28
Shot of the Month – February 2019
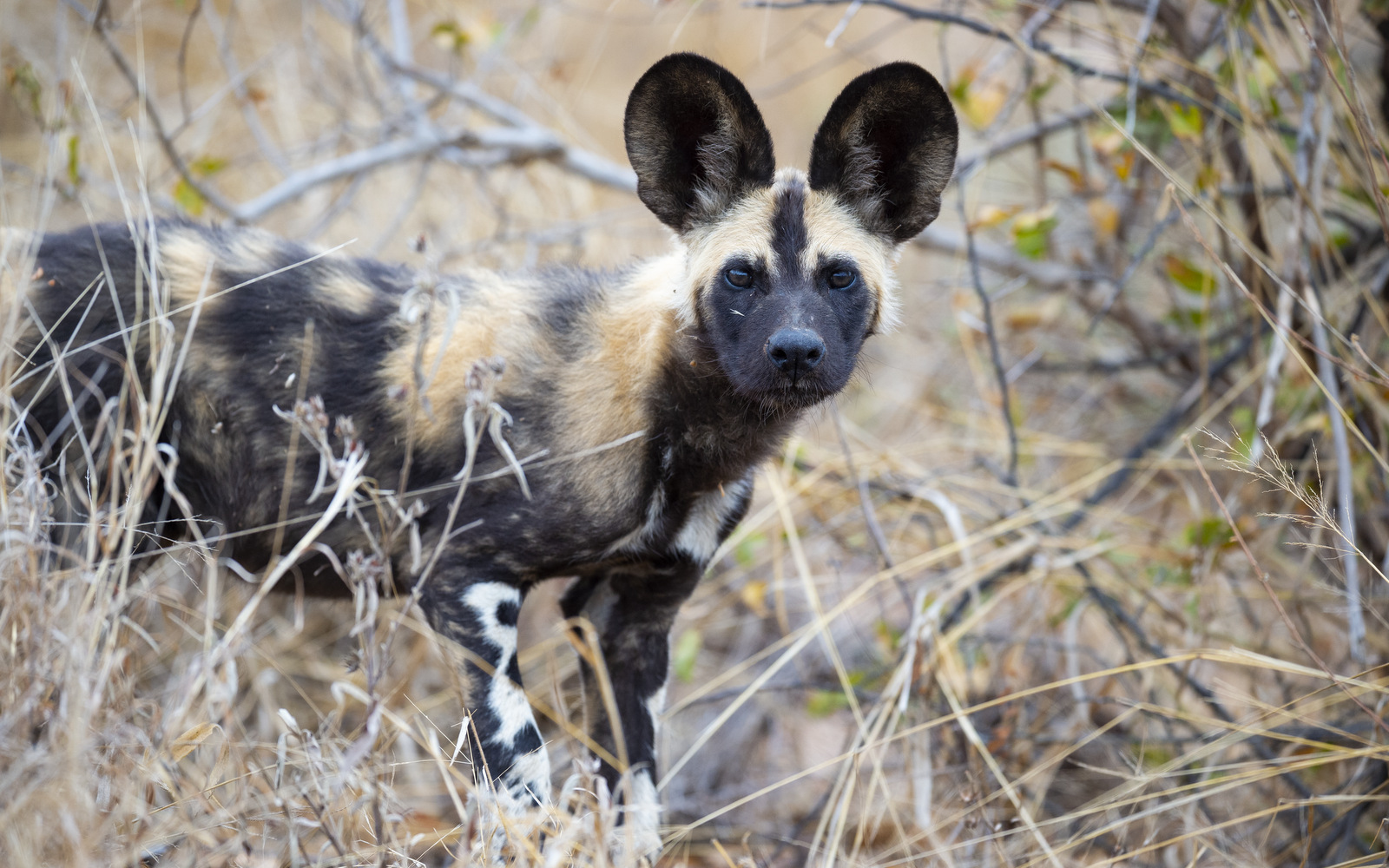
One of the highlights of our 2018 trip to Kruger NP (South Africa) was the magical three hours we spent with a pack of 24(ish) wild dogs. We counted 12 puppies(!) and about 12 adults in one of the largest packs I have ever seen. The pack spent most of the morning sprawled out on both sides of the road. The puppies were on one side and the adults on the other. About every 30 minutes or so, the alpha female would get up and walk over to make sure that the puppies were doing fine. After a few visits by the female, the alpha male got up (trying to be helpful?) and went over to check on the youngins. Well, Dad got too close and woke up the pile of puppies. Chaos ensued with all sorts of yelping and clamoring and assorted mayhem. The alpha female, very annoyed, had to get up and go over and severely reprimand the whole crew. She “bit” a couple of them (in a lovingly, mother kind of way, ouch!), snapped at a few others, and eventually got them to lie back down. Future monitoring visits were done by Mom…..
In case you were wondering, wild dogs are not feral domestic dogs that live in Africa. Wild dogs, also known as the
painted hunting dog,
painted wolf,
African hunting dog,
Cape hunting dog, or
African painted dog
have never been domesticated.
The scientific name for these canids is Lycaon pictus which means “painted wolf” in Latin. The painted hunting dog is part of the Canidae family which includes jackals, foxes, coyotes, wolves, dingoes, and domestic dogs. People often confuse wild dogs with hyenas but hyenas are bigger and more powerful and different enough that they belong in their own taxonomic family, Hyaenidae.
The theme song for a pack of wild dogs would be “We Are Family” (If animals had theme songs, that is. Which for the record, I heartily endorse. I like what the sharks have done with theirs…). The social structure of the pack is much like that of wolves but much gentler. There is a tenderness to wild dog life, unlike anything I have ever seen. Like other pack animals, there is a strict hierarchy with the pack led by an alpha breeding pair. All other adults are subordinate to this couple. Only the alpha female will breed and can produce 10 to 12 puppies per litter — the most of any canid. However, the entire pack raises and cares for the puppies. While the puppies are small the pack will go off to hunt while some adults stay behind to protect the puppies in the den. After a successful hunt, the adults will return and regurgitate food to feed both the puppies AND the “babysitters.” When the pups are old enough to travel they will be escorted to a kill site and they are always the first to feed before any of the adults, even those that participated in the hunt. If an adult becomes ill, injured or elderly, and is unable to hunt, the other dogs will share food and take care of the ailing member. It is reported that the alpha female of a pack in Botswana lost one of her forelegs during a hunt. Normally, this would be a death sentence for a predator. Not for a wild dog — she remained the alpha female for a few more years continuing to breed and raise pups while being taken care of by the pack. (source)
Wild dogs are so team-oriented that they vote on whether to go on a hunt. Yes, really.
So how in the heck does that work?? Well, if a dog wants the team to get going to look for a meal s/he can sneeze to rally the pack to get going. However, voting is weighted depending on rank. If an alpha dog sneezes then only about three other “yea” votes are needed to launch a hunt. If a lower-ranked dog kicked off the voting, a hunt would not start unless about ten other sneezes were counted. (Source)
Wow, that is some bad-ass-African-plains-wild-dog democracy right there — definitely nothing to sneeze at. (the crowd moans…)
Until next month….m
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, f/4, 1/500 sec, ISO 1000, EV +1.0
01
Here are a few of my favorite images from 2018. These photos are not necessarily the best images I captured this year, but are ones that I like for one reason or another and/or give a good sense of the environments that I explored in the past 12 months.
I recommend viewing the photos on the biggest screen you have — click on an image to see it larger.
Drop me a line and let me know which one(s) you like best.
In no particular order:
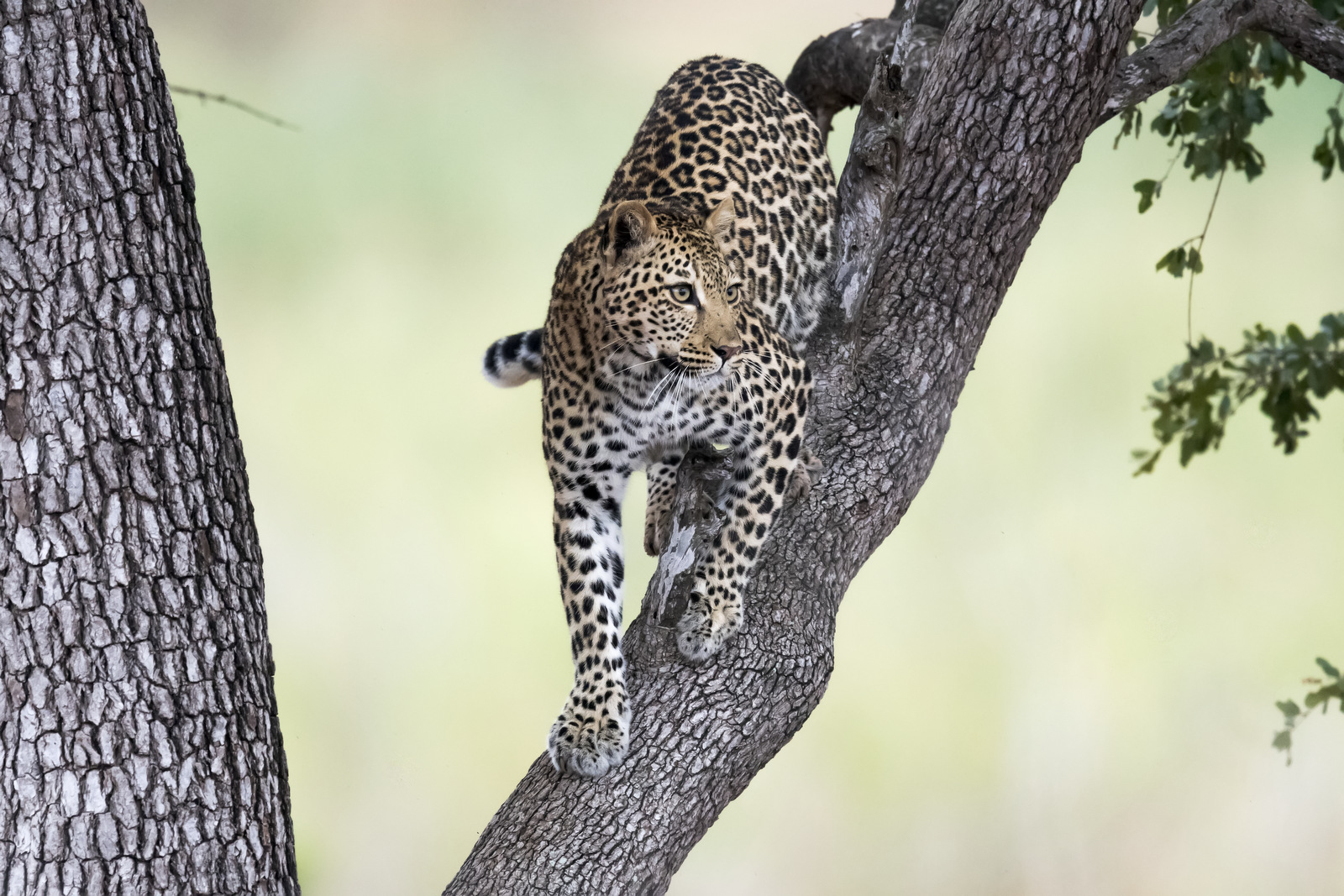
1. Leopard
Probably my favorite image from our visit to Kruger National Park. The vantage point of this shot makes it special.
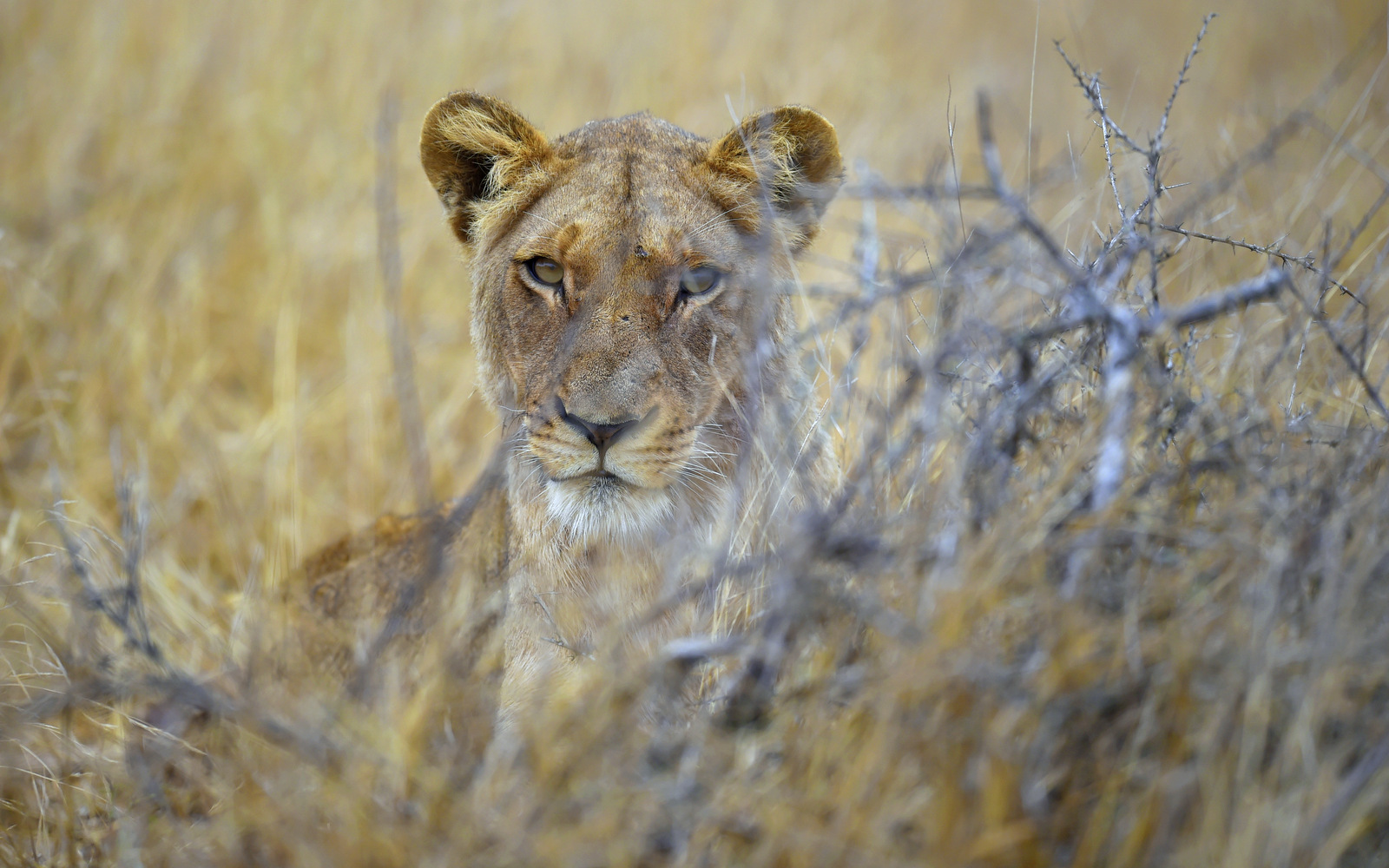
2. Lion
An ominous gaze from a female lion. Click on the image to see it larger and to get a good fright…
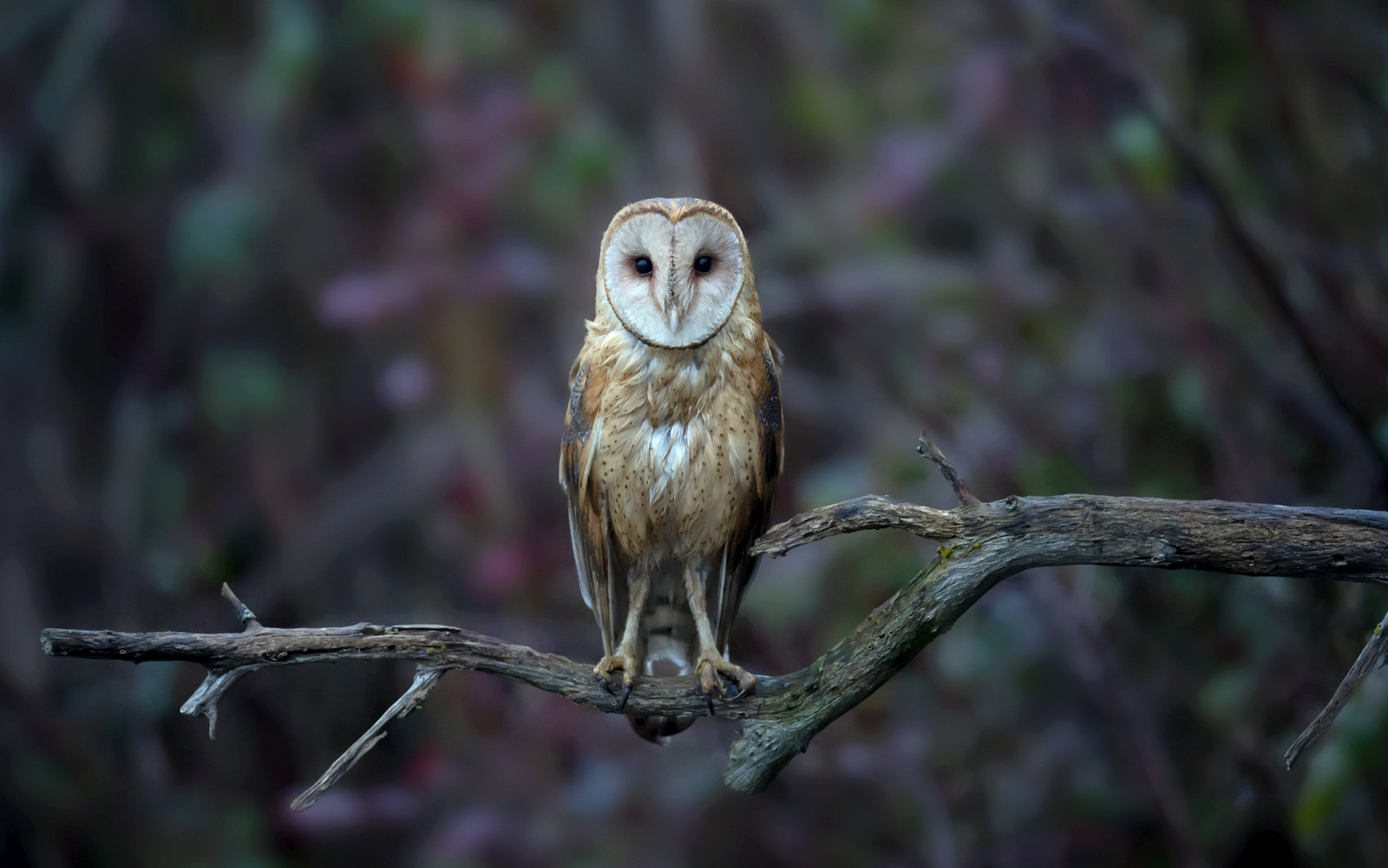
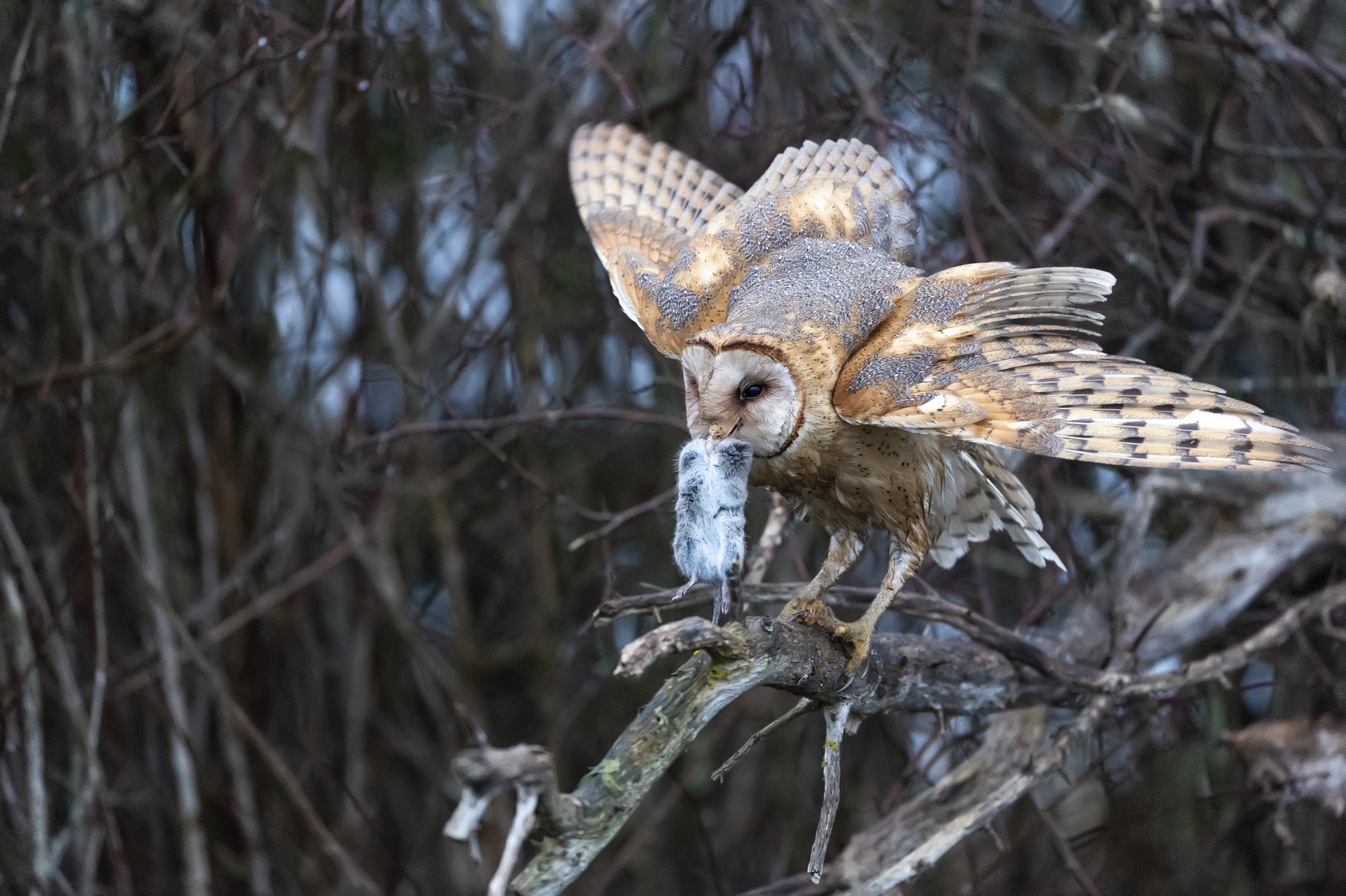
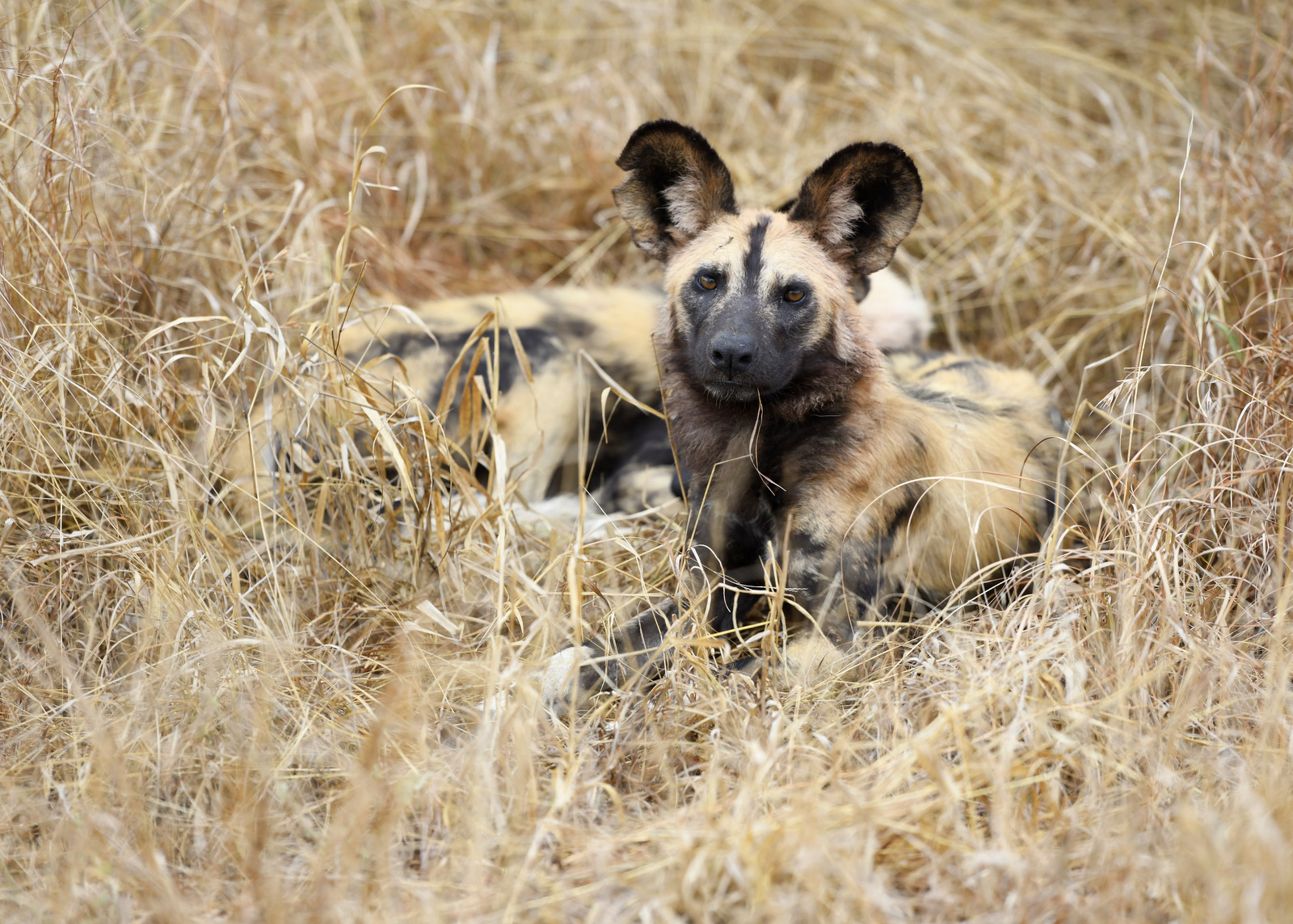
3. Wild Dog
My first decent image of a wild dog!
