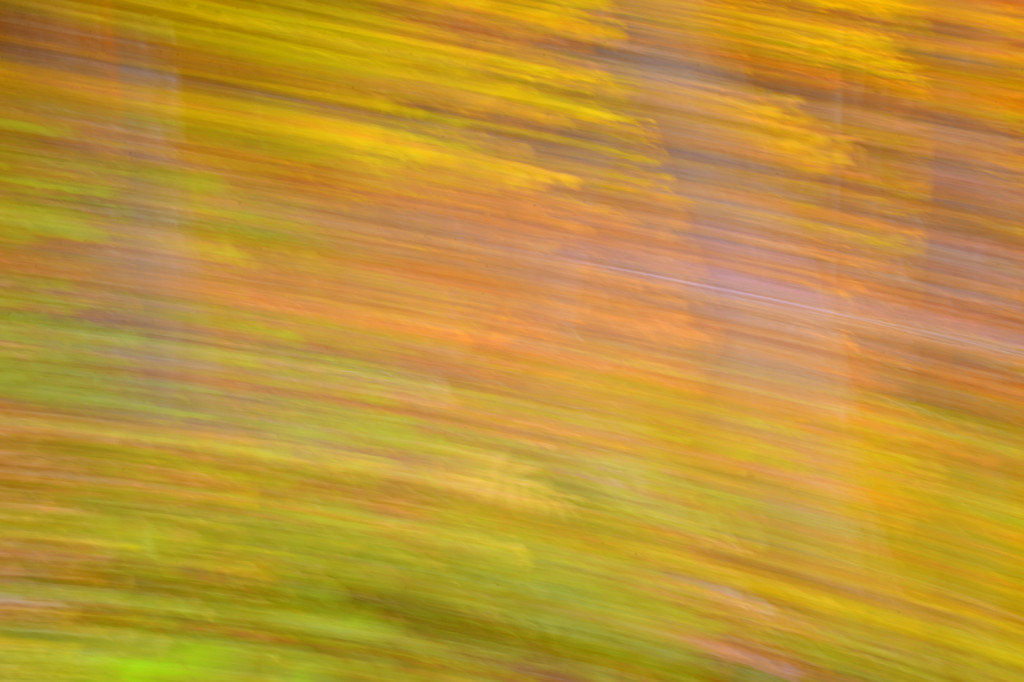
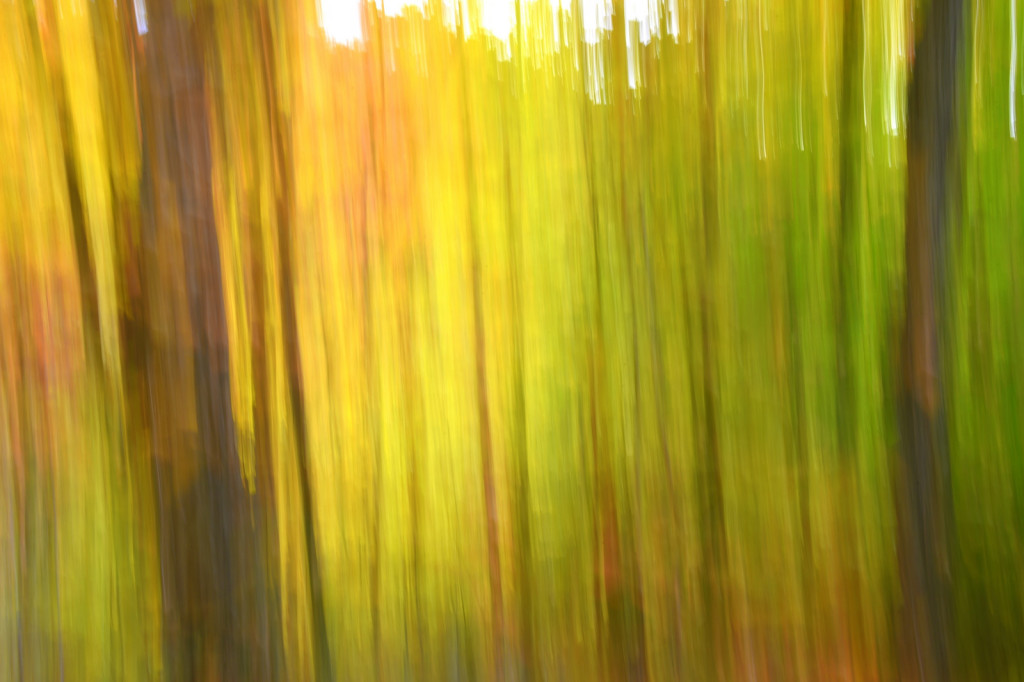
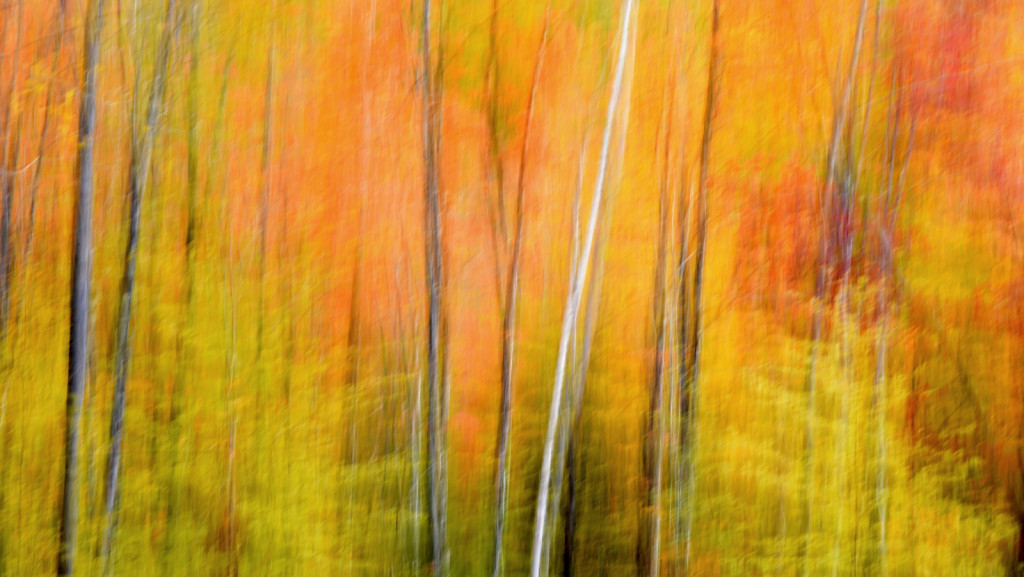
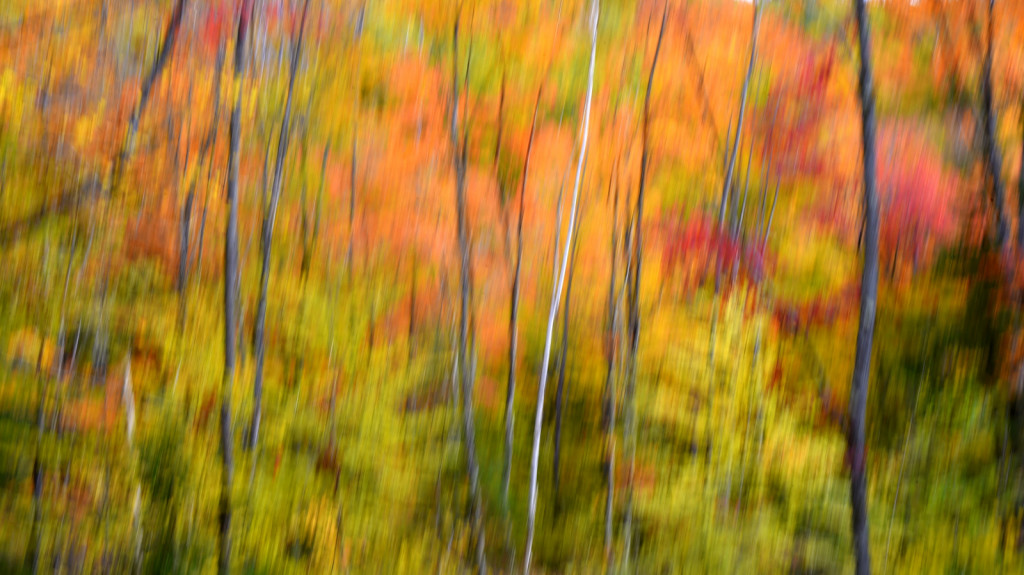
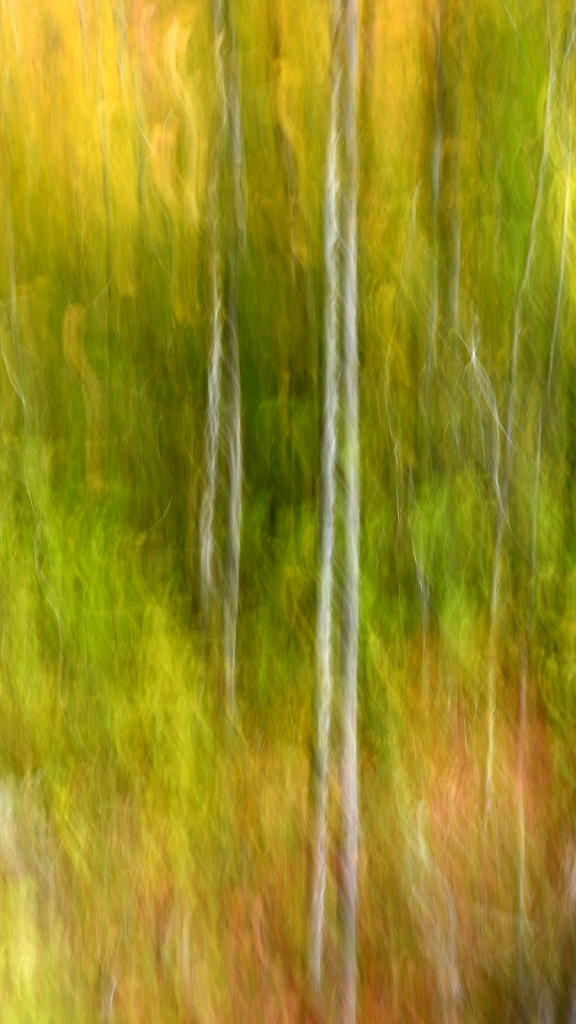
However, last fall I experimented with a motion blur technique that I read about in one of my photography magazines — the Vertical Pan. For the first time, I created images that conveyed the cacophony of color that enveloped me on my walks through the woods. Realism is nice, but these images much better reflect the imprint these experiences have left on my being.
There are three parts to this technique:
Find a Scene that Strikes Your Fancy
Get out there and walk around and look for scenes with bold colors, or great contrast in texture, or some cool shaped tree trunks, or a nice mix of colors…or…or…