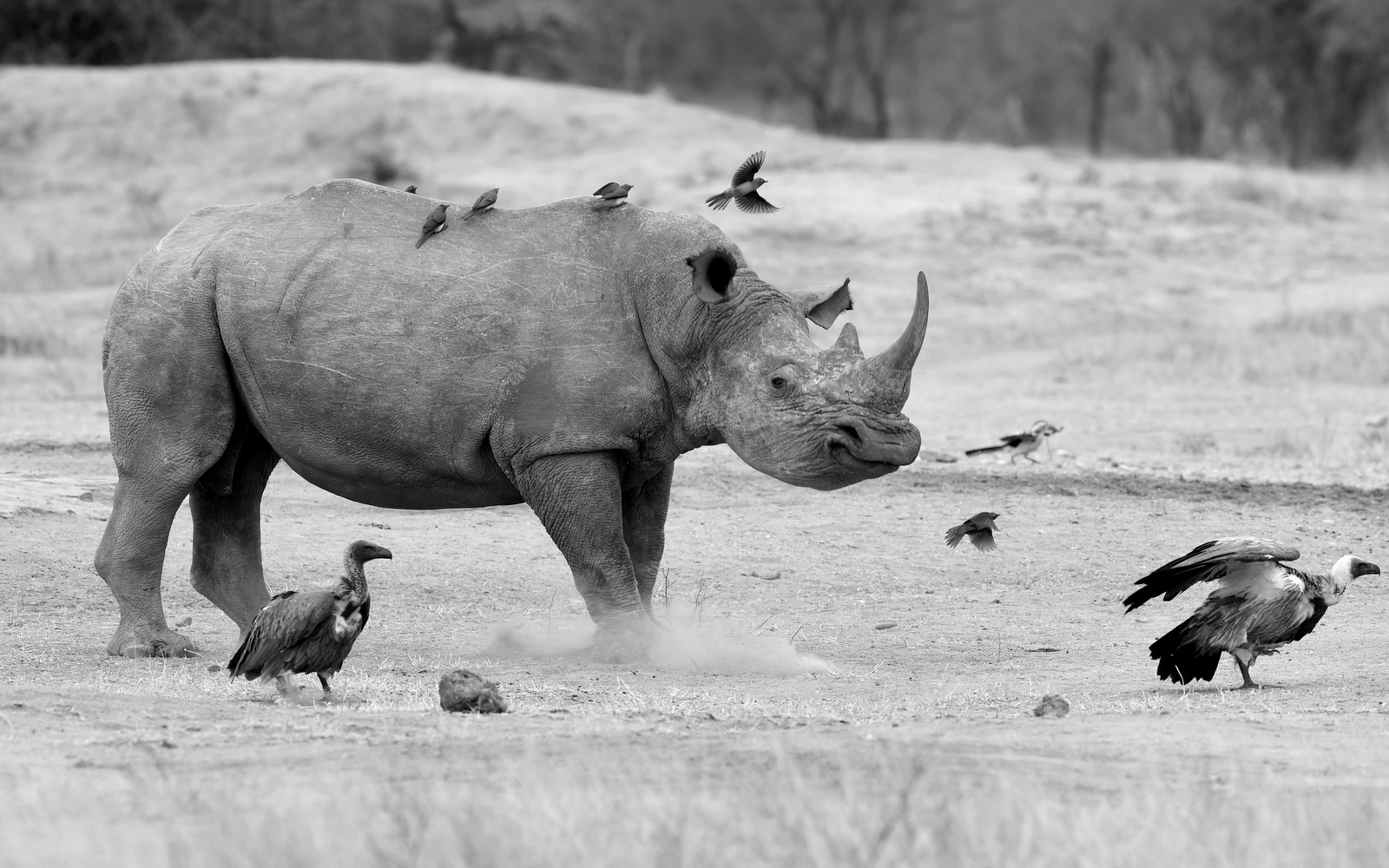
4. White Rhino
Seeing a rhino in the wild is a life-changing event. Click here to see my recent post to learn more about these amazing animals.
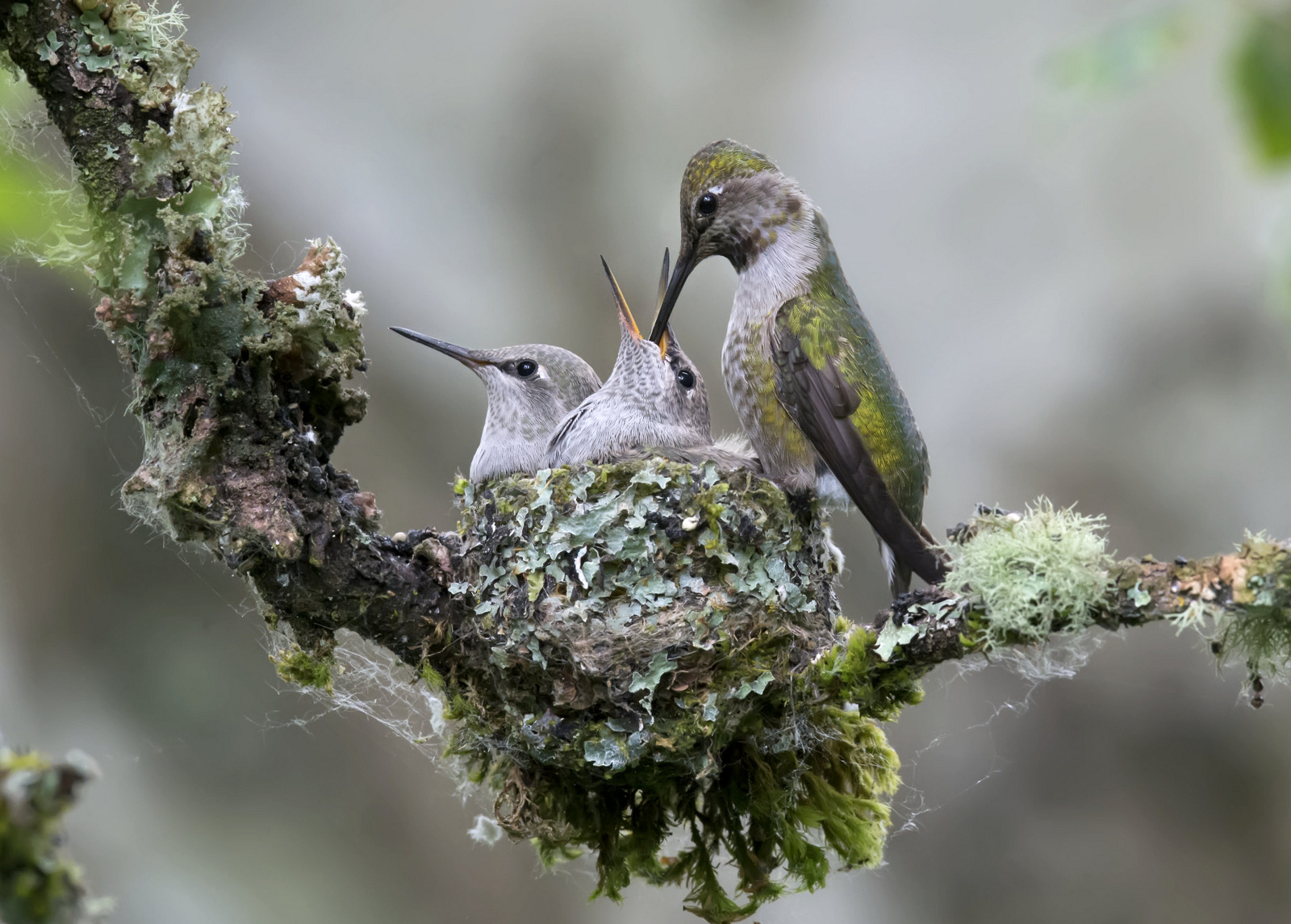
5. Anna’s Hummingbird
I spent three weeks this year watching these chicks grow up. Wow. Click here to see the entire story.
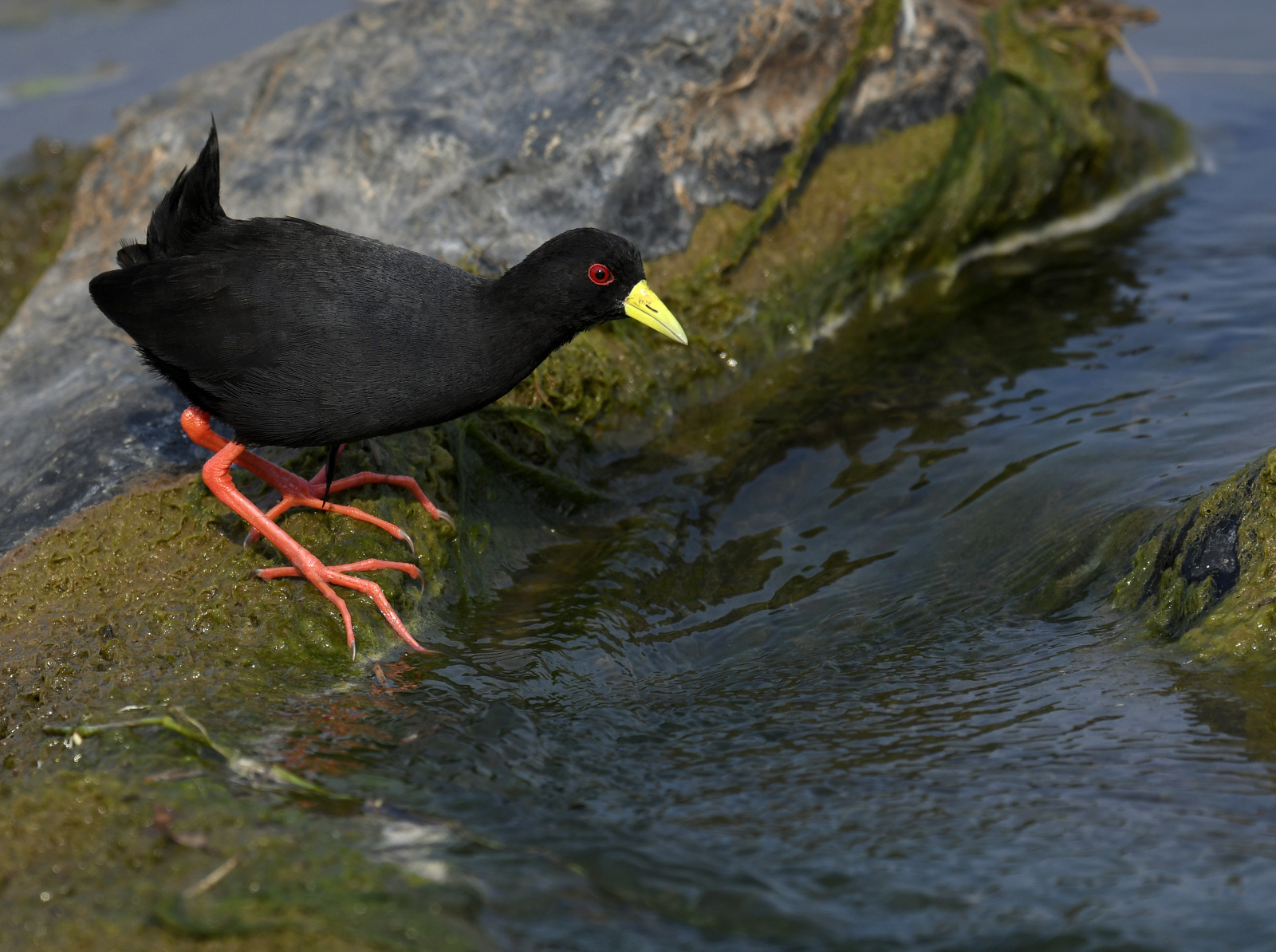
6. Black Crake
I found this guy in Kruger NP and shot hundreds of images of him over an hour as he explored every nook and cranny of the river. I had an absolute blast. I am mesmerized by his bold colors. And those feet!!
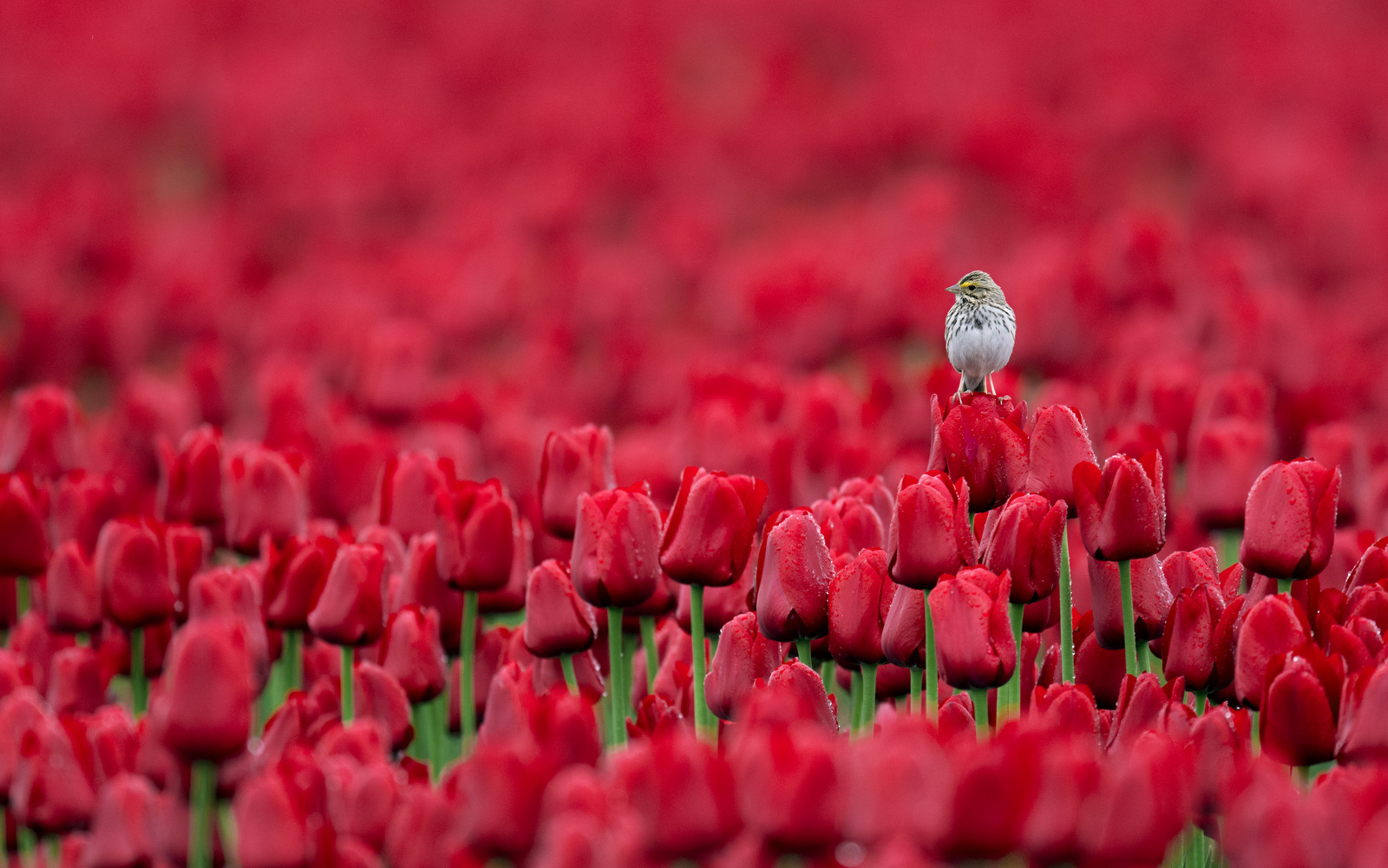
7. Birdscape
I made a first-time visit to some tulip fields in Washington in 2018 and I had the time of my life creating bold birdscapes like this one. Click here to see a few more.
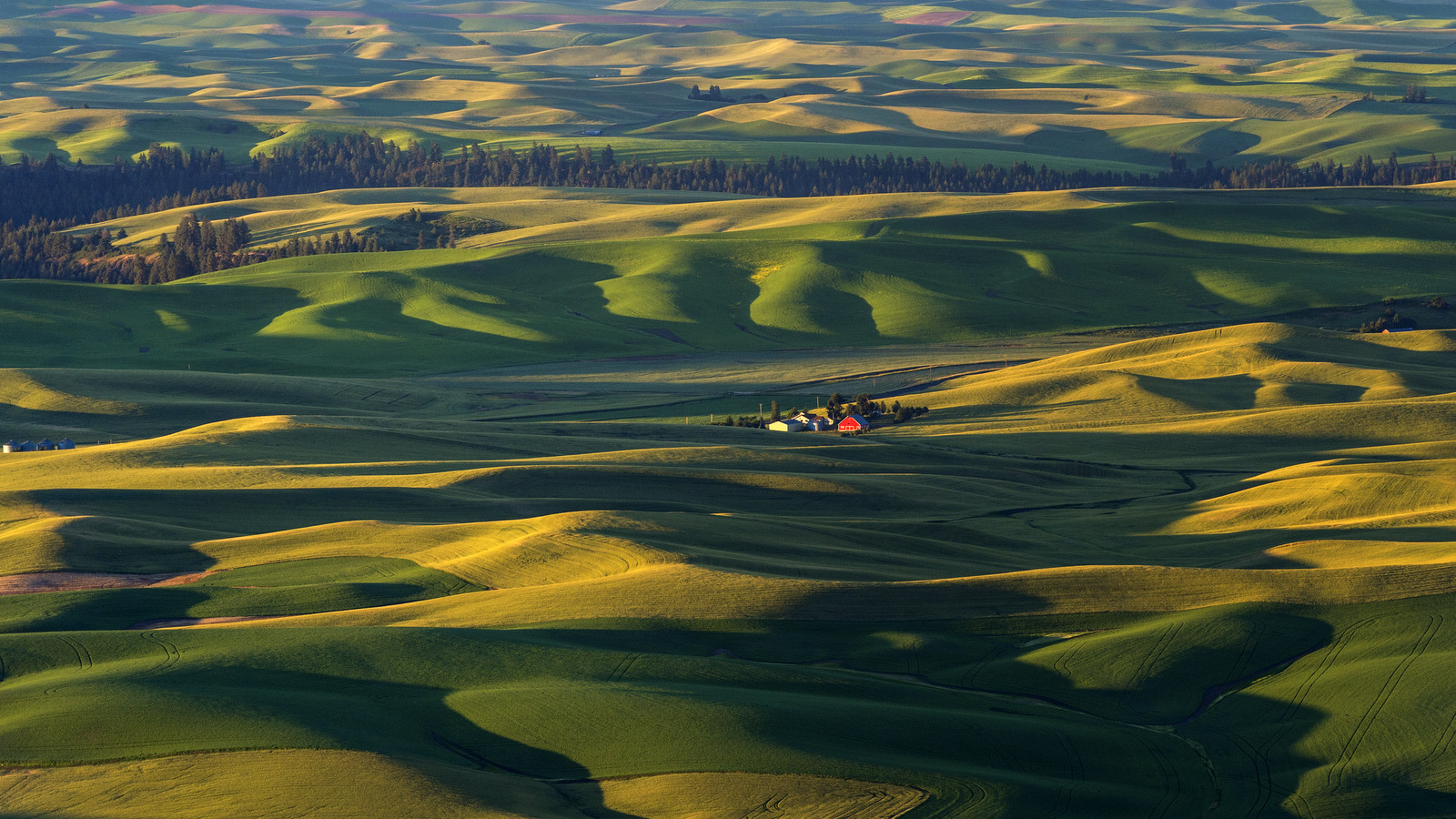
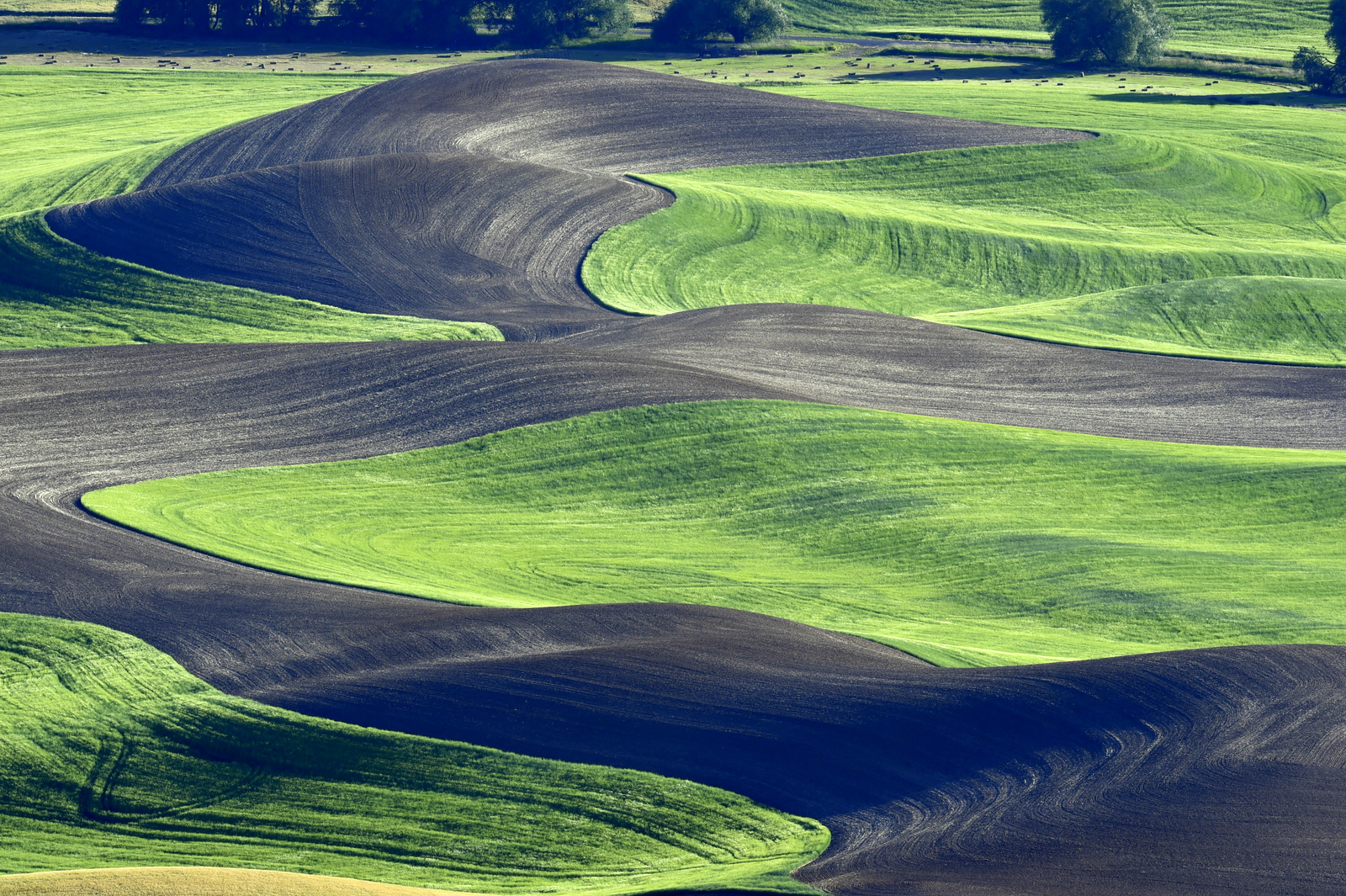
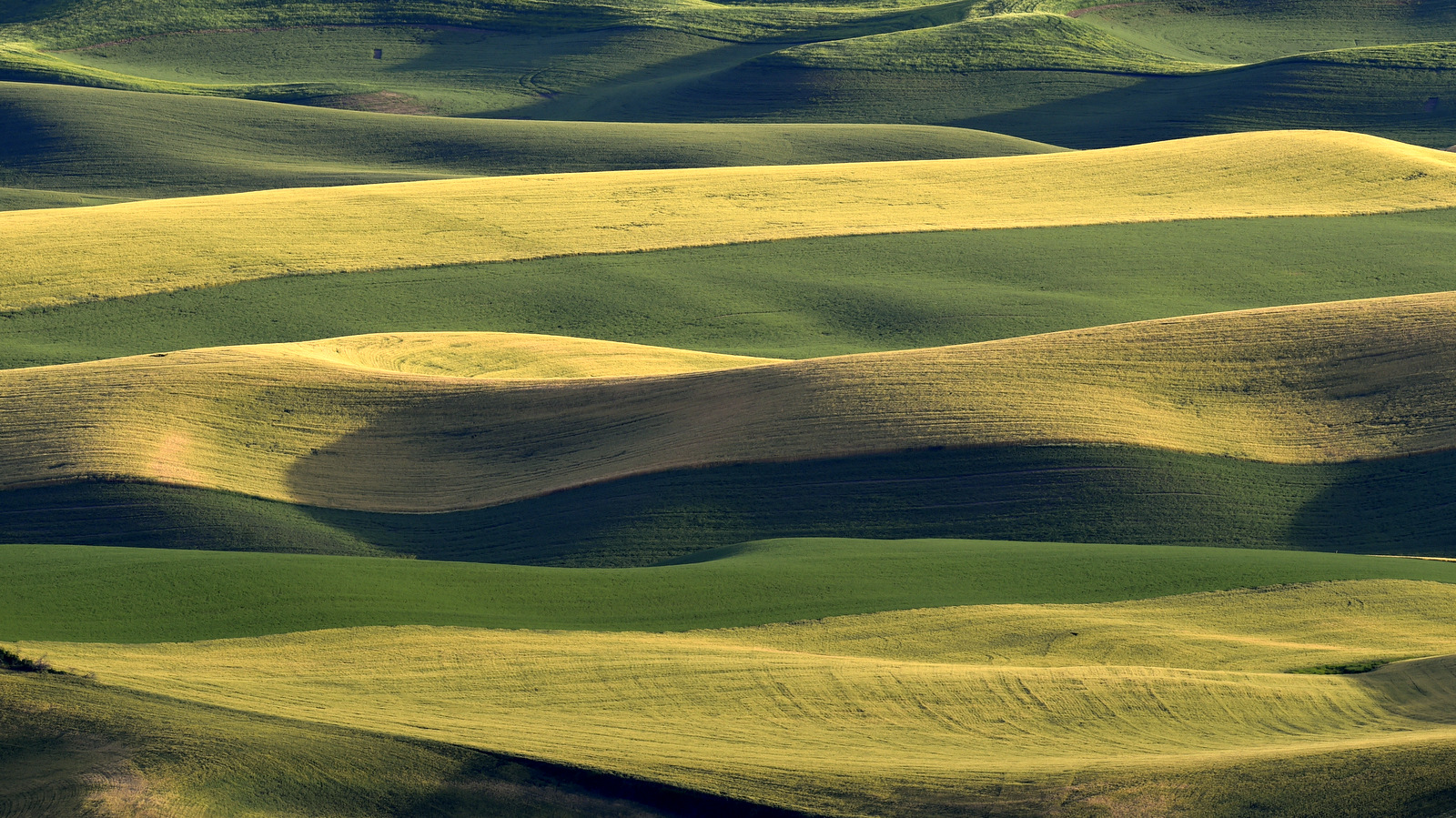
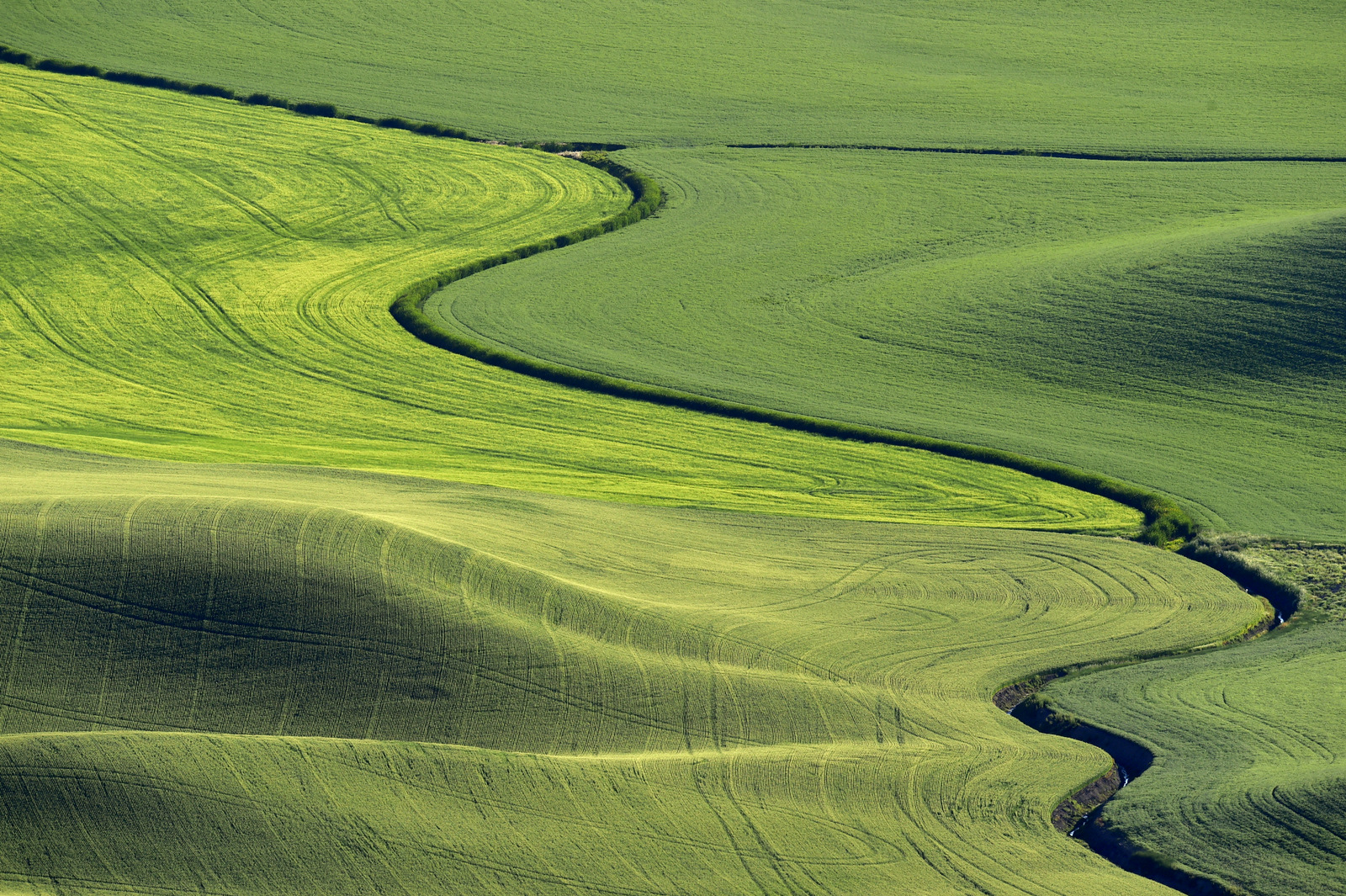
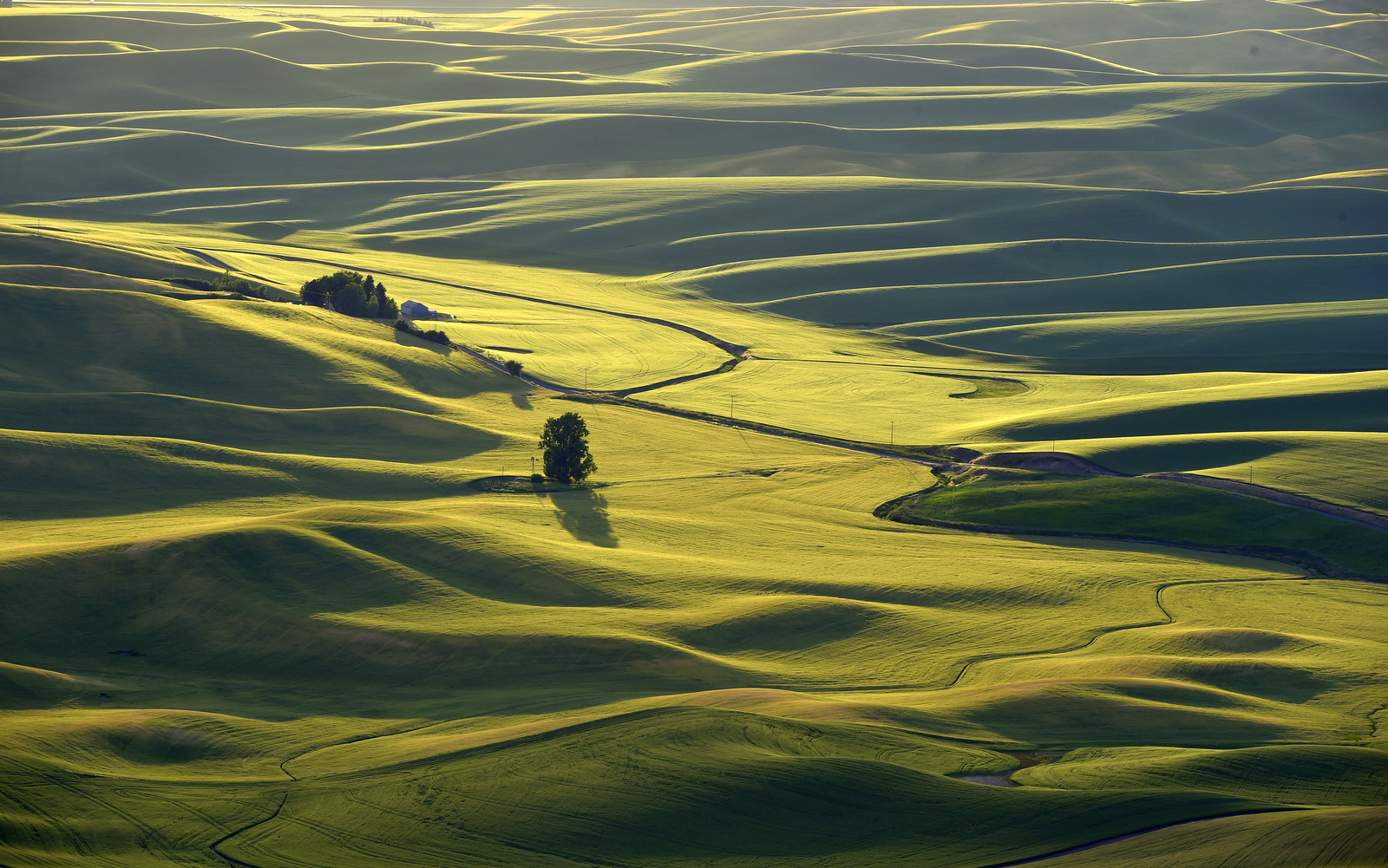
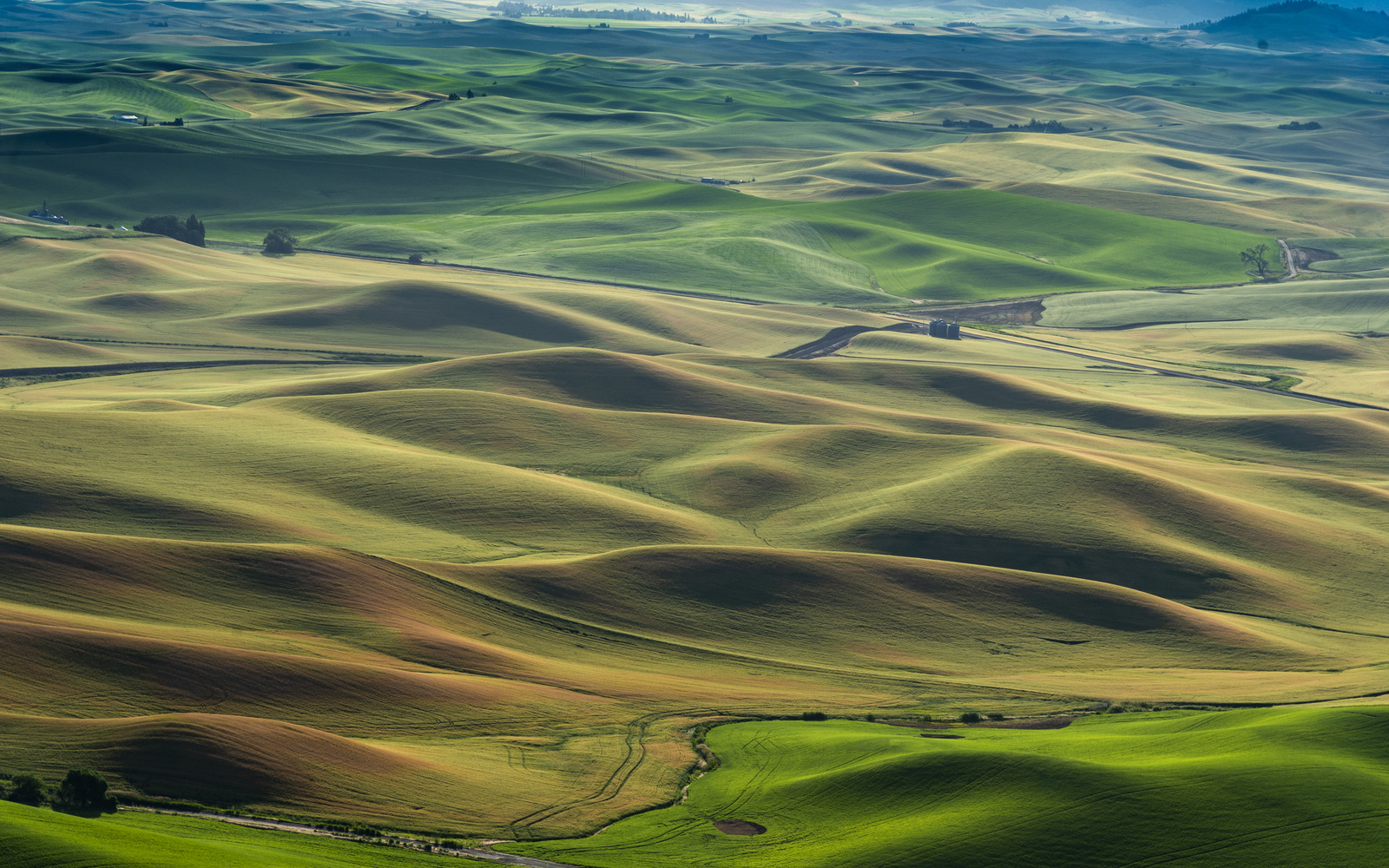
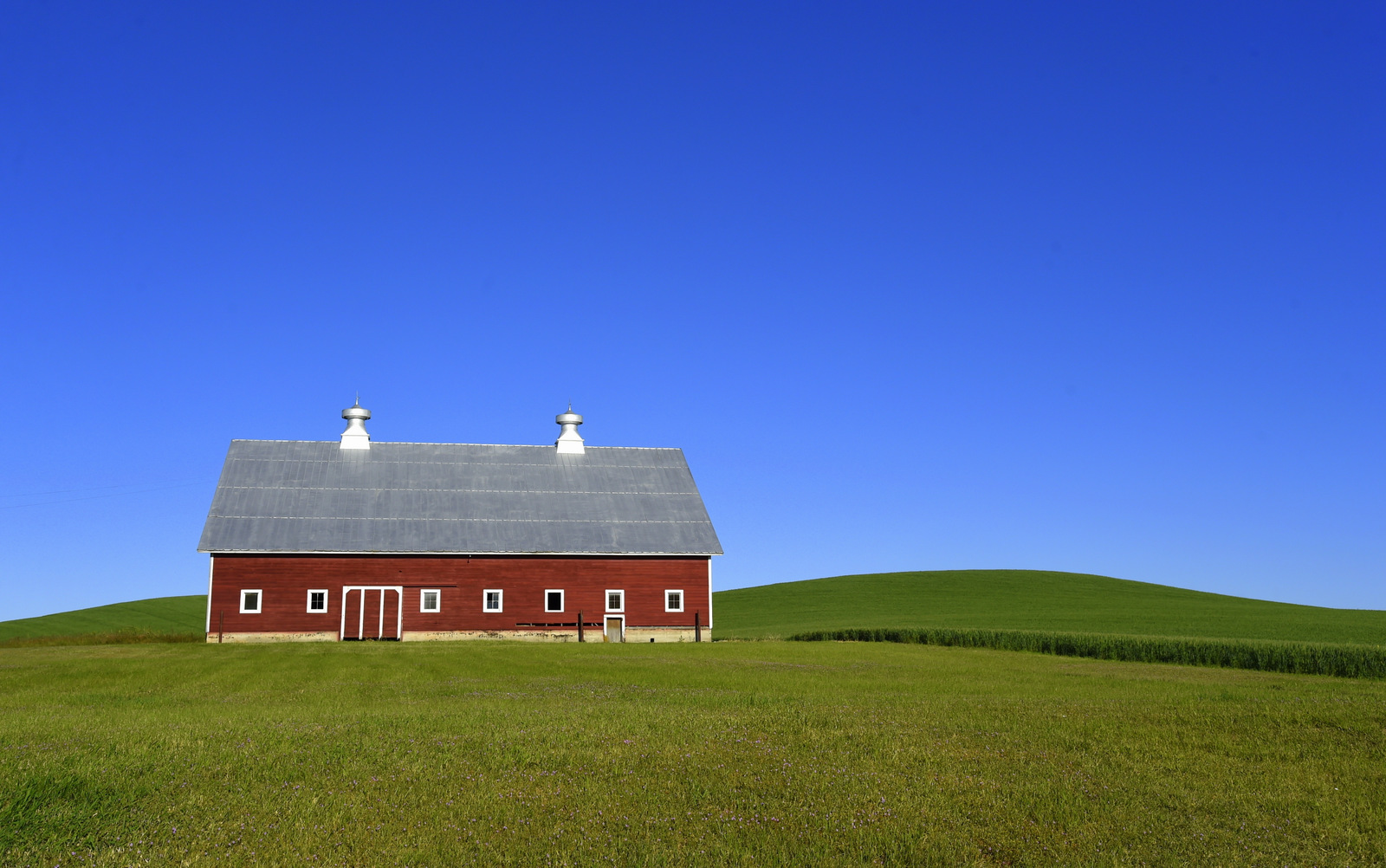
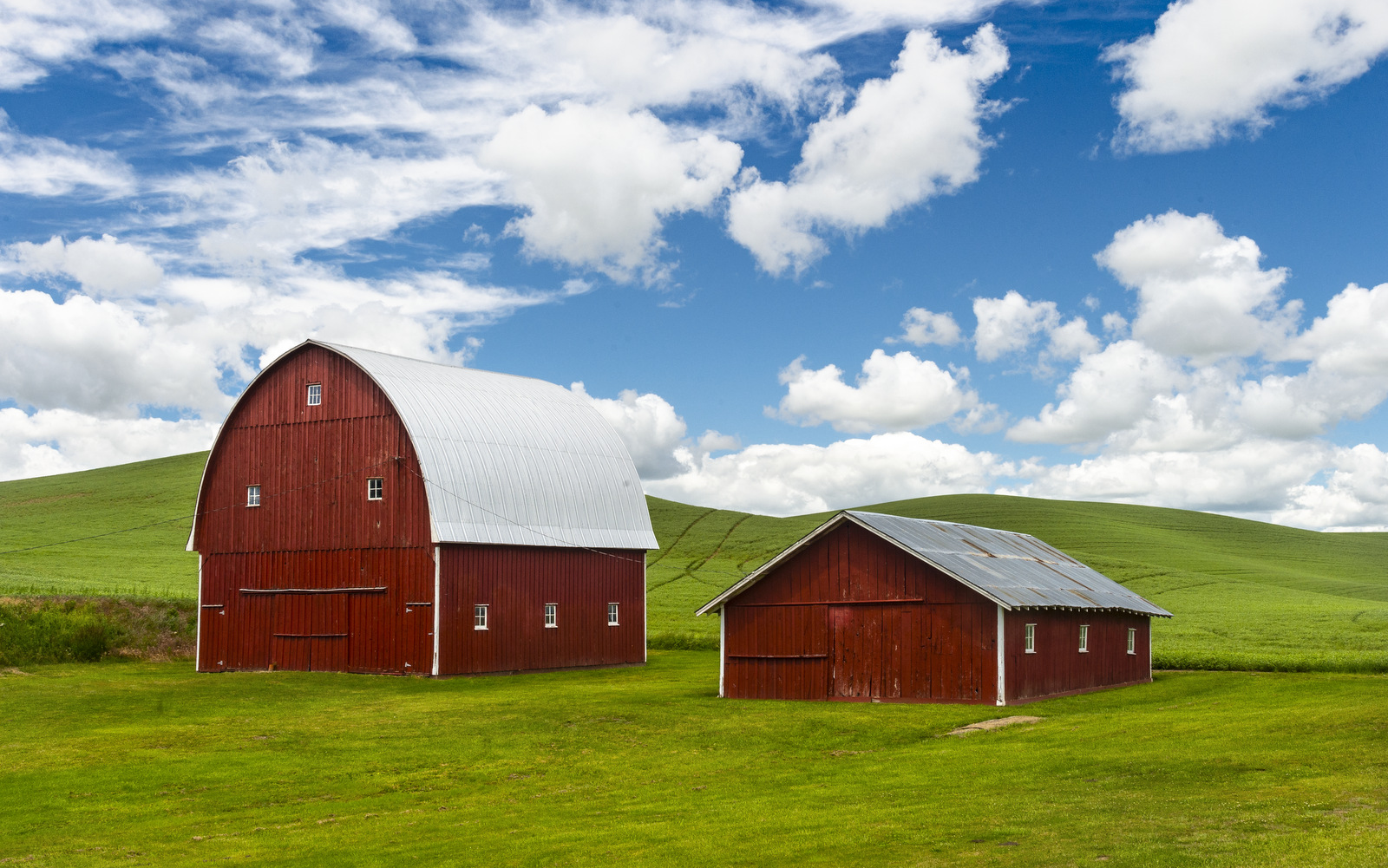
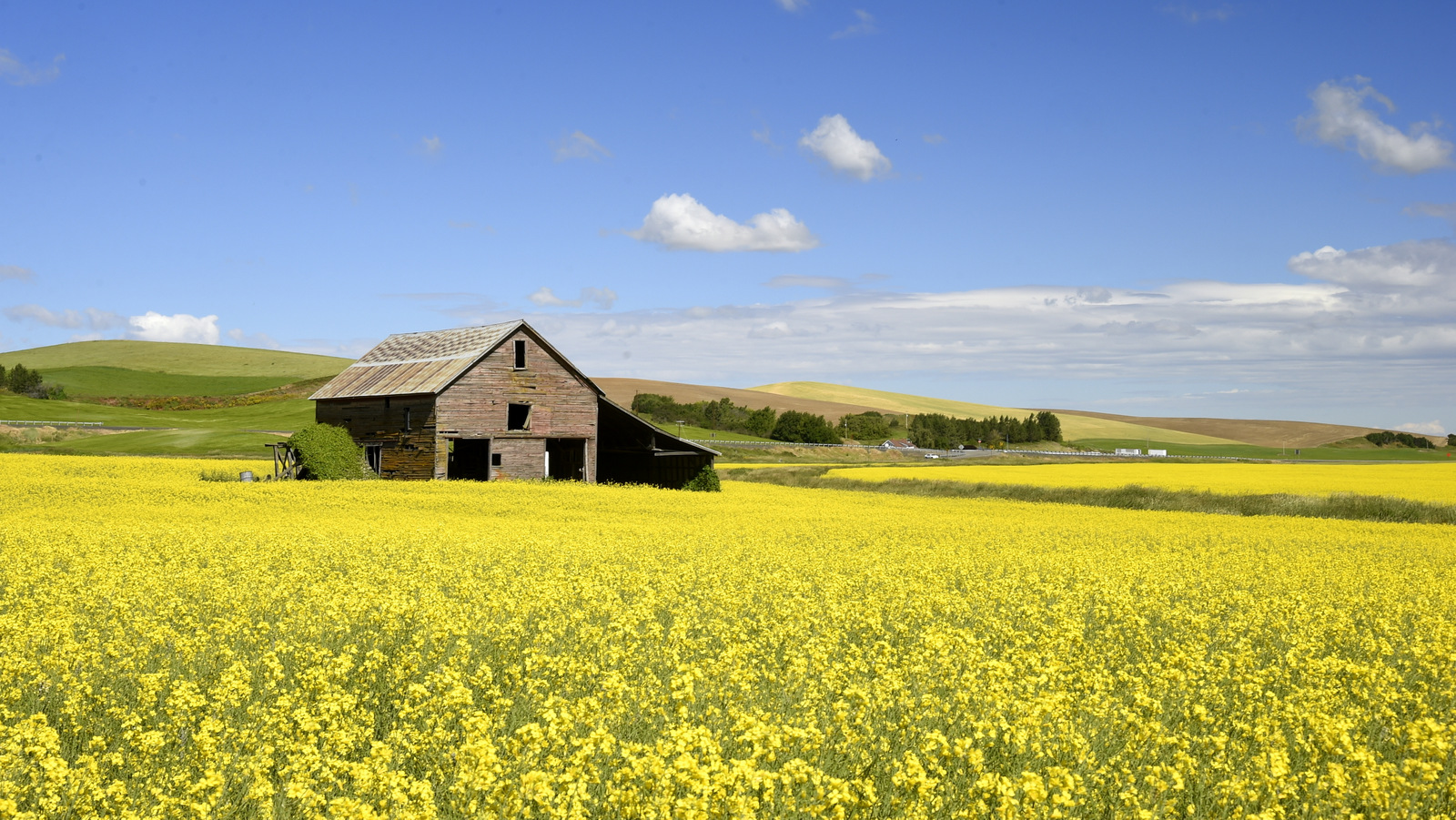
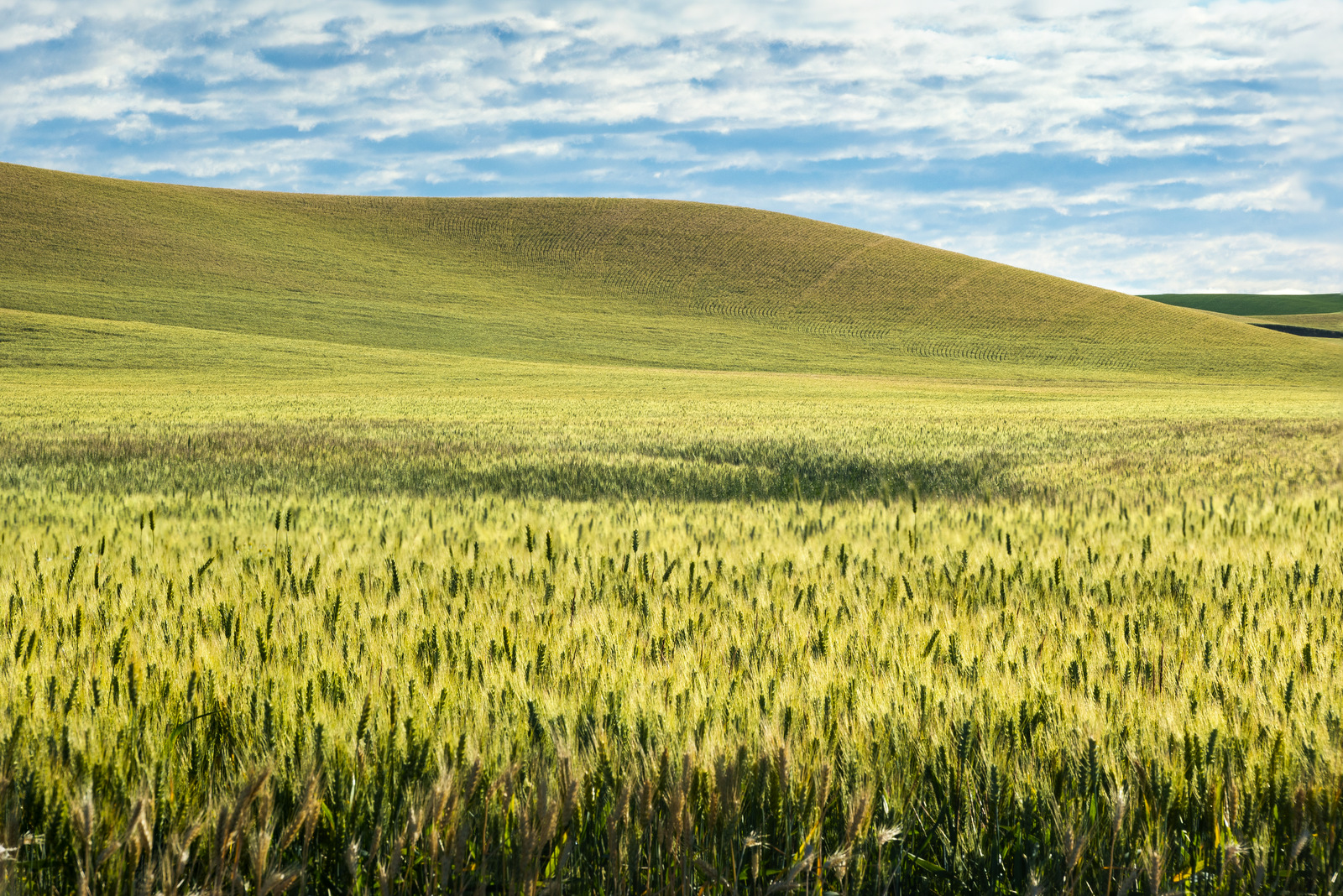
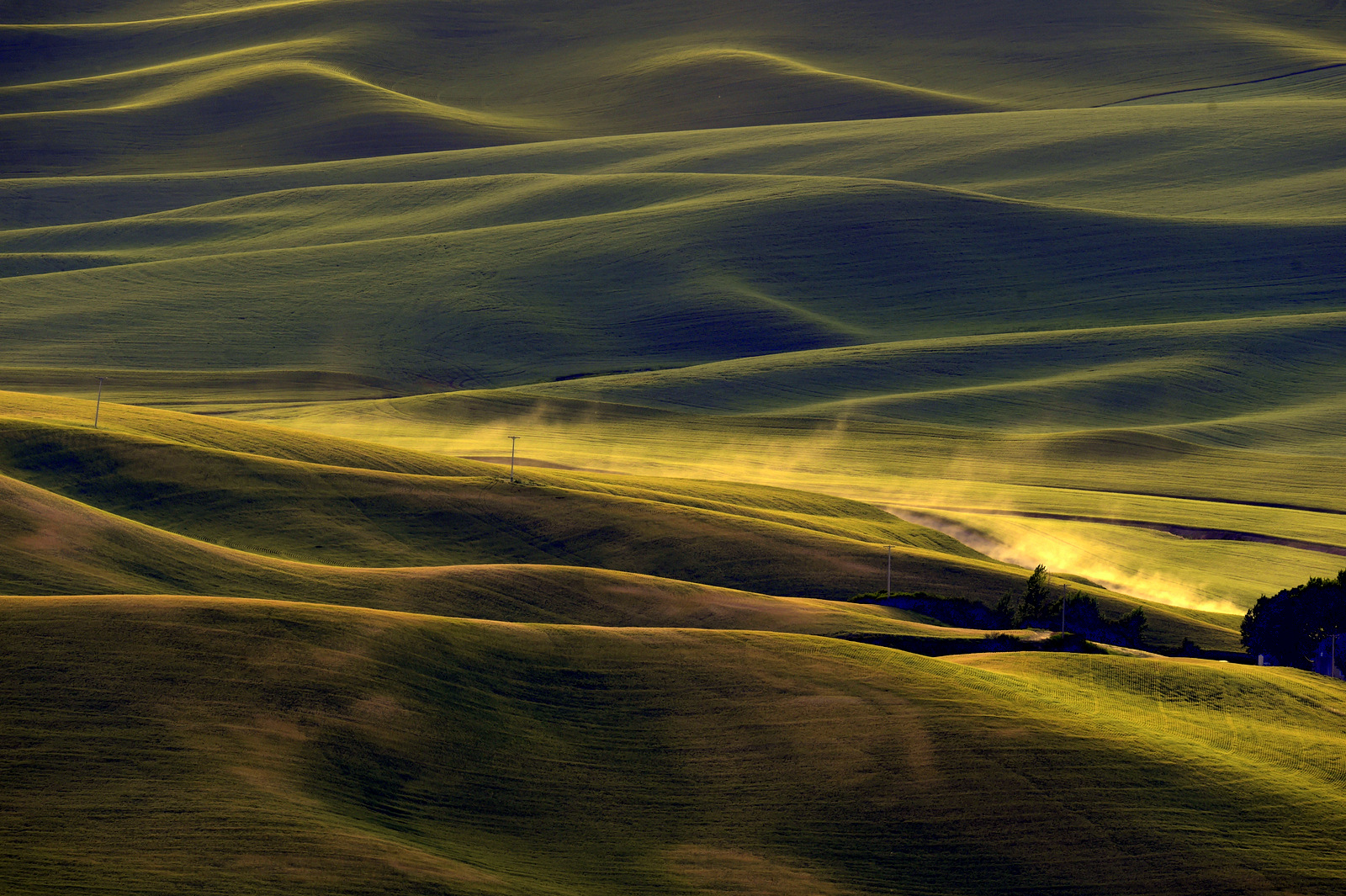
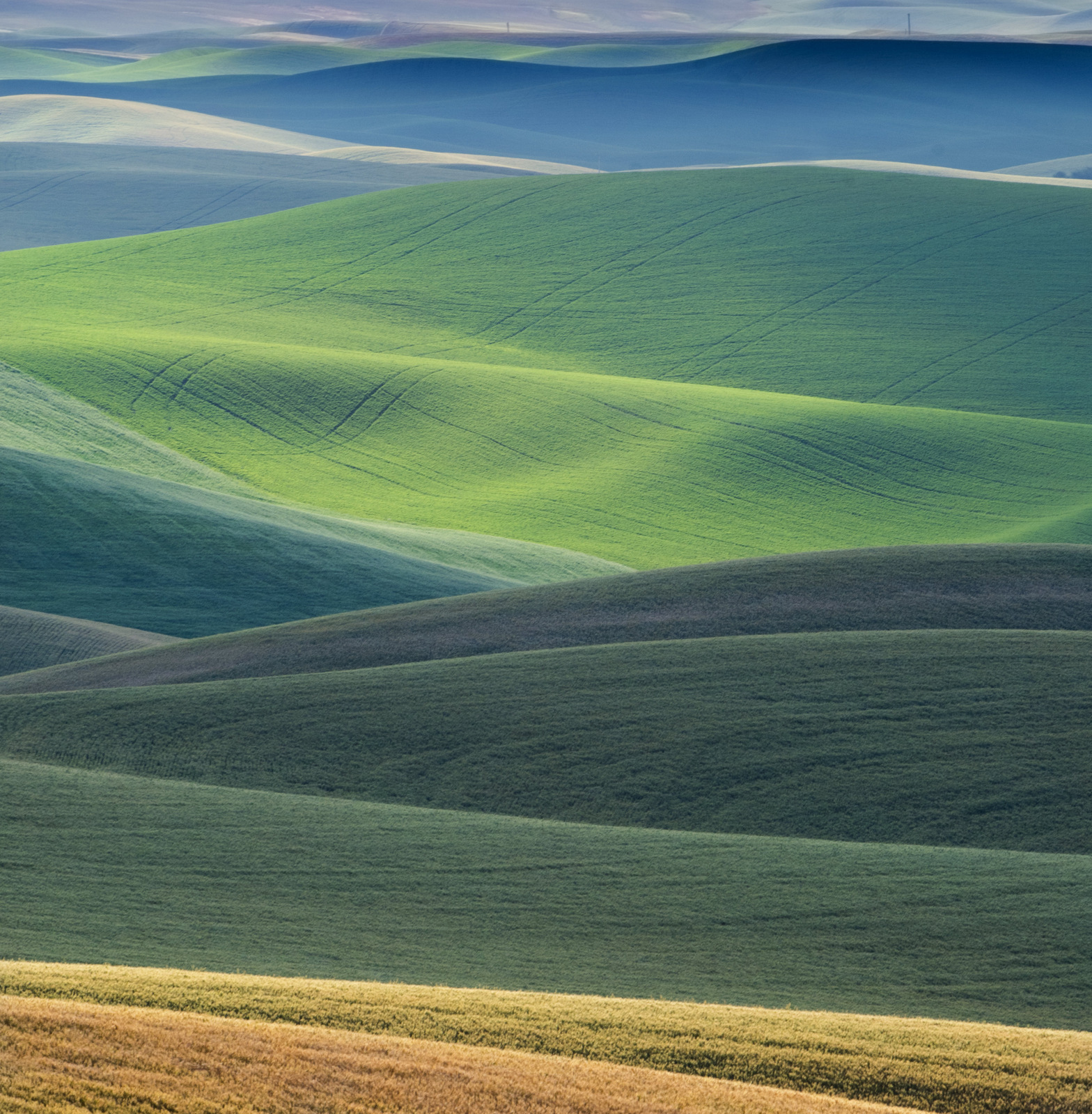
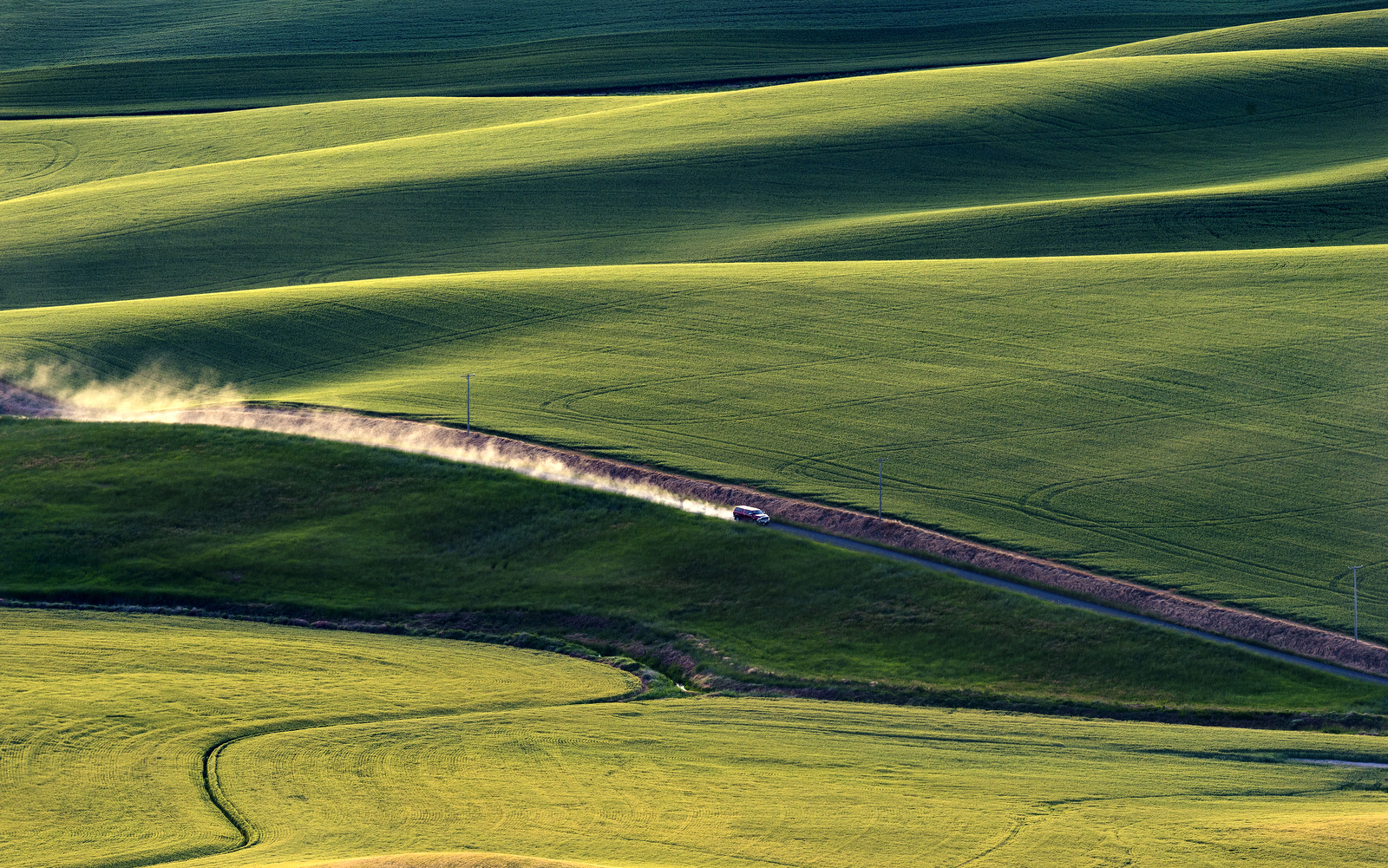
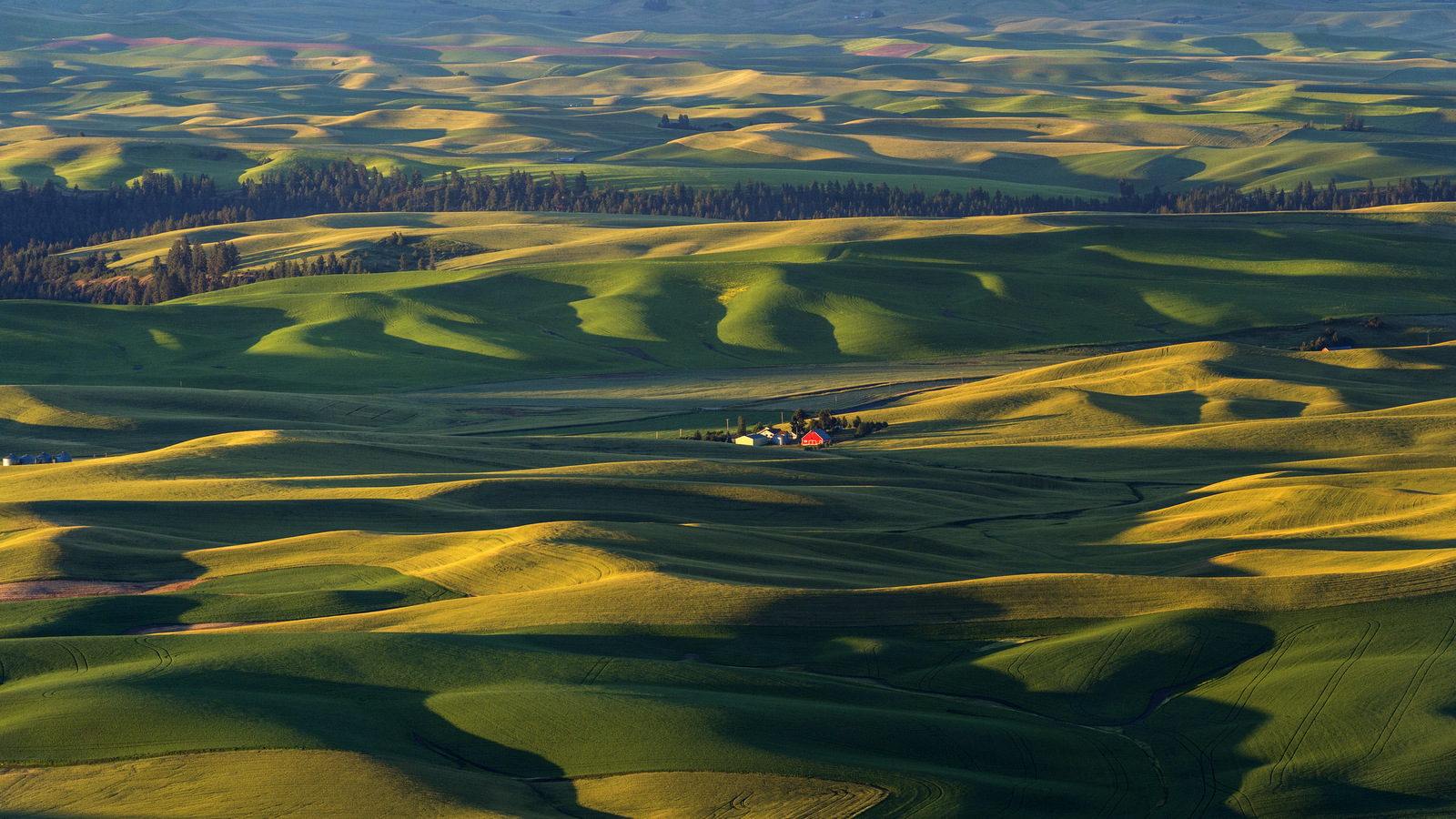