Low Shutter Speed
The slower the shutter speed, the greater the blur and the more abstract the image. I experimented with shutter speeds that ranged from 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/10, 1/20, and 1/30th of a second. There is no right speed. It depends on the scene before you and the look that you are going for. To lower the shutter speed you can set your ISO at its minimum and then close your aperture till you get the shutter speed that you want. On bright days, you may need to use a polarizing filter to help slow things down, or you can use a neutral density filter to reduce the light to your camera sensor to get slower shutter speeds.
Move the Camera
Point your camera at the scene of choice and lock the focus. Then, as you press the shutter release button to expose the image tilt the camera down with a smooth motion. Again, you will need to experiment to find the right mix. You can tilt slowly, quickly, or somewhere in between. Sometimes I begin the pan before I release the shutter button. You can pan down (my usual preference), up, or to the side.
There are endless possibilities. Keep playing with the shutter speeds as you vary your movement of the camera. Most will look like junk. Delete and move on.
Others will be, well, magical.
(I recommend viewing the images below on the biggest screen you can find. And once you click on one, you can move through the series easily by using your right or left arrow button.)
- See the falling leaf??!!
- Horizontal Pan
- Horizontal Pan
Until next month…..m
Nikon D4S, Nikkor 28-105mm (@ 105mm), f/29, 1/8 s, ISO 400