8. Palouse
I also explored the farmlands of the Palouse in eastern Washington for the first time in 2018. Heaven on earth for landscape photographers…
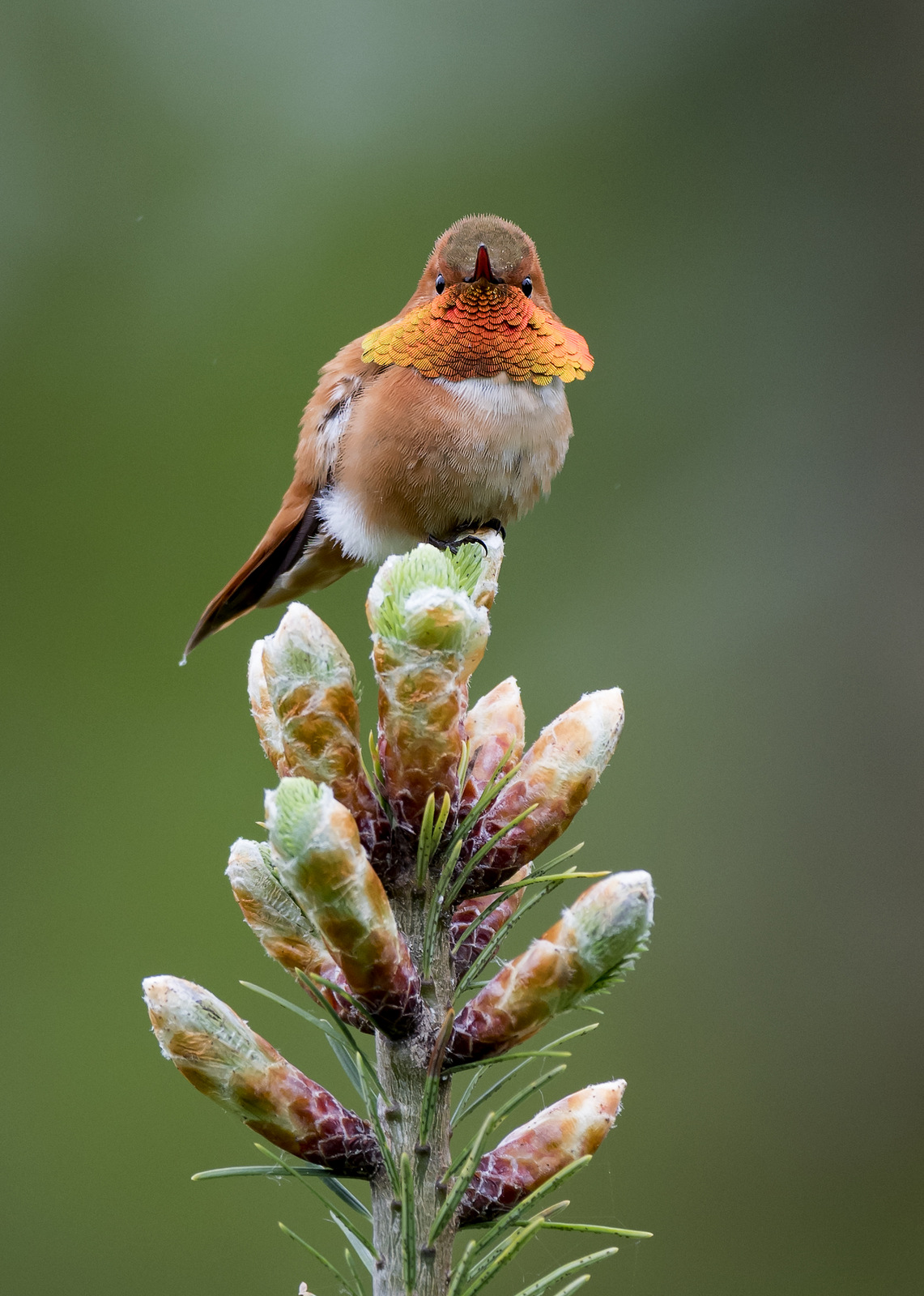
9. Rufous Hummingbird
My first image of a male Rufous Hummingbird in all his iridescent glory.
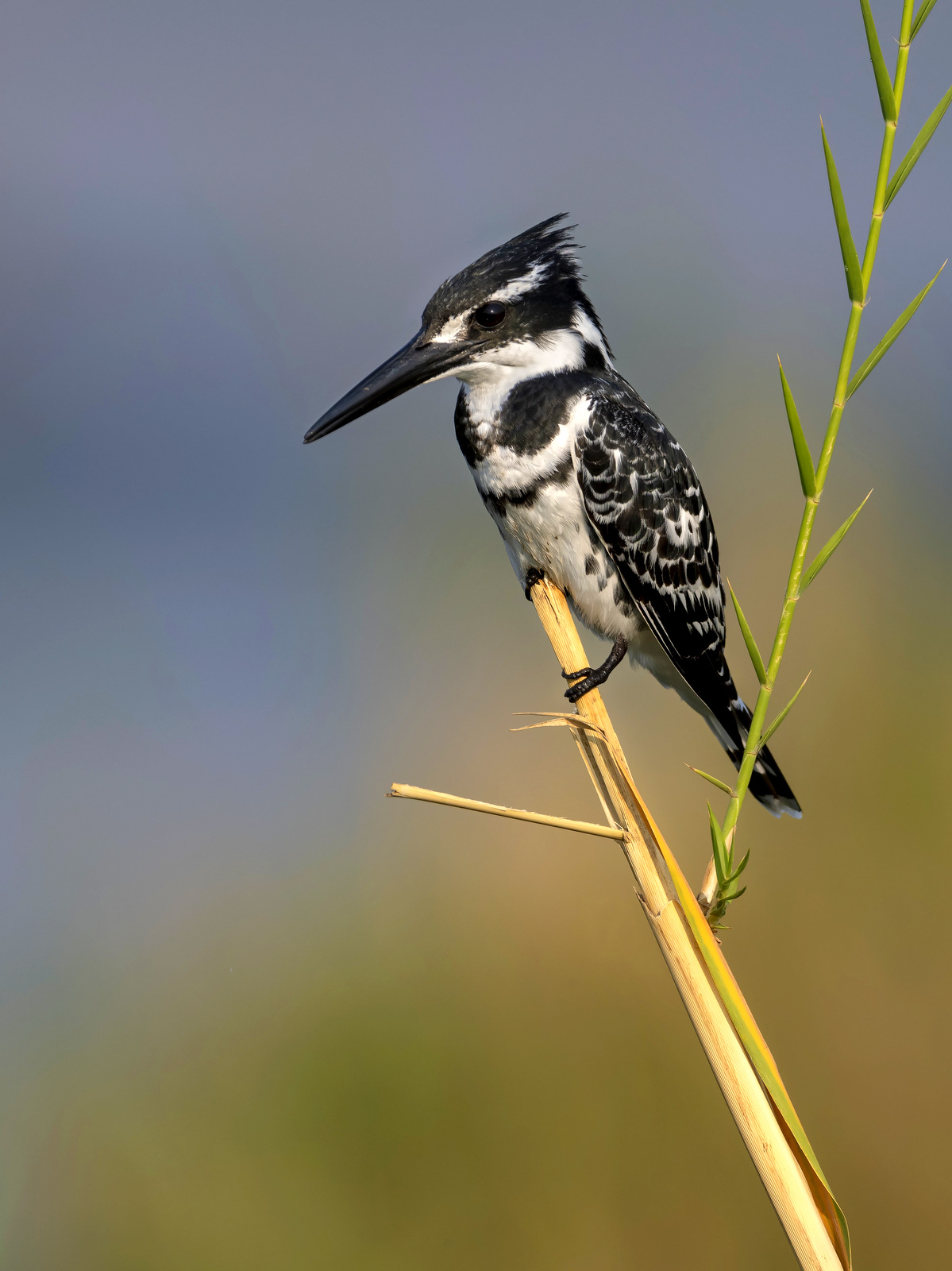
10. Pied Kingfisher
My first decent image of a Pied Kingfisher. Nabbed this guy in Kruger, NP.
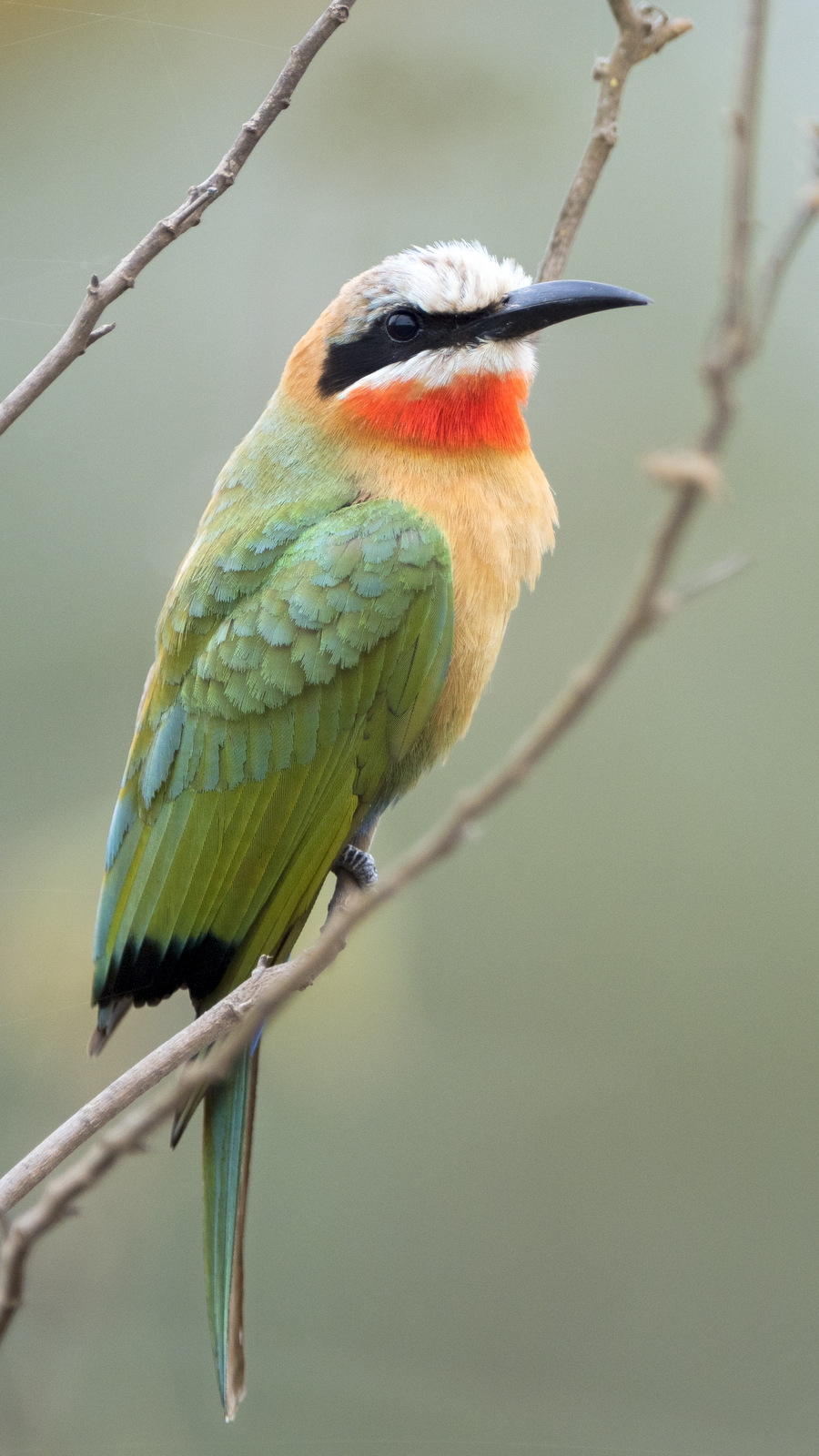
11. White-fronted Bee-eater
And my first image of this lovely bee-eater. Another gift from Kruger NP.
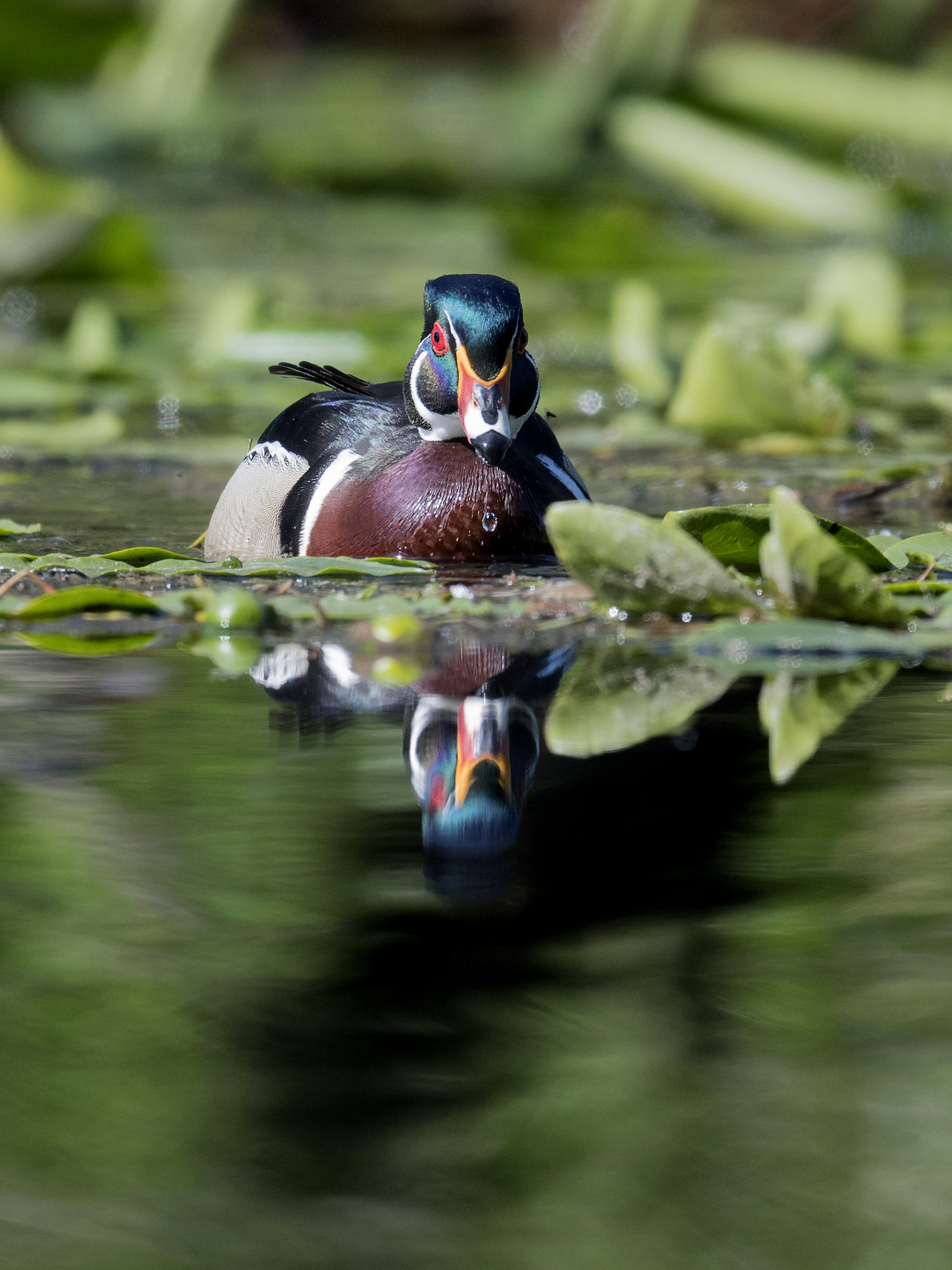
12. Wood Duck!
I have been trying to get a photo of a wood duck for years. Finally….
Ok, so that was 12 images — hope you don’t mind.
Wishing you a wonderful 2019!
31
Shot of the Month – December 2018
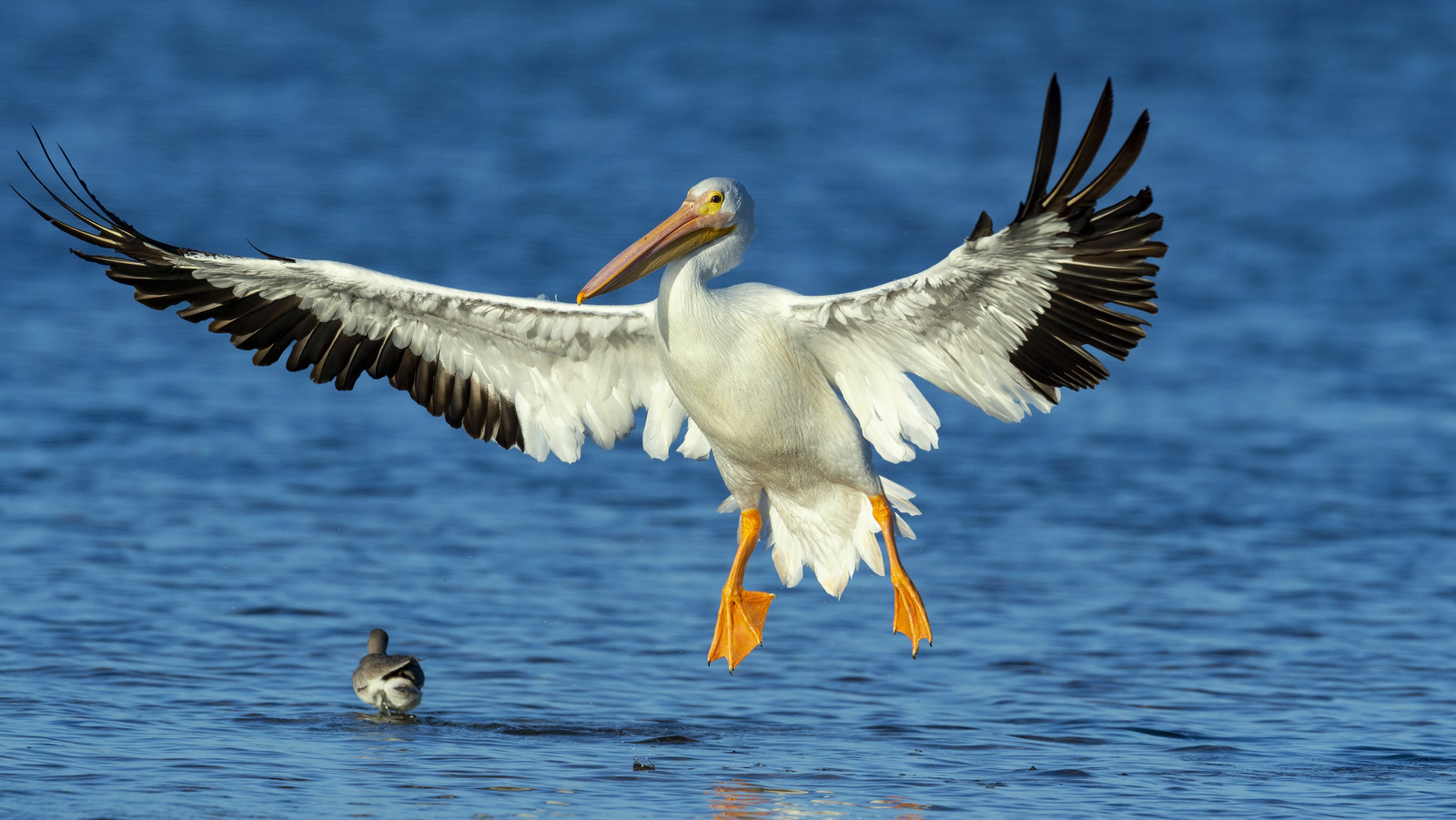
In North America, a snowbird is a slang term used to describe someone (often a retiree) who migrates each winter from his northerly, typically very cold home state to spend the winter in a warmer state like Florida or Arizona. While living in Vermont – a very northerly, and VERY coldly state in the winter, we adopted some sunbird-esque habits and spent Christmas visiting family in Florida two years in a row. These trips allowed me the opportunity to photograph a range of wildlife in Ding Darling Nature Reserve. During one outing I captured a photo of a big bird — not THE Big Bird, but his cousin, the American White Pelican (AWP).
How big? Well, the AWP has a nine-foot wingspan, which you can see in all its glory in the image above. A male can stand almost 4 feet tall and can weigh thirty pounds! That massive bill can add almost another 2 feet to the length of this bird. These Goliaths are among the heaviest flying birds in the world. Despite their size, those massive wings allow the pelican to excel at soaring and they can be seen traveling long distances in V-formation.
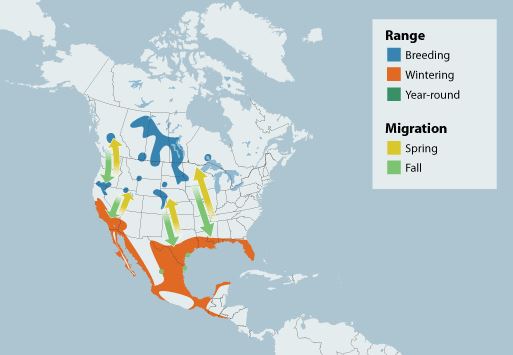
These birds breed and spend the warmer months in the heart of northern North America and spend the colder months in warmer locales as you can see in this range map.
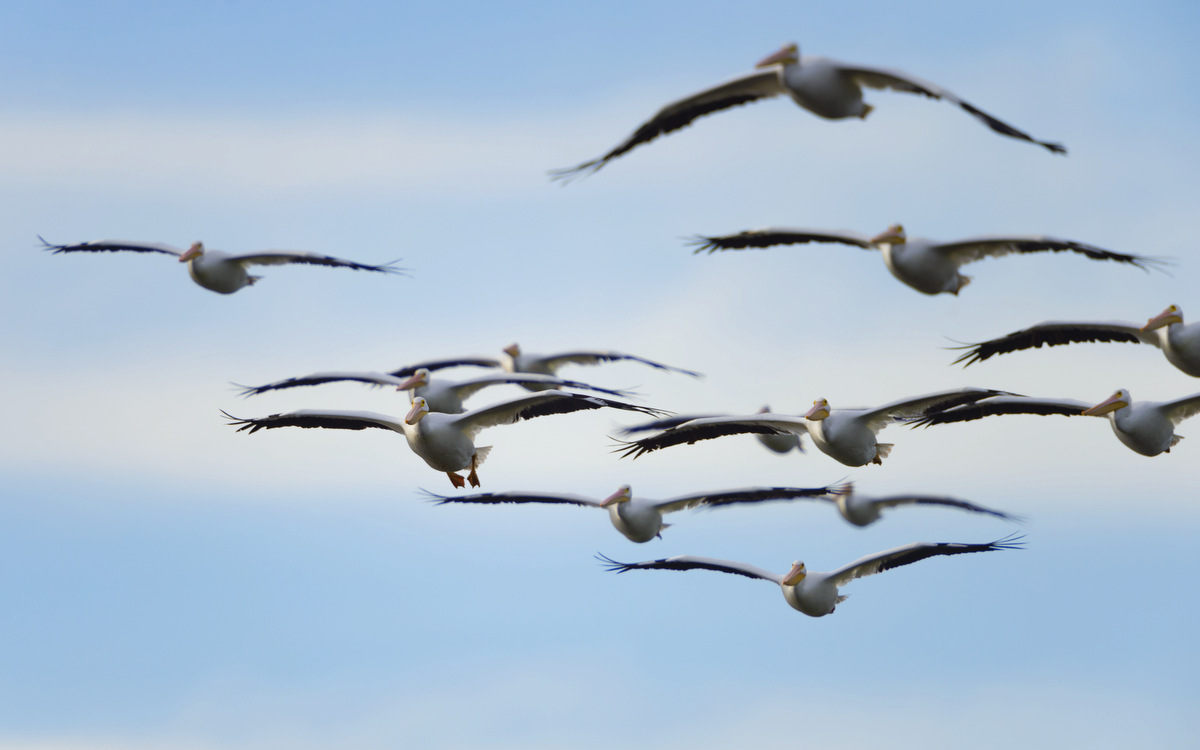
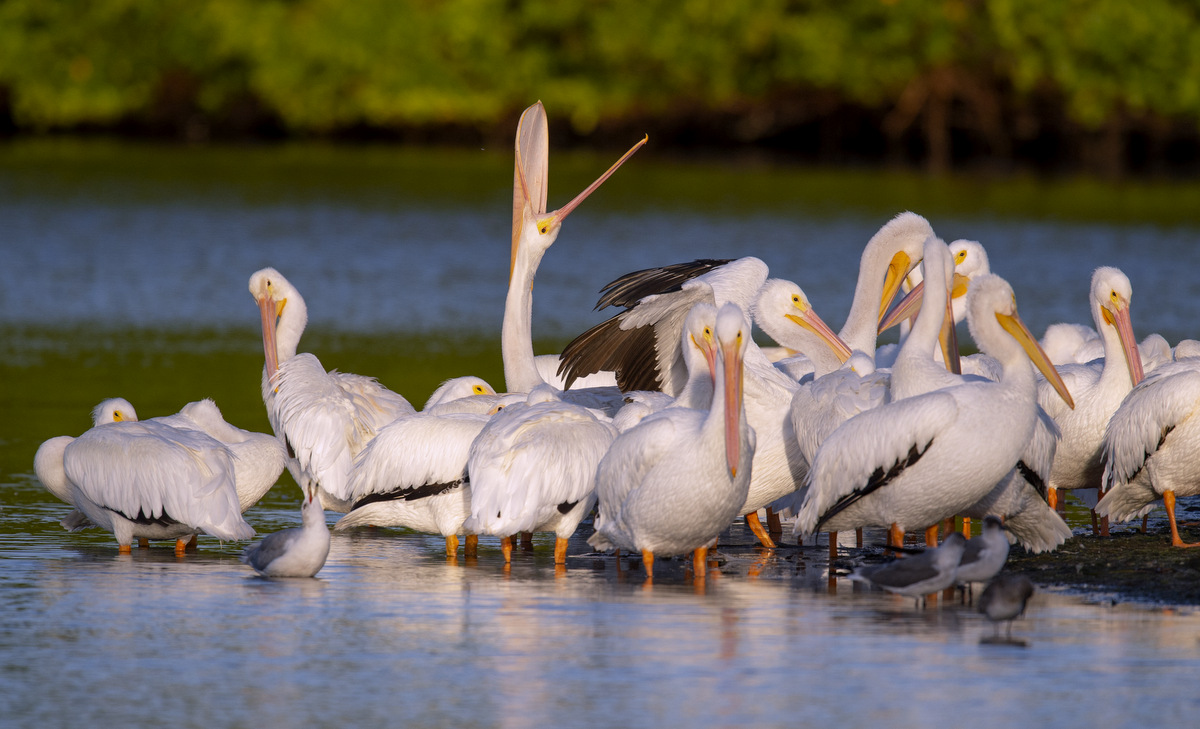
The AWP is very gregarious and they often travel and forage in large flocks. Some pelican species plunge-dive to catch their prey — not these guys. The AWP feeds from the water’s surface, dipping their beaks into the water to catch fish and other prey. The birds will often work together to corral fish to one another. Sometimes a group of birds will dip their bills into the water together and flap their wings to drive fish toward the shore where the water is shallow. This then allows for a very efficient, collective feast.
The American White Pelican can eat up to four pounds of food a day with fish (carp, Tuie chub, shiners, perch, rainbow trout, jackfish, catfish, etc.) being the preferred meal. The AWP is not above theft, known as kleptoparasitism in the animal world, to catch a meal and they can often be seen stealing fish from other pelicans, gulls, and cormorants.
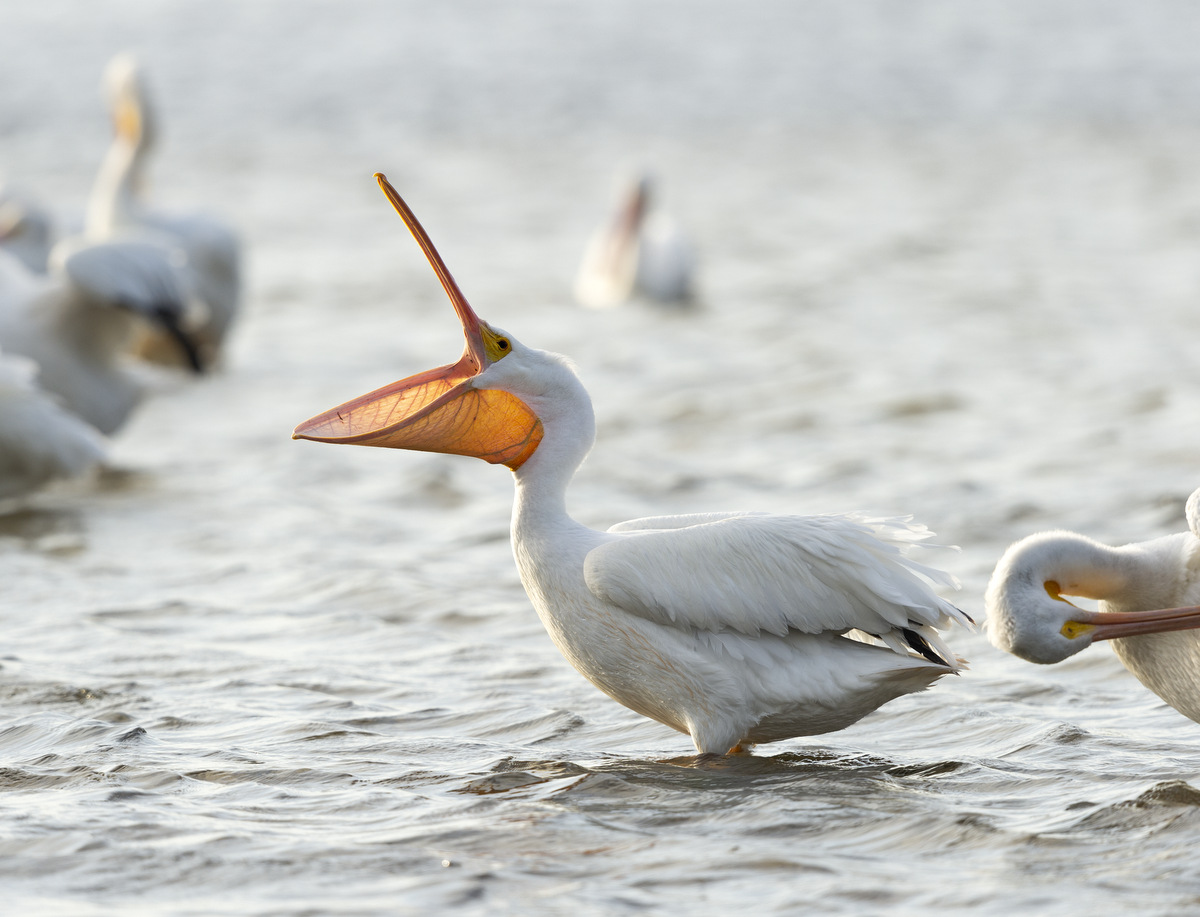
Once a fish, or two, has been caught the pelican will raise its bill to drain the water and swallow the prey.
Gregarious, larger than life, a healthy appetite, and seasonal migrations — it sounds like this pelican might be a subspecies of snowbird. If you get my drift….. 😉
Until next month…
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, 1.4X TC (effective 850 mm), 1/2500 sec, ISO 400, -1 EV
30
Shot of the Month – November 2018
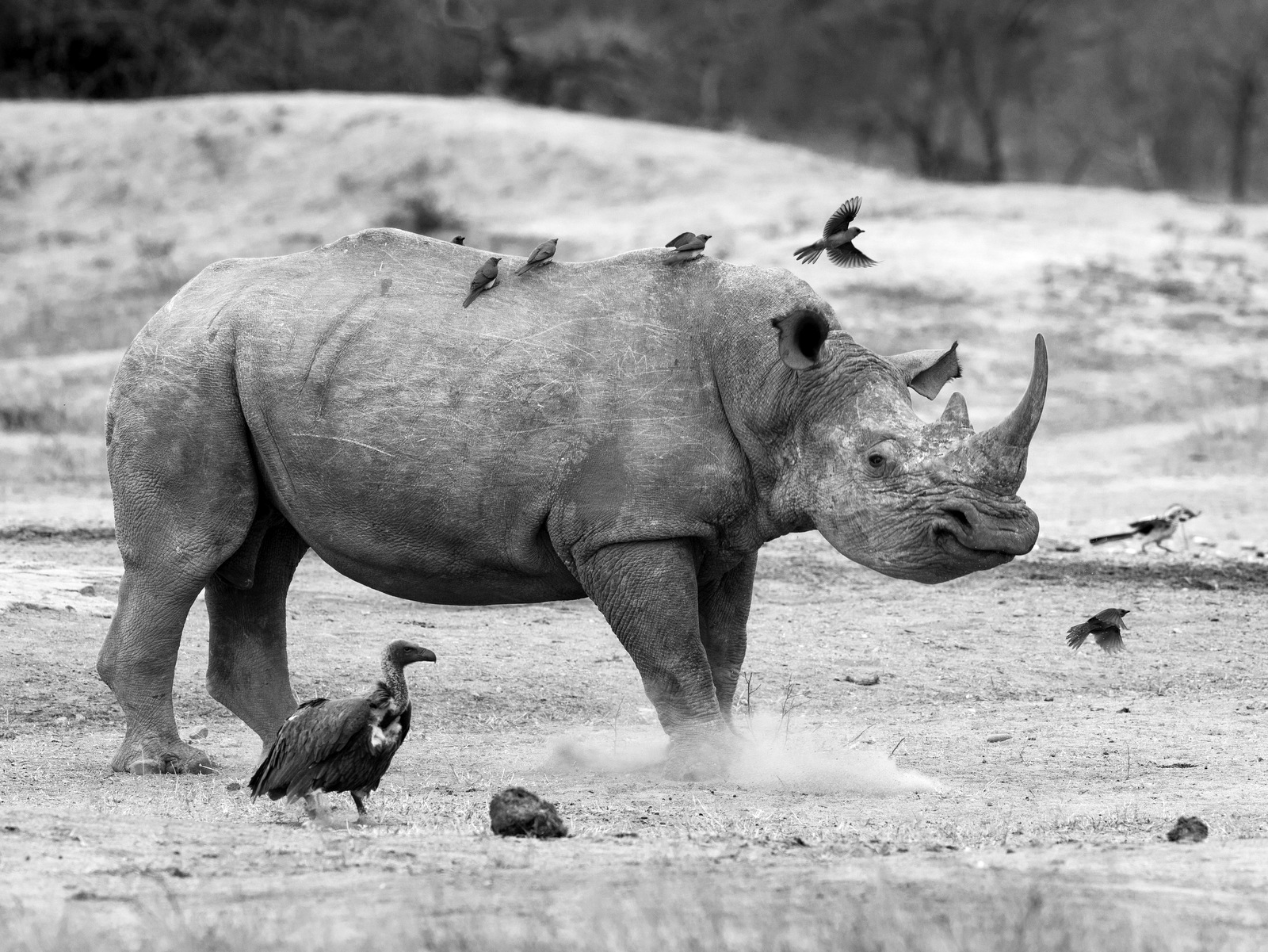
It looks like somebody is having a bit of a tantrum. Check out those pursed lips and the dust caused by the stamping of the foot. The thought bubble may say something like “Everybody off!” I photographed this white rhino, and his bird friends, in Kruger NP, South Africa.
Despite the humorous nature of this photo, the reality is that any image of a rhino is bittersweet. We are obliterating these beasts and they are hurtling toward extinction. Any photo taken now could simply be capturing the last of a kind.
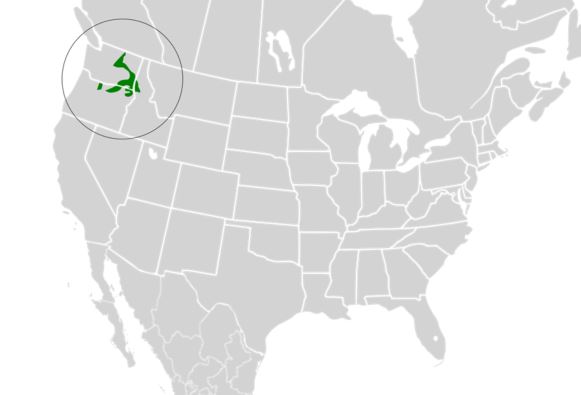
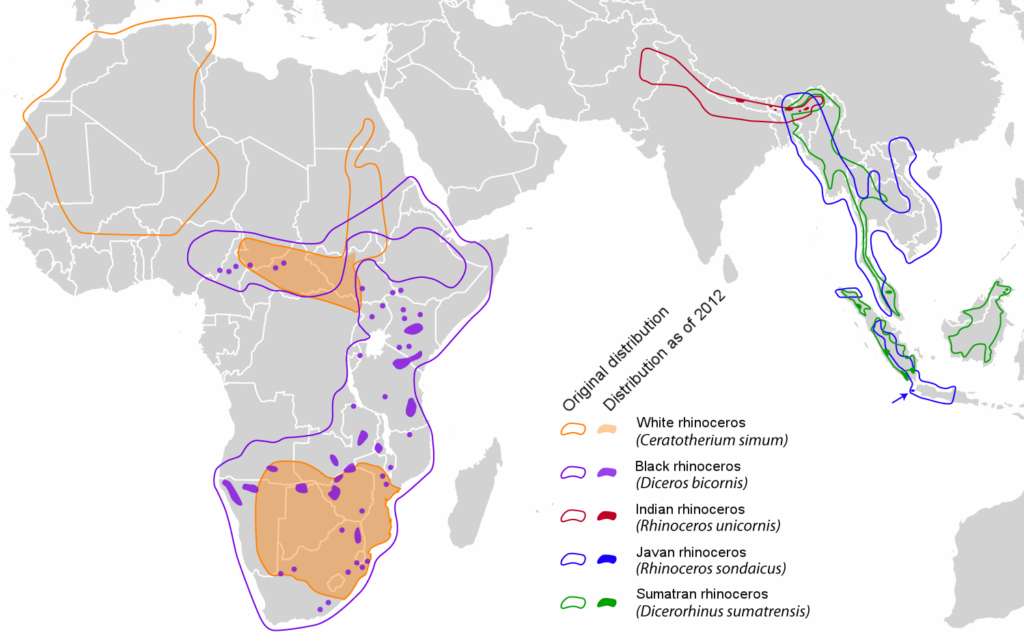
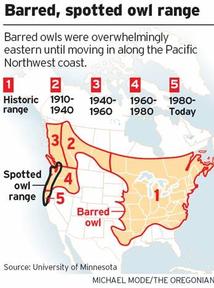
There are five remaining species of rhino. Look closely at this map (click on it to see it larger) and take note of the former range of these animals compared to the reality today. Can you find the dot that represents the last enclave for the Javan rhino?
In the last hundred years we have decimated the rhino population (Source):
Africa is home to 2 species (Black and White) and Asia is home to 3 (Indian (also known as the Greater One-horned Rhino), Javan, and Sumatran). How are they doing? Not great (Source):
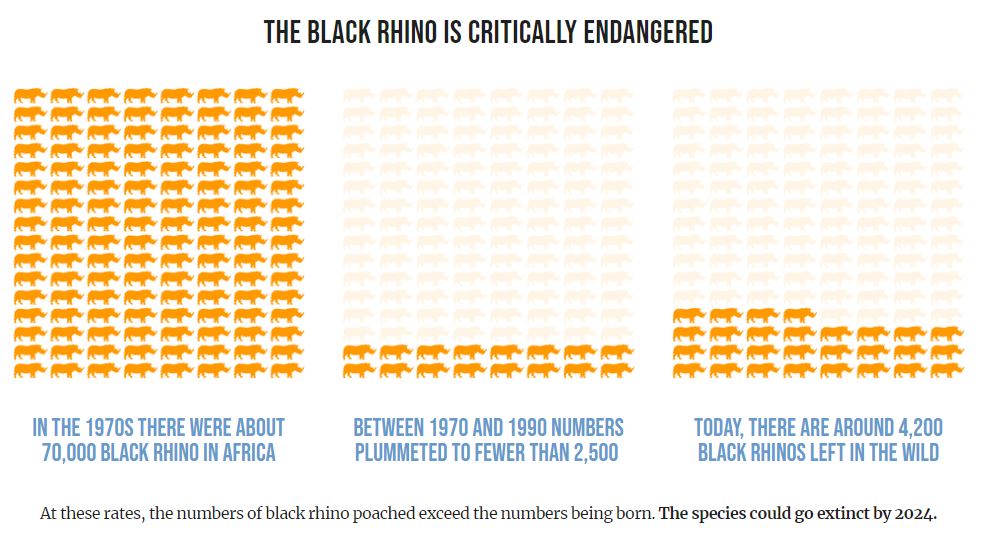
The Sumatran and Javan rhinos are just about gone with less than a 1oo remaining of each in the wild. And the Black Rhino numbers have plummeted since the 1970s (Source):
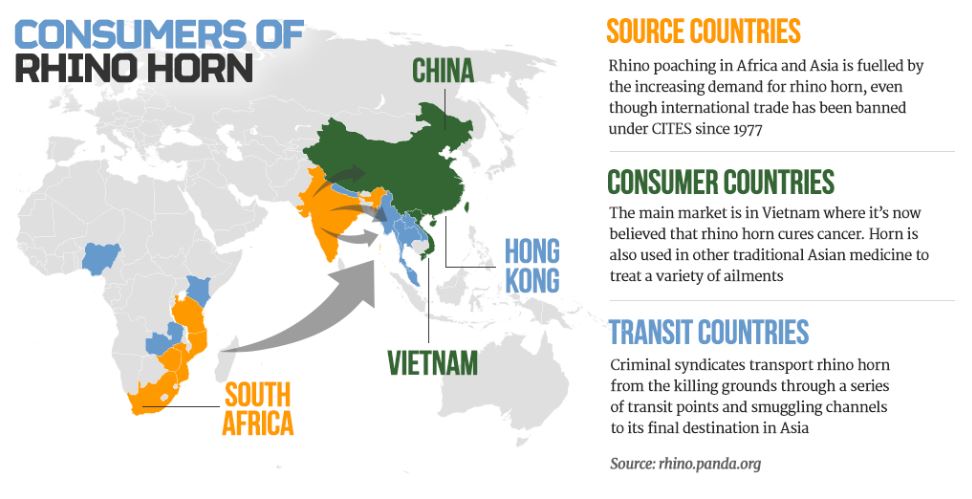
South Africa is an important country for rhinos with 80% of the world population living there. Look at the trend in poaching since 2007!!!!! (Source)
We are killing the rhino for its horn. The main culprits are Vietnam, China, and Yemen. (Source)
This is where we need to direct our anger to stop this insane slaughter. (Source)
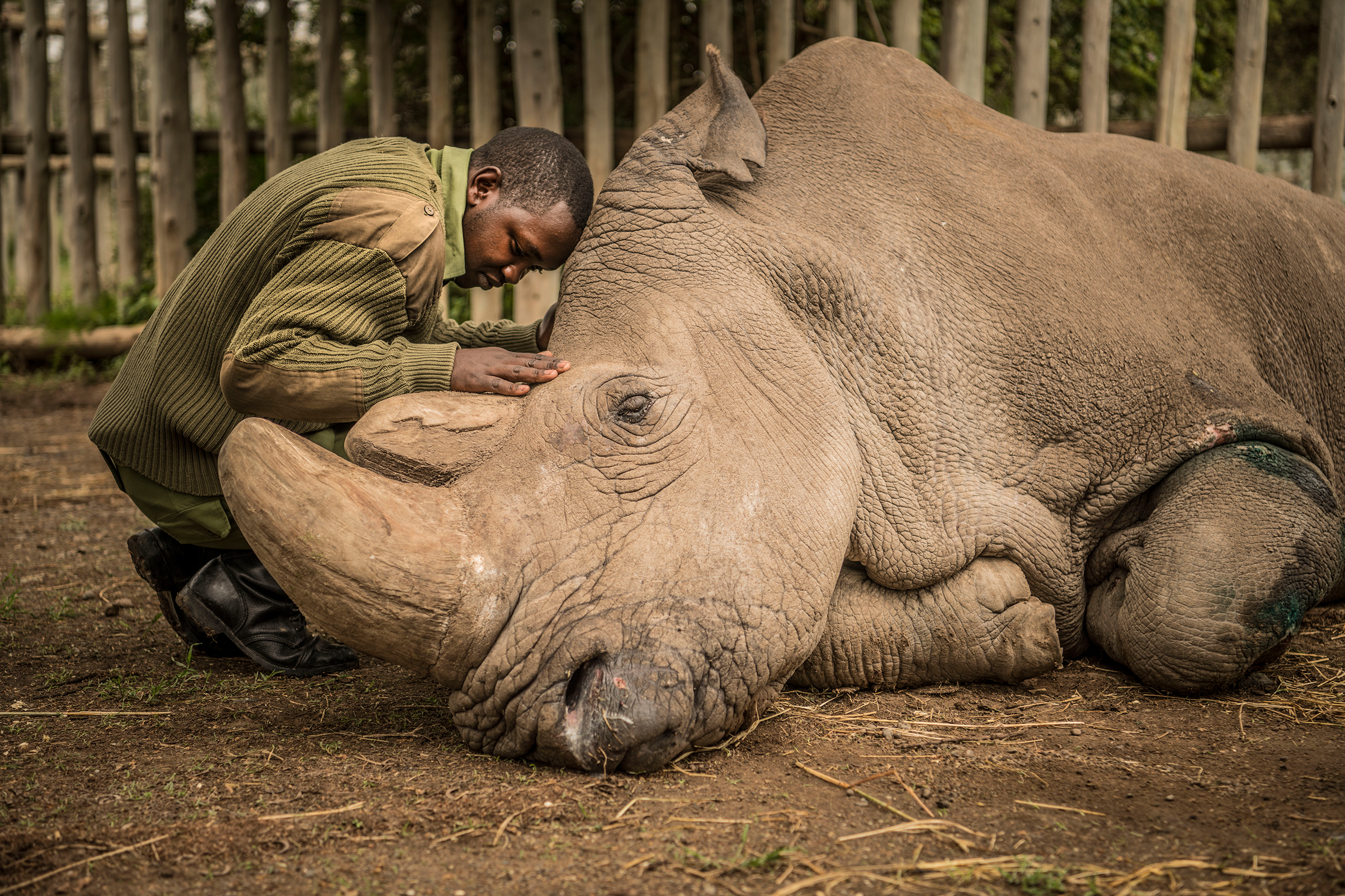
I find the data in these graphics to be powerful, but the image below knocks the wind right out of me. There are two sub-species of Africa’s White rhino — the Northern White Rhino (NWR) and the Southern White Rhino (SWR). The NWR lived in Uganda, South Sudan, the Central African Republic, and Democratic Republic of Congo. The SWR can be found in South Africa, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Kenya and Uganda). In this image, we see the world’s last male Northern White Rhino. He died on March 19, 2018. Only two more remain on the planet, and they are both female.
So this sub-species of rhino is now functionally extinct. There were about 500 NWRs left in the 1980s but poachers killed them until these last three remained. His name was Sudan, and he lived under armed guard in Kenya. He died of old age, and one of his guards is seen here saying goodbye just before he passed away. This image captures the last of his kind.
What else can one say?
Until next month…..m
Nikon D4S, Nikon 600mm, f/4, (@ f/8) 1/500 sec, ISO 640, +0.5 EV
30
Shot of the Month – September 2018
Ahhhh, isn’t it beautiful? What a lovely, albeit frightfully dangerous, scene.
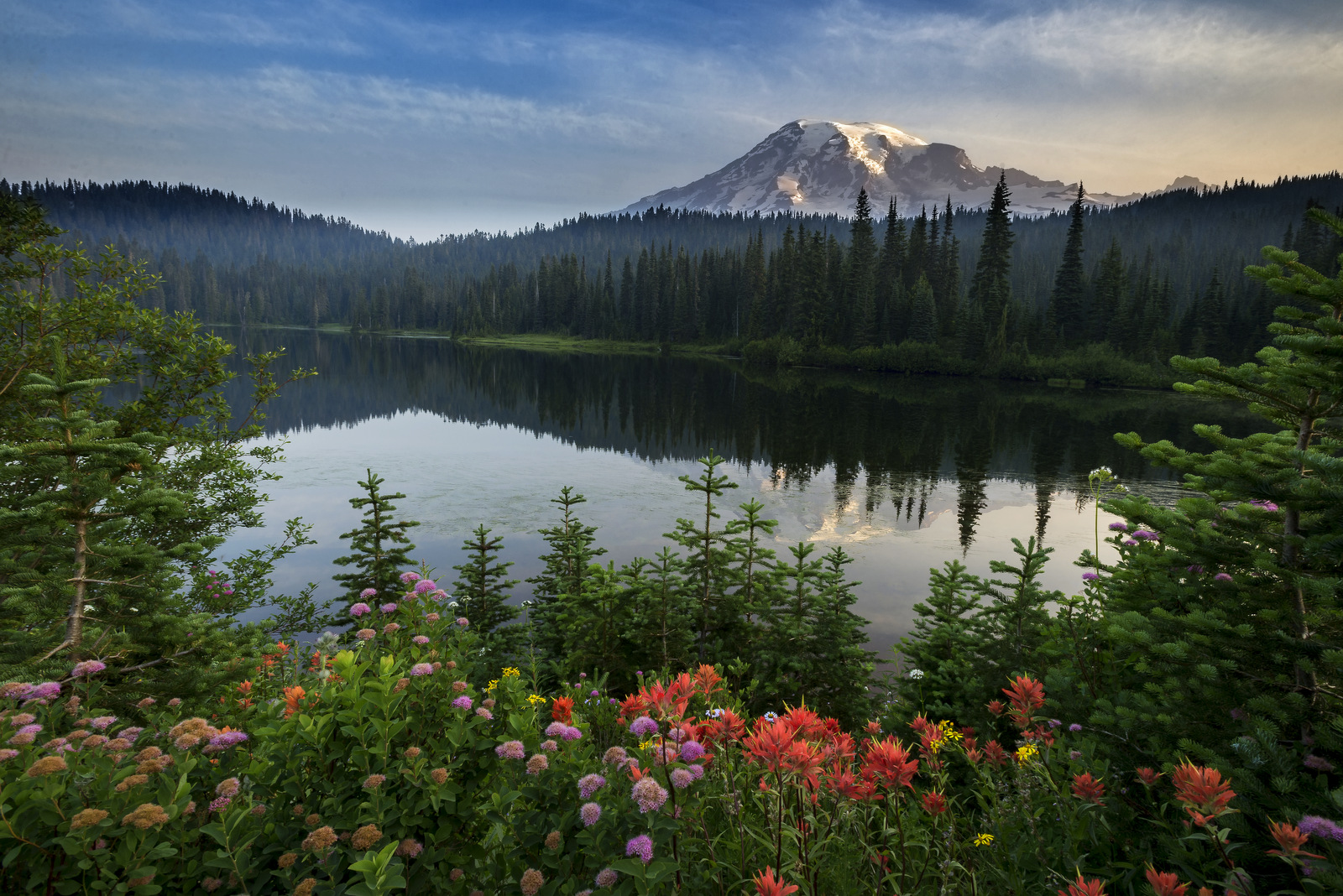
Say what? Dangerous? How could this tranquil spot be dangerous? Where are we?
This image was taken at Reflection Lake in Washington State. What is said lake in fact reflecting? Why that would be Mt. Rainier — the state’s tallest mountain with a summit reaching just over 14,000 feet. This lake is a tourist and photographer favorite as it can offer a wonderful view and reflection of this epic mountain. An image of Mt. Rainier from this vantage point is pretty much a portfolio requirement for any nature photographer visiting the area. In late summer one can include blooming wildflowers in the shot as I have done with the image above to add a dash of color to the composition. Sunrise is the best time to shoot from this spot as the water is most calm at this time of the day and offers the best chance for the still water needed to capture the reflection of the mountain. Soon after the sun is up the the water’s surface begins to ripple with the stirring winds and the iconic shot will often be gone until the next day.
Yeah, yeah, all very interesting, but what about the d-a-n-g-e-r-o-u-s part??
Are bears or cougars lurking nearby? No, no cougars but there are black bears in the park but they are not much of a risk. It turns out that Mt. Rainier is considered one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world. Who knew?!! The mountain is so dangerous that it is on the Decade Volcanoes list — this is the list that all bad-ass-wanna-be volcanoes aspire to be on. Mt. Rainier is on the list because it has a great deal of glacial ice — an eruption could create massive lahars that could threaten large population centers near the city of Seattle.
Lahar? Yeah, me neither. Lahars are a violent type of mudflow made up of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris, and water. They can have the consistency of wet cement when moving. These flows can be super fast, potentially reaching speeds of 60 mph, and may be hundreds of yards wide and up to almost 500 feet high. These massive, fast flows can wipe out any structure in their path and provide very little time to react offering little chance to get out of the way of this wet cement freight train. You can’t outrun a fast-moving lahar…
Wow, so it seems that I just barely escaped the jaws of death. Who knew that landscape photography could be so risky? I may go back to photographing lions and jaguars where it is safe…
Until next month…michael
Nikon D4S, Nikon 17-35mm (@17mm), f/16, 1/15 sec, ISO 400
31
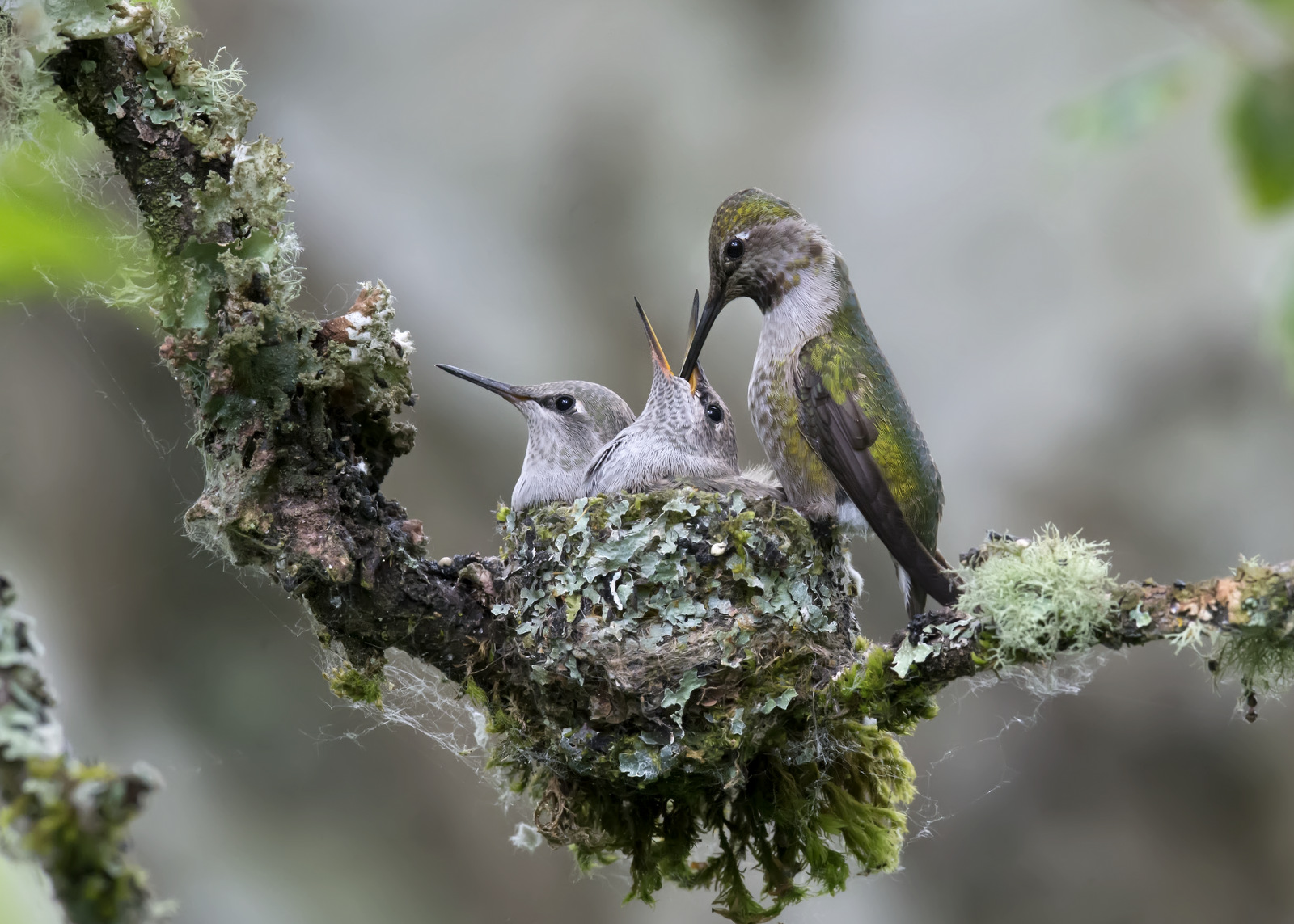
Shot of the Month – August 2018
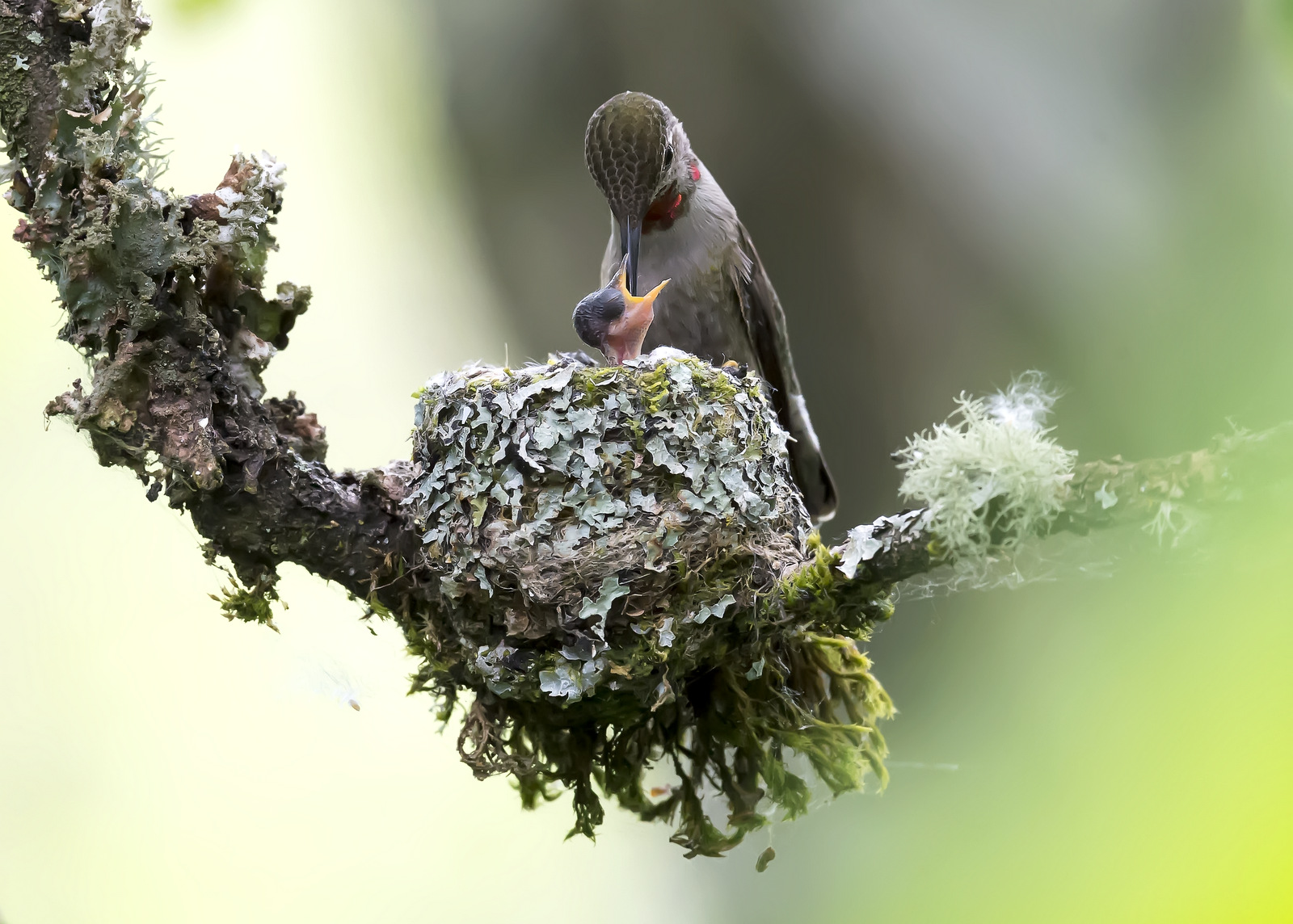
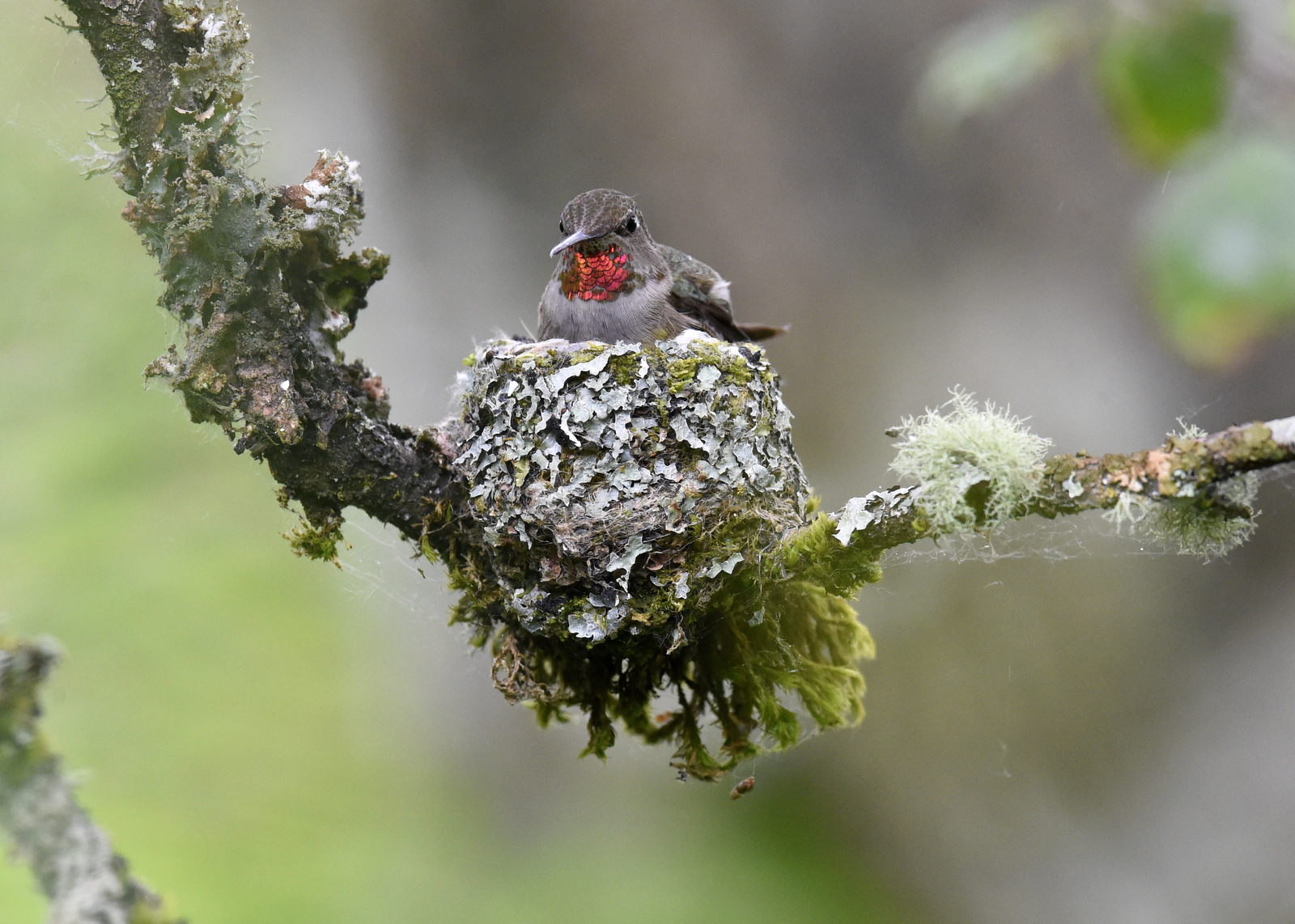
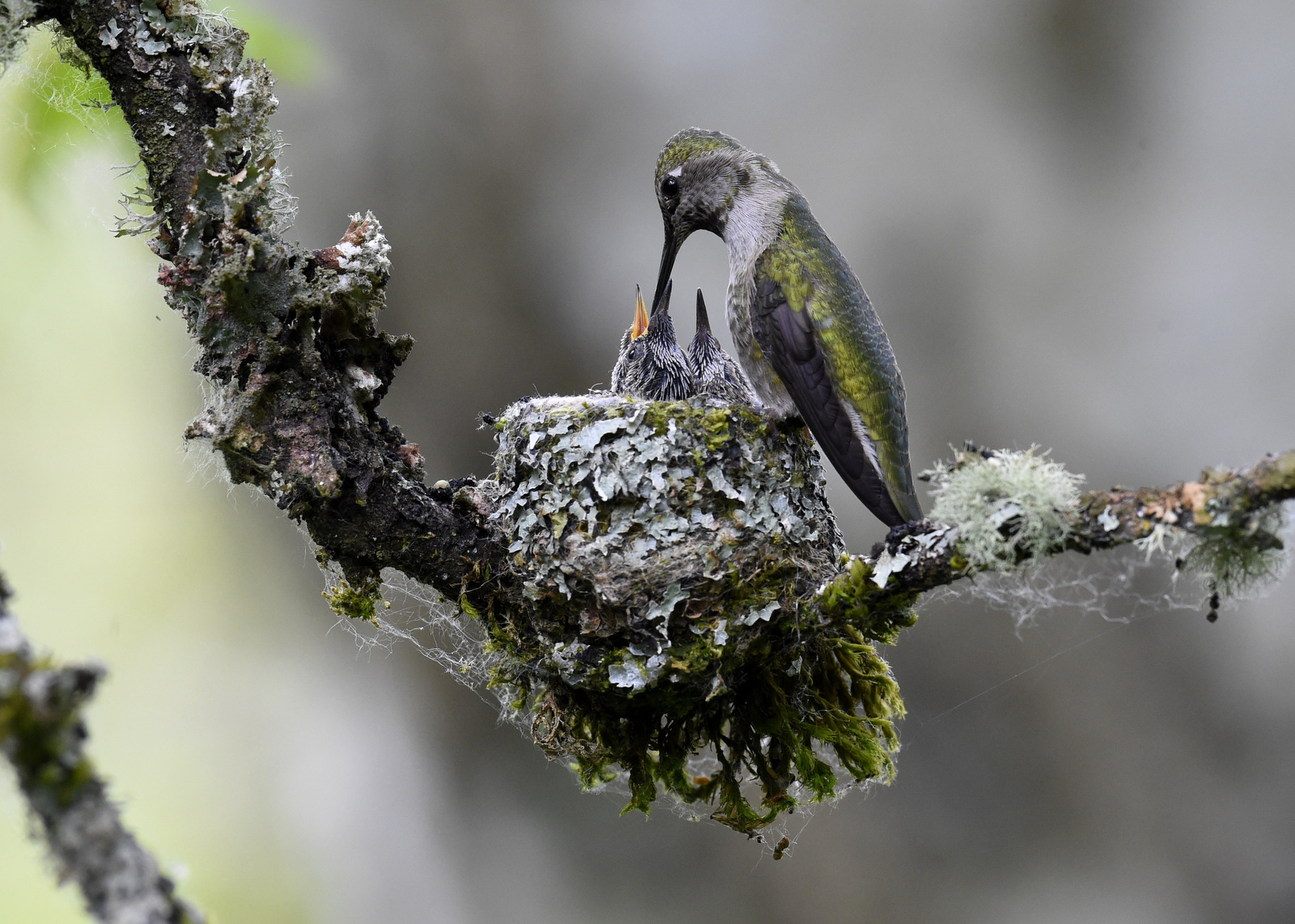
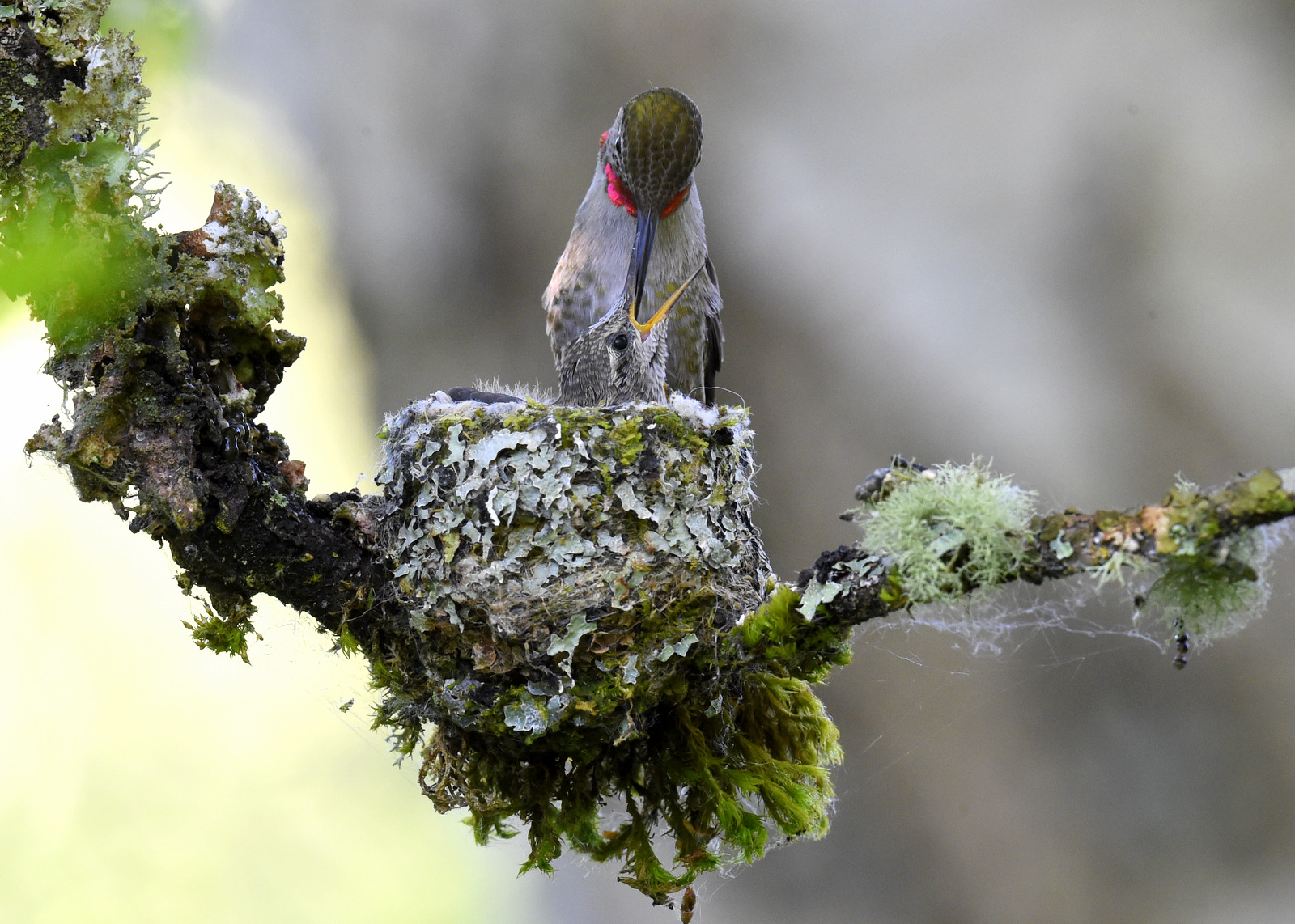
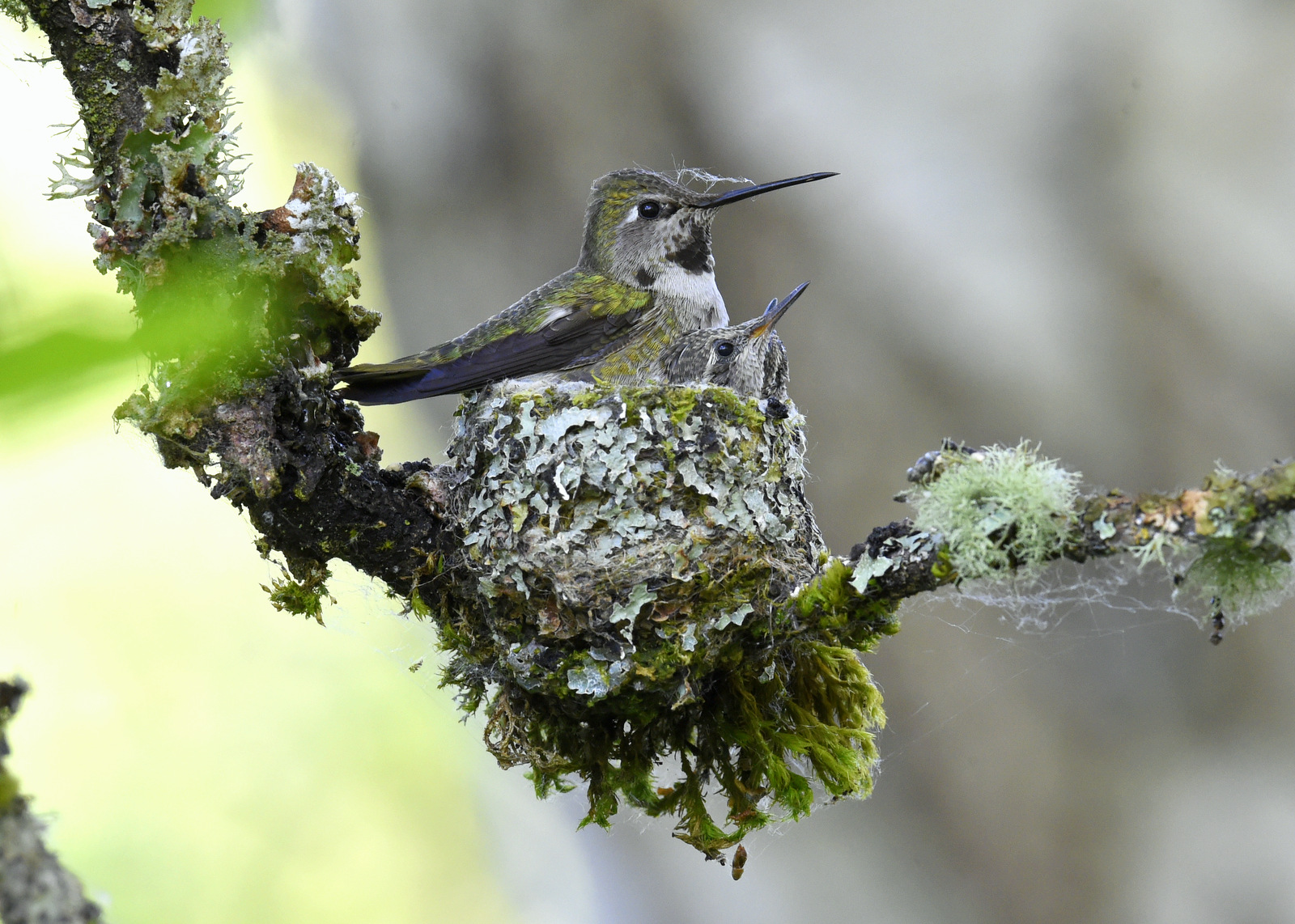
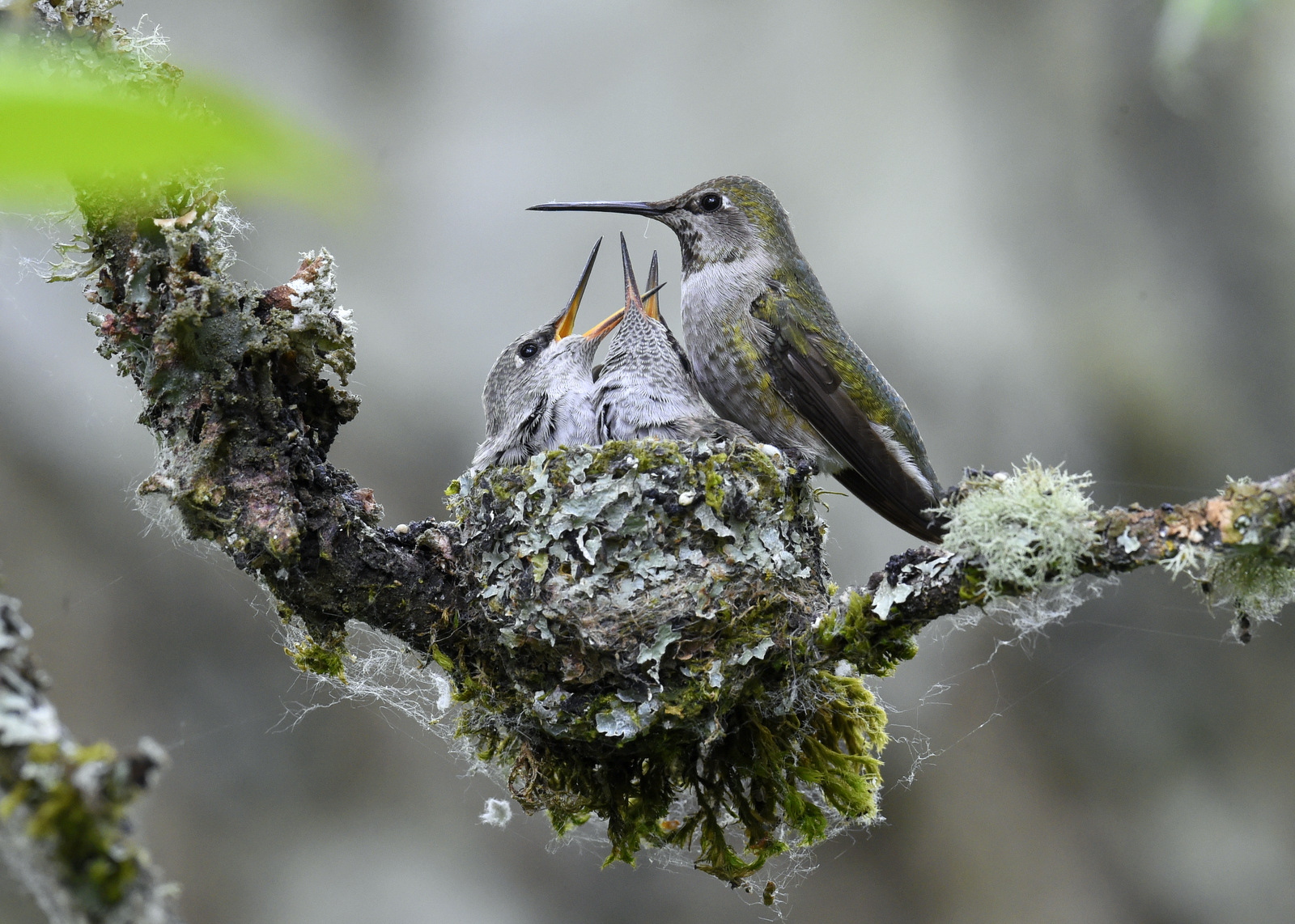
Earlier this summer I had the good fortune to find an Anna’s Hummingbird nest in a park near my house. Let me share my three-week journey with this lovely family.
The Nest
First, let’s stop to admire the nest — it is stunning. The female builds the nest by sitting in the middle and building the cup rim around her. The nest can be made out of plant fibers, cattail, willow, leaves, thistle, or small feathers and it is bound together with spider webs or insect cocoons. The nest can be decorated with lichen and moss to blend in with the surroundings. The nest is about 1 inch tall and 1.5 inches in diameter. And the one I saw, was perfect. I was blown away by how perfect it was. Perfectly round. Perfectly decorated. Perfectly camouflaged.
It belongs in a museum.
Did I mention that it was perfect?
They Grow Up So Fast
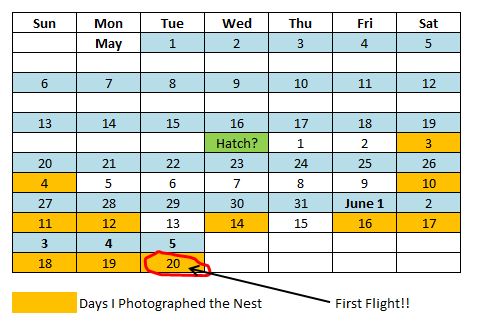
I spent about three weeks visiting this glorious little nest because that is about how long it takes for an Anna’s Hummingbird chick to grow up and develop its wing feathers to fly away. When I first found the nest the chicks were barely visible as they were so tiny. Here is a breakdown of my visits to the nest.
I discovered the nest on May 19th – given the size of the chicks and from information from other photographers, I estimated that the chicks were 3 days old at this point, as indicated on my calendar to the left. In total I made 11 visits to the nest, when the chicks were about 3,4,10,11,12,14,16,17,18,19, and 20 days old. On the 20th day, I had the opportunity of a lifetime — I was there when the fledglings took their FIRST flight. Even more amazingly I was video-taping (boy that term is outdated) and got the first flight on “film.” But I am getting ahead of myself. Let’s look at our little “photo album” from the kids’ childhood…
Day 3
Below, if you look closely you can the little yellow beaks of the two chicks in the nest. They are so tiny that they barely reach the top of the rim of the nest.
And here is the only clear view of a chick I got at this age. Eeeek! Uh, I mean, “Aww, he is so beautiful” “He looks just like you!” At this age, the eyes are not open yet and there is not a feather to be found on this naked little beast. He must be standing on his tippy toes to reach out this high to reach Mom’s food. Remember that the diameter of the nest is only about 1.5 inches, so the chick’s head is about the size of your fingernail!
Day 4
The chicks are so small that mom can still sit on the nest.
Day 10
Let’s jump ahead to May 26 – day ten of their little lives. Look at how much they have grown – their heads clearly stick out above the rim of the nest. Their eyes are open. And we can see the stems of their feathers coming through.
Day 12
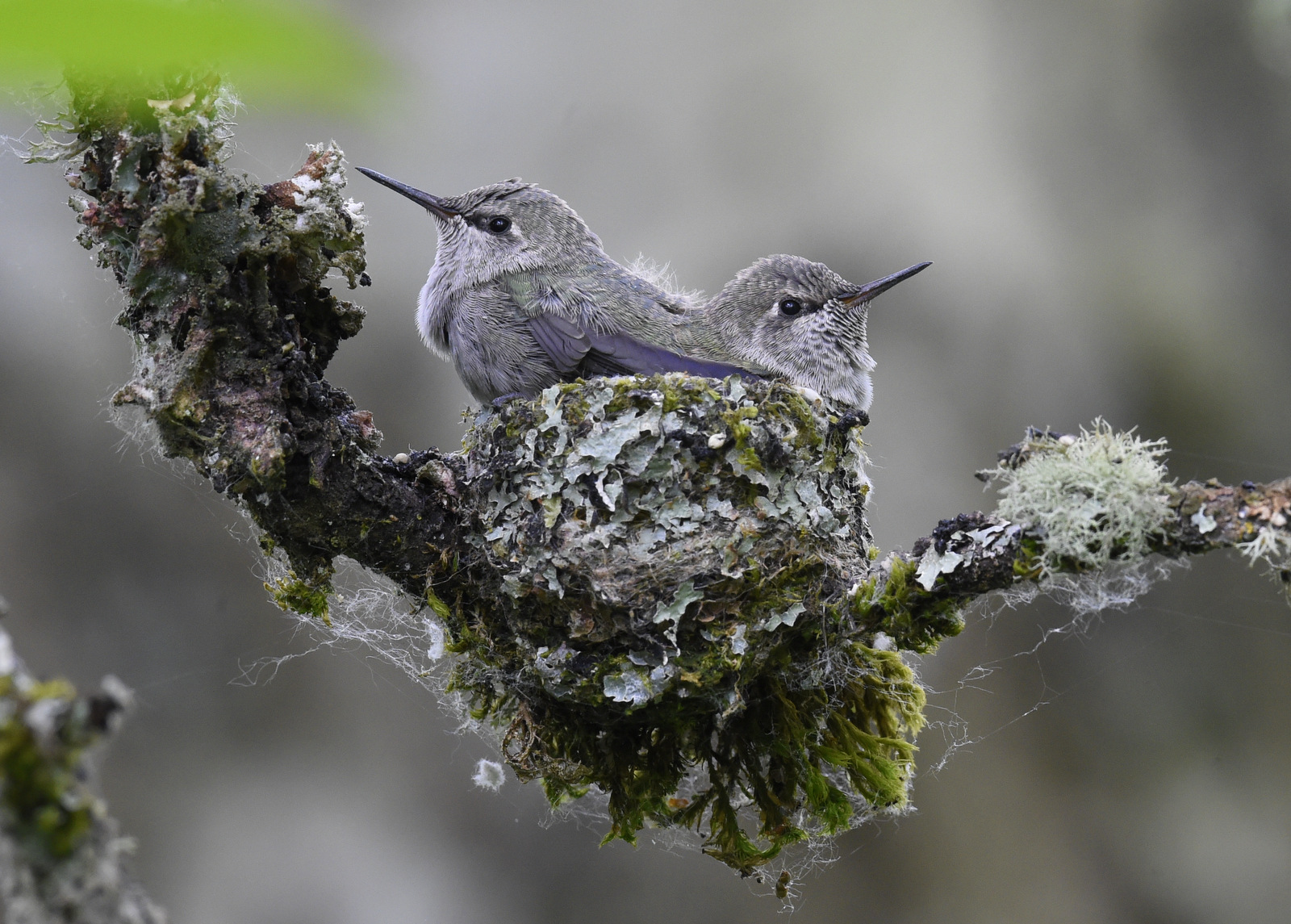
Getting bigger and their feathers are filling out.
At this stage, it is starting to get crowded in the nest.
Getting bigger but the wing feathers are still filling in…
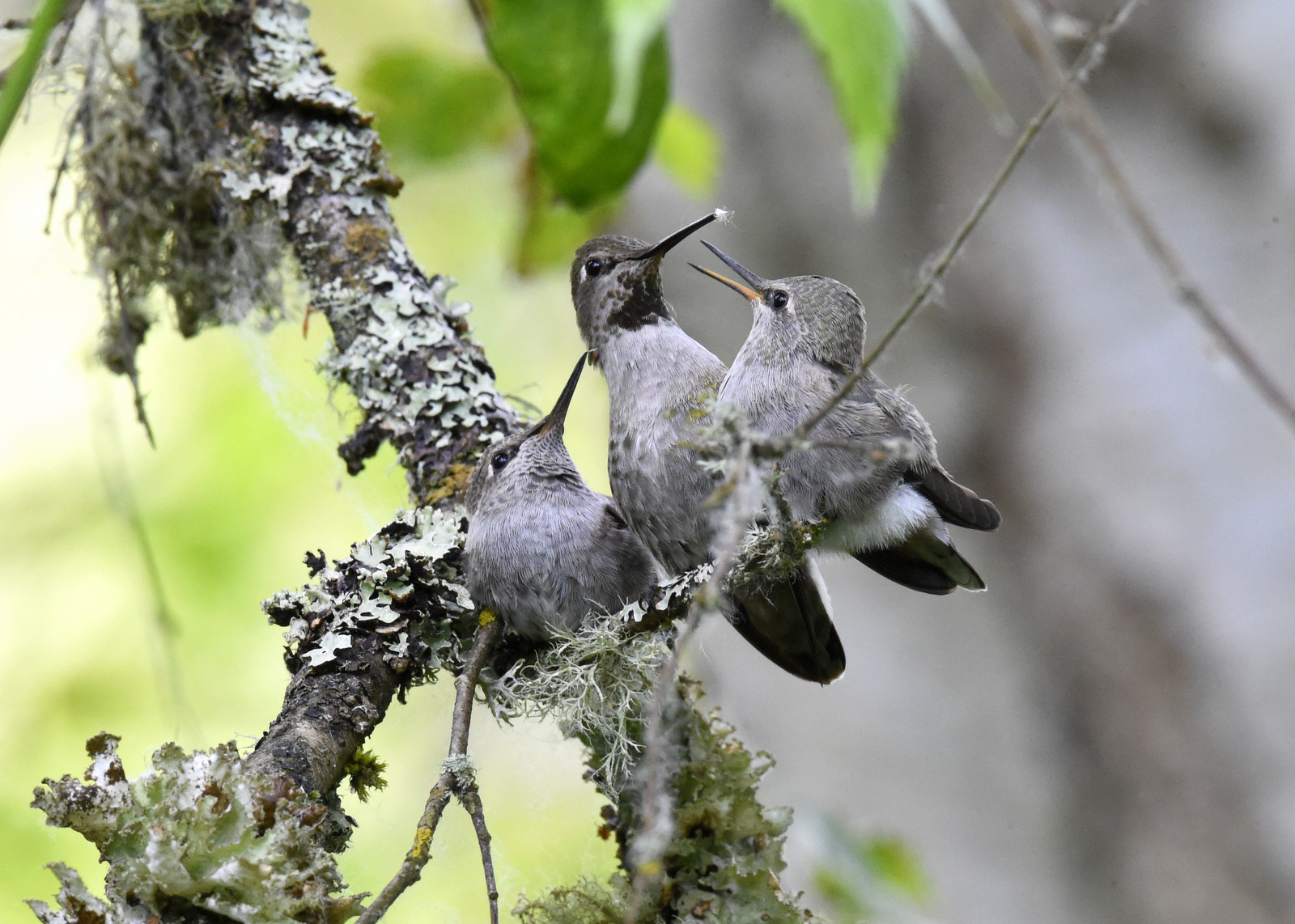
Day 17
Just over 2 weeks old and look how refined their feathers are now.
Day 18
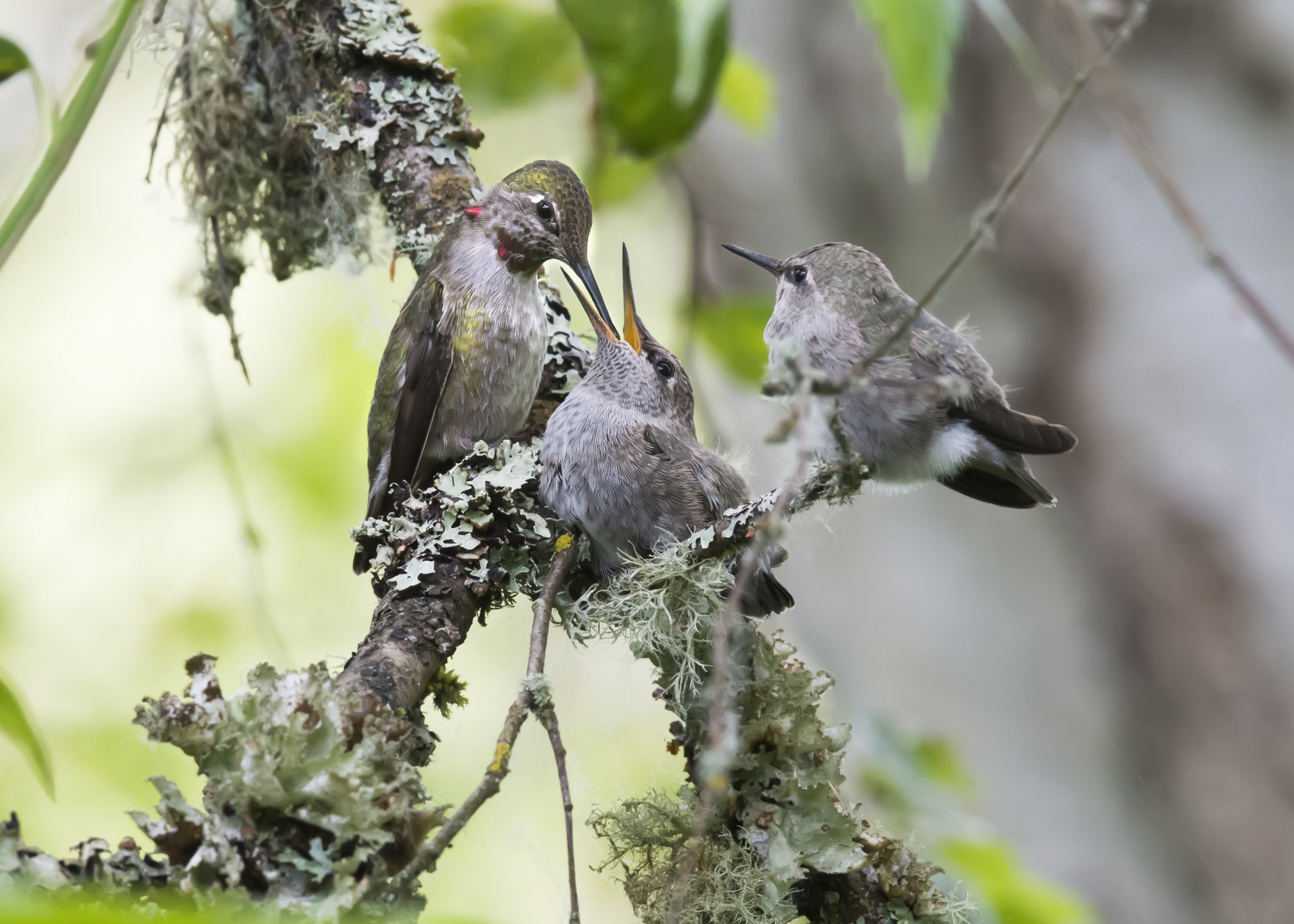
Beautiful, though, we are going to need a bigger boat.
Demanding kids…
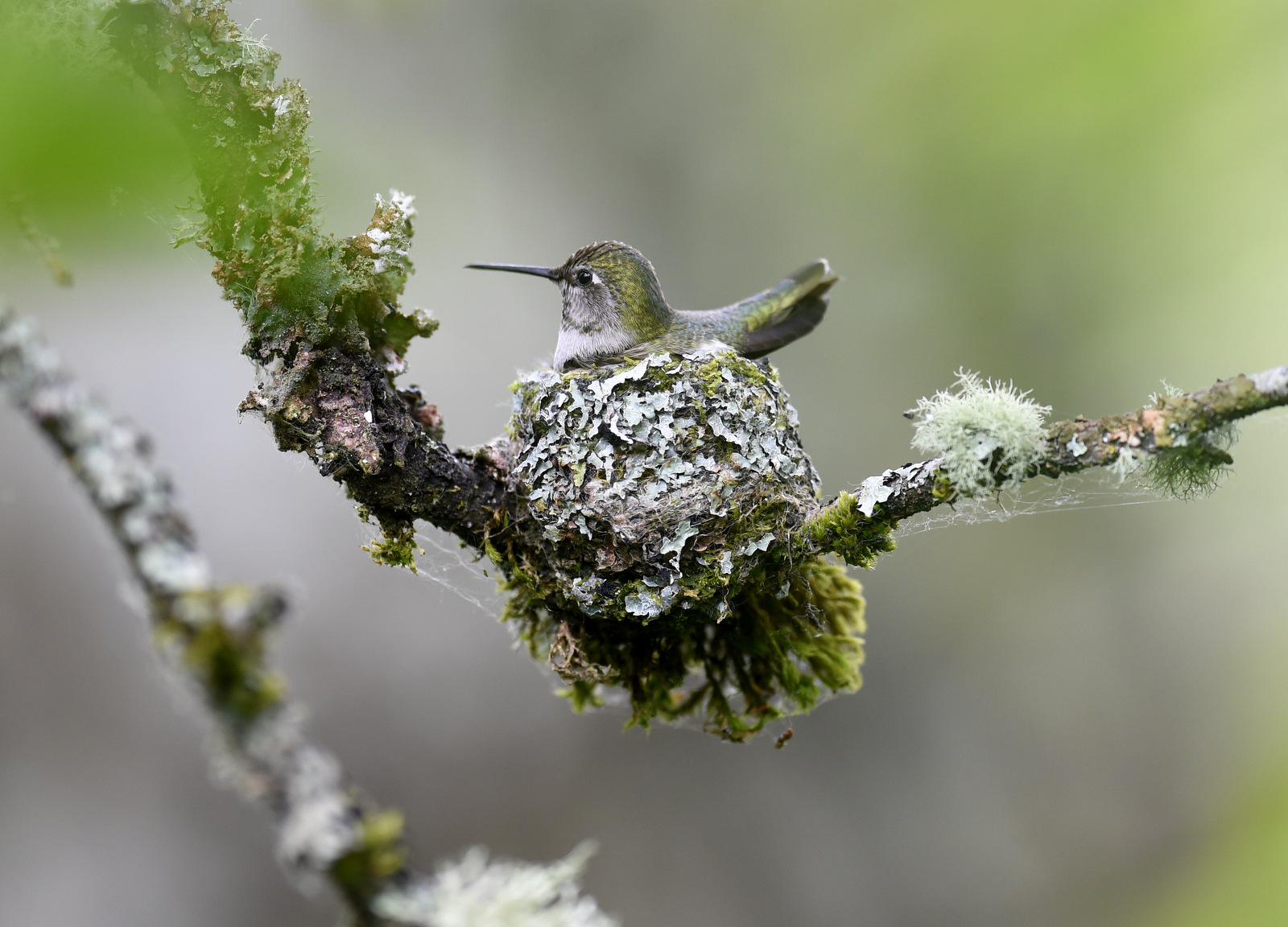
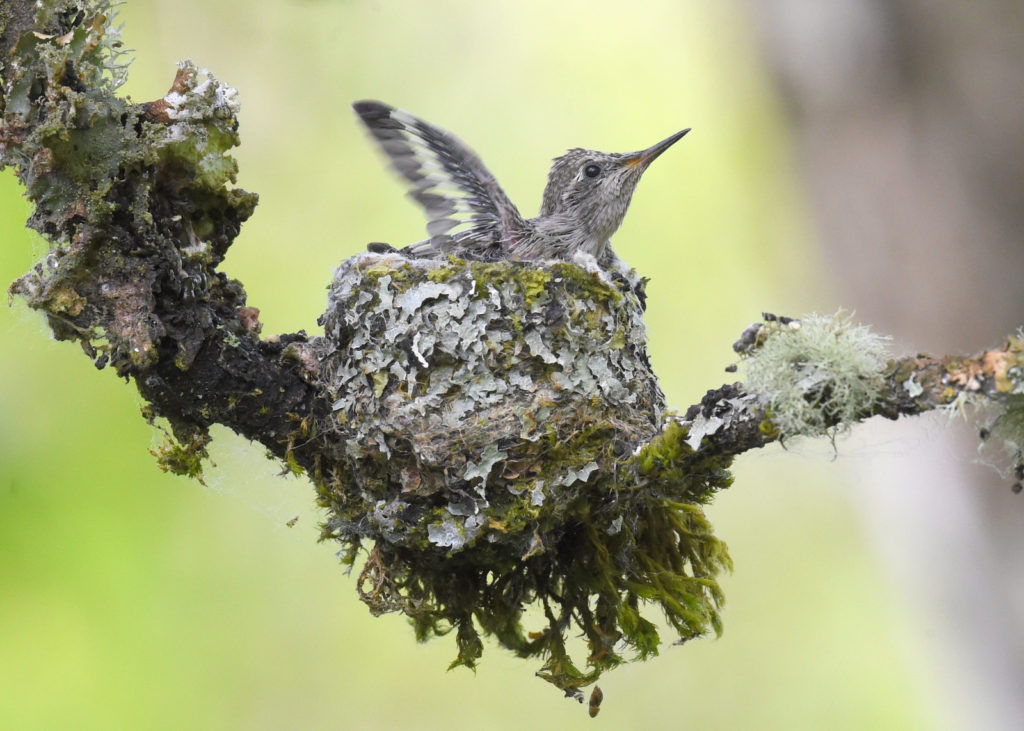
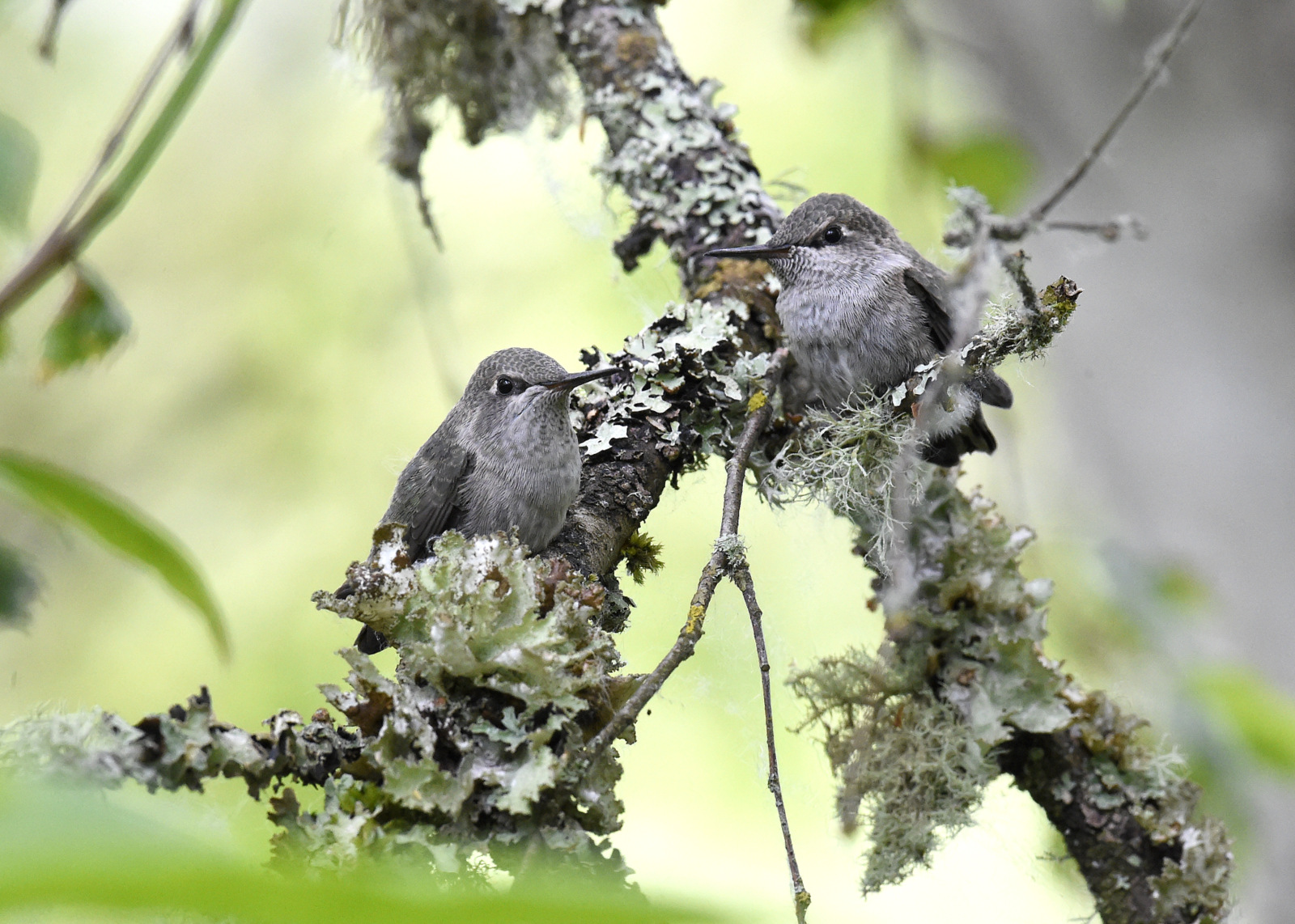
Day 20
And before you know it, they are proper little birds. Here is Junior’s first flight. Sniff, I am so proud…(you can also see the video here)
The chicks only flew a few feet away to a nearby branch in the same tree.
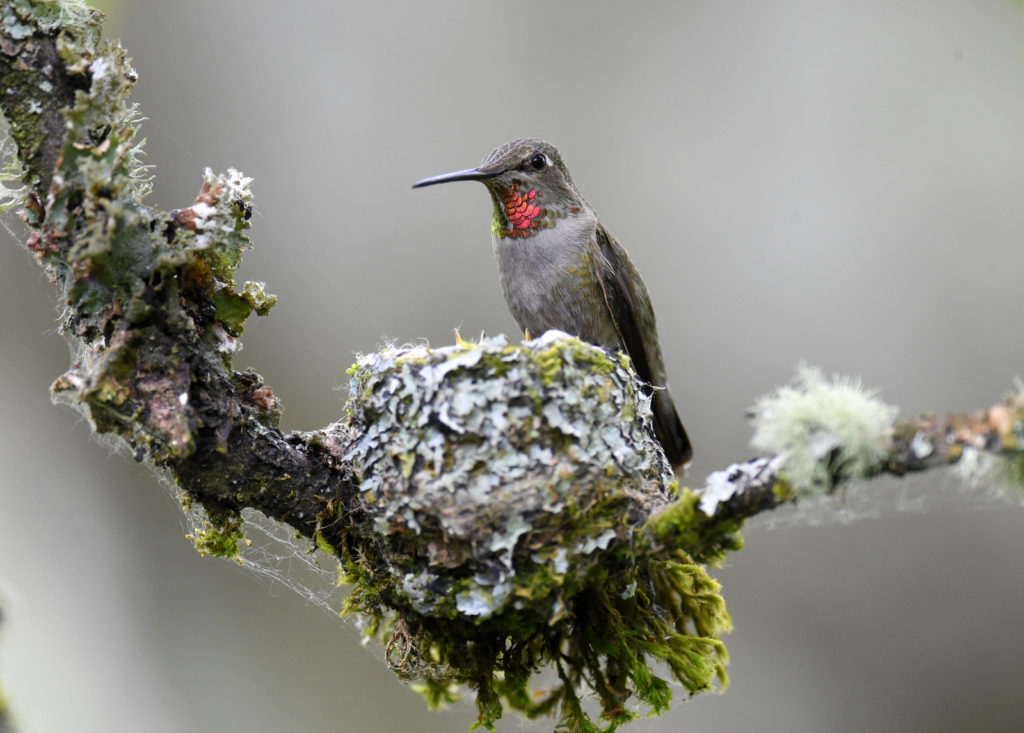
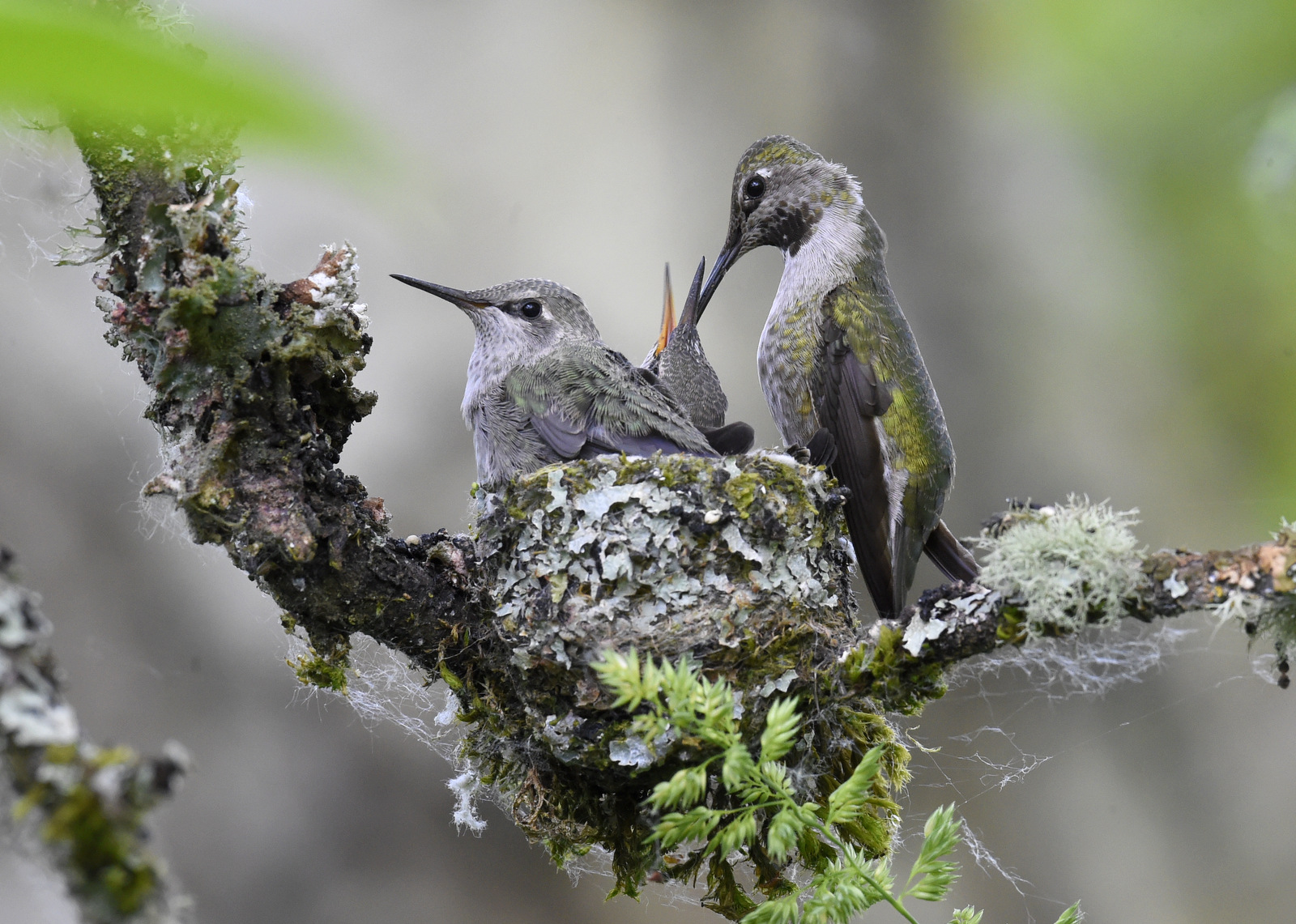
Mom’s duties continued, however, most likely for a few more days:
And so ends our time together. Well done, mum. You have raised a lovely pair of hummingbirds…
Until next month…..m
Nikon D4s, Nikon 600mm @ f/11, 1/125 ses, ISO 6400
31
Shot of the Month – July 2018
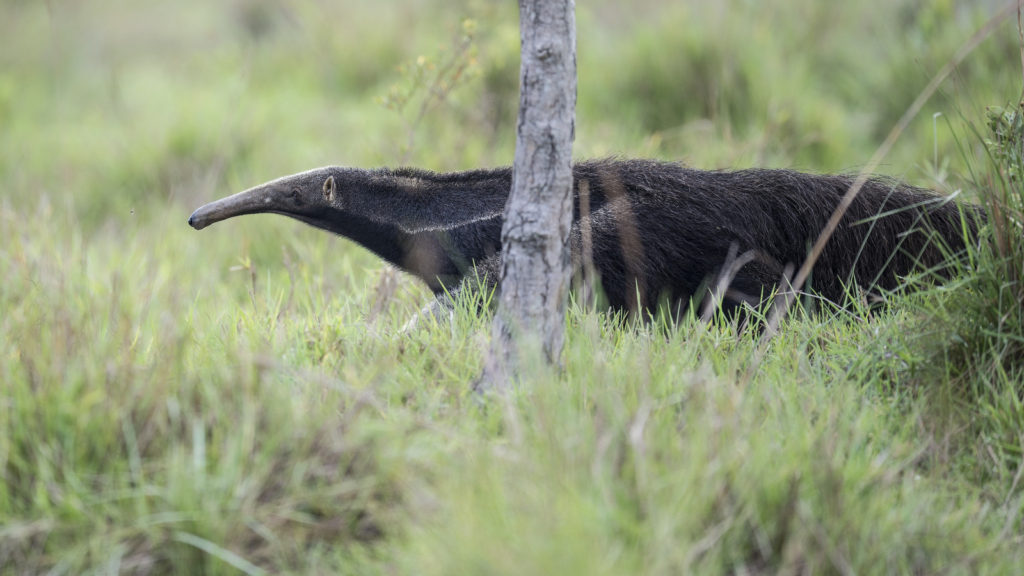
So there I was sitting in the back seat of the car. I was tired but feeling content — it was the final day of our trip to the Pantanal to see, primarily, jaguars. We were driving to the local airport to begin our series of flights home. We had some amazing sightings and I had gotten some very nice photos. I always hate to see a trip end but my wistfulness was less than usual given all that we had experienced. By the second hour of our three-hour drive, the scenery went by like a blur as my mind wandered. I was jolted from my dreamy state when Naun, our guide, yelled.
“STOP! STOP! Michael get your camera ready!!!”
Huh, What? I didn’t bother to look as I knew that if Naun was this excited, it must be something good. The problem was that all our gear was completely packed up. My camera bodies were in one bag next to me. My lenses were in another bag, in the back of the vehicle. As we pulled over I yanked a camera body out and got out of the car. I opened the rear hatch of the car, yanked my camera bag out, and quickly pulled off all of the covers and caps and put the kit together. Naun waited impatiently by the edge of the road and motioned for us to go through the wire fence that he was holding up. We walked into the field and there it was — a Giant Anteater (GA)!! And he was ambling across the field with purpose!! He was still a fair distance from us but he was heading in our direction. I raised my camera to try and at least document this amazing sight. As I looked through the viewfinder I could see nothing. The car was air conditioned and when we jumped out into the heat of the day the sudden temperature change caused the front element of my lens to fog over.
F&^%$$!!
I took the bottom of my shirt and used it to wipe off the glass (I normally loathe to touch the glass, but this was an emergency!). I got a few shots off but then the anteater saw us and went in another direction. We got back in the car and moved forward. We set up and waited — it was clear that the Giant Anteater wanted to cross the road.
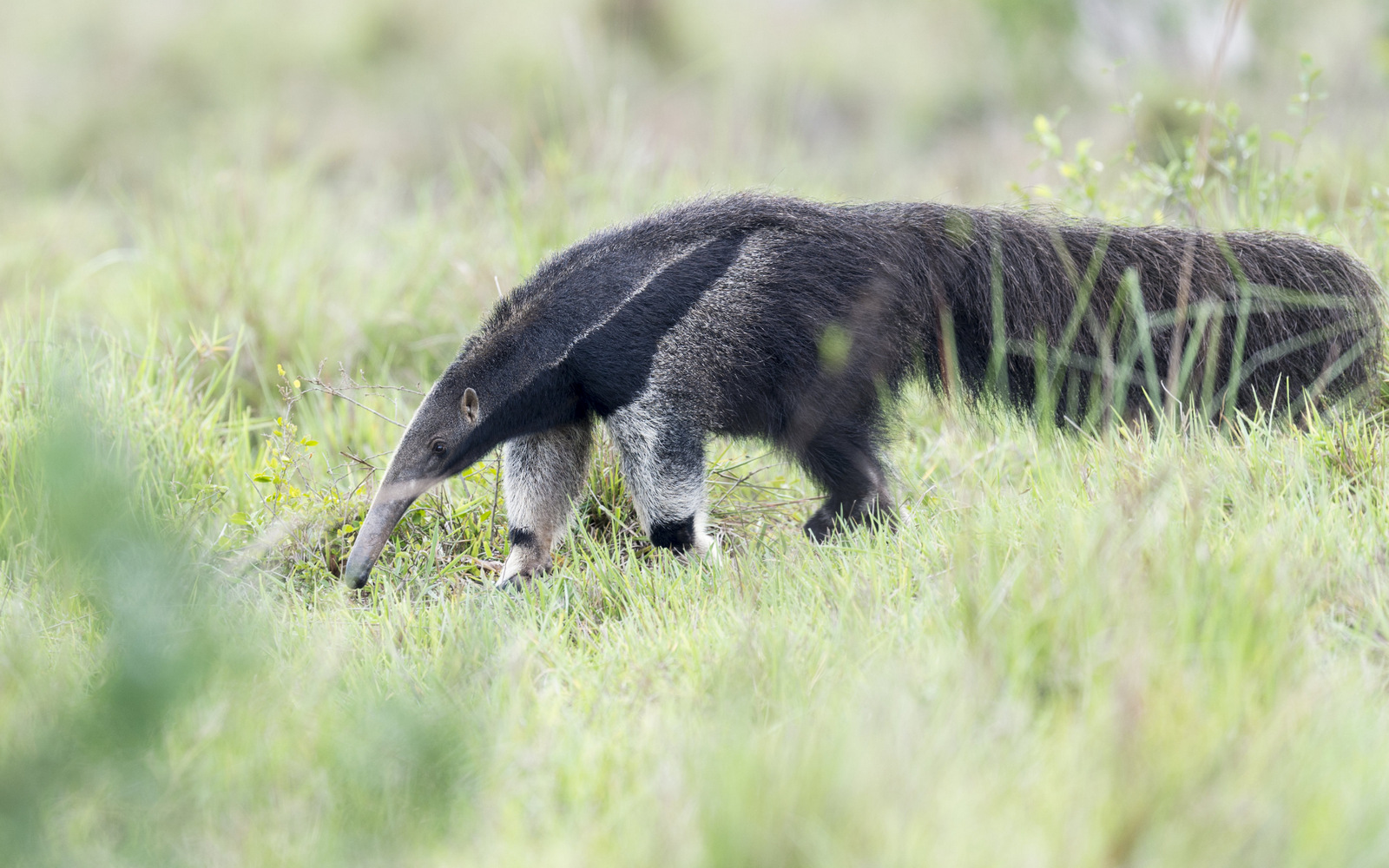
In the end, I managed to get a few shots and eventually, the GA crossed the road just a few feet from us. Wow! Even though the images are not great, I had to share this wonderful, other-worldly beast. The Giant Anteater is surely one of the world’s stranger-looking creatures.
Refuge from another dimension?
At a distance, the GA looks supremely flat – as if he escaped from the pages of a purely two-dimensional world. The Giant Anteater can reach seven feet in length from head to tail and he just looks soooo looong. His width seems so oddly out of proportion to his length giving the appearance of a “flat screen” creature. They say that black is thinning, but come on…
Winner by a nose
 And then there is that snout. Try not to stare but that is a doozy of honker. The snout takes up most of his head and ends with a tiny mouth and nostrils. As you may have guessed from his name the Giant Anteater specializes in eating ants and termites. That nose is well shaped for plunging into the narrow passageways of the termite mounds in search of the small insects. The Ant Bear, a much more endearing moniker, can eat 30,000 insects a day. That tiny mouth has no teeth so the GA crushes the insects against its palate before swallowing them.
And then there is that snout. Try not to stare but that is a doozy of honker. The snout takes up most of his head and ends with a tiny mouth and nostrils. As you may have guessed from his name the Giant Anteater specializes in eating ants and termites. That nose is well shaped for plunging into the narrow passageways of the termite mounds in search of the small insects. The Ant Bear, a much more endearing moniker, can eat 30,000 insects a day. That tiny mouth has no teeth so the GA crushes the insects against its palate before swallowing them.
The GA has a narrow tongue that is 2 feet long. is shaped like a strand of spaghetti, and is covered in tiny backward-pointing spines covered in sticky saliva — making it a great tool for catching insects. The GA can dart its tongue inside a mound up to 150 times a minute to catch its prey.
The ant bear has terrible eyesight and equally bad hearing but its sense of smell is 40x more sensitive than ours – he can smell termites and ants that may be miles away. Ok, respect for the nose!
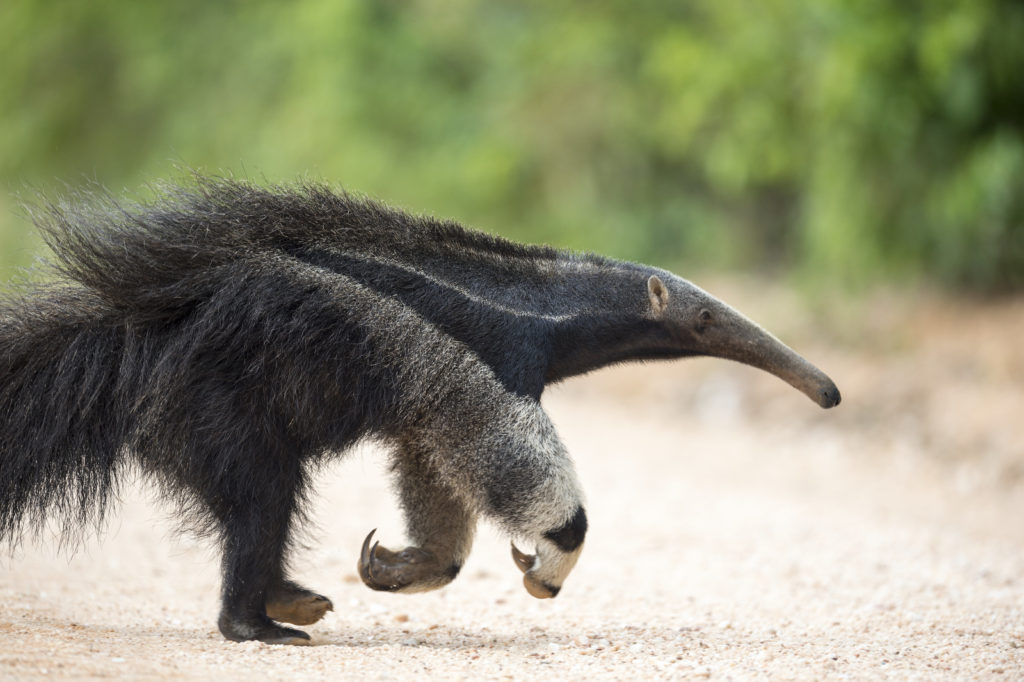
The Claw! (obscure movie reference)
Adding to the peculiar nature of this beast, the GA walks on its knuckles, like a gorilla. Why? To protect those impressive claws that it uses to tear apart termite mounds, of course. Below we have a GA in full gallop providing a good view of the claws and how he folds his front feet over while walking to keep these vital tools sharp. The ant bear has five toes on each foot — the front feet have claws, which are particularly elongated on the second and third digits. The GA is careful to not completely destroy a mound to ensure a reliable food supply. He tears a mount open just enough to allow his narrow snout to reach inside. He only spends about 1 minute feeding at a site before moving on and in a given day he may visit up to 200 nests. These claws can also be used for defense. If a GA is attacked, say by a puma or a jaguar, the GA will stand up on its tail and slash those claws from side to side with great effect. These creatures are very shy but they have been known to kill humans when cornered or if startled in the wild.
That Tail
The body of the GA is about 3-4 feet in length and that wonderful tail can add another 2-3 feet to the length of the animal. The tail has extra long hairs and helps make the GA seem much bigger than he really is. When resting the GA will carve a shallow cavity in the ground and then curl up and use its tail as a blanket!! A-dorable! The tail can help conserve heat and act as camouflage.
Wow, what a gift to see what is becoming an increasingly rare animal. In just 10 years, from 2000 to 2010 the total population of GAs has declined by 30%. Tragically, in 1994 close to 350 Giant Anteaters died due to wildfires at Emes National Park in Brazil. Currently, scientists think there may be about 5,000 ant bears left in the world. Giant Anteaters are native to Central and South America though it seems that they have been extirpated from most of Central America. (source)
Why did the ant bear cross the road?
Heck if I know, but I am eternally grateful that this one did! Until next month…..m
Check out this amazing interaction between a jaguar and a giant anteater